
Atmospheric entry is the movement of an object from outer space into and through the gases of an atmosphere of a planet, dwarf planet, or natural satellite. There are two main types of atmospheric entry: uncontrolled entry, such as the entry of astronomical objects, space debris, or bolides; and controlled entry of a spacecraft capable of being navigated or following a predetermined course. Technologies and procedures allowing the controlled atmospheric entry, descent, and landing of spacecraft are collectively termed as EDL.

A waverider is a hypersonic aircraft design that improves its supersonic lift-to-drag ratio by using the shock waves being generated by its own flight as a lifting surface, a phenomenon known as compression lift.

A spaceplane is a vehicle that can fly and glide like an aircraft in Earth's atmosphere and maneuver like a spacecraft in outer space. To do so, spaceplanes must incorporate features of both aircraft and spacecraft. Orbital spaceplanes tend to be more similar to conventional spacecraft, while sub-orbital spaceplanes tend to be more similar to fixed-wing aircraft. All spaceplanes to date have been rocket-powered for takeoff and climb, but have then landed as unpowered gliders.

An orbital spaceflight is a spaceflight in which a spacecraft is placed on a trajectory where it could remain in space for at least one orbit. To do this around the Earth, it must be on a free trajectory which has an altitude at perigee around 80 kilometers (50 mi); this is the boundary of space as defined by NASA, the US Air Force and the FAA. To remain in orbit at this altitude requires an orbital speed of ~7.8 km/s. Orbital speed is slower for higher orbits, but attaining them requires greater delta-v. The Fédération Aéronautique Internationale has established the Kármán line at an altitude of 100 km (62 mi) as a working definition for the boundary between aeronautics and astronautics. This is used because at an altitude of about 100 km (62 mi), as Theodore von Kármán calculated, a vehicle would have to travel faster than orbital velocity to derive sufficient aerodynamic lift from the atmosphere to support itself.

HOPE was a Japanese experimental spaceplane project designed by a partnership between NASDA and NAL, started in the 1980s. It was positioned for most of its lifetime as one of the main Japanese contributions to the International Space Station, the other being the Japanese Experiment Module. The project was eventually cancelled in 2003, by which point test flights of a sub-scale testbed had flown successfully.
JP Aerospace is an American company that aims to achieve affordable access to space. Their main activities include high-atmospheric lighter-than-air flights carrying cameras or miniature experiments called PongSats and minicubes. They are also engaged in an Airship to Orbit project.
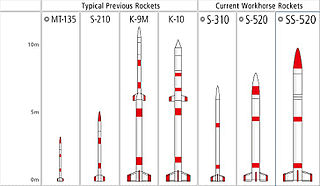
S-Series is a fleet of sounding rockets funded by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) that have been in service since the late 1960s. Manufactured by IHI Aerospace and operated by the Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS). The nomenclature of the S-Series rockets is the number of "S"s indicates the number of stages, and the following number details the diameter of the craft in millimeters. For example, the S-310 is a single stage rocket with a diameter of 310 mm.

A reentry capsule is the portion of a space capsule which returns to Earth following a spaceflight. The shape is determined partly by aerodynamics; a capsule is aerodynamically stable falling blunt end first, which allows only the blunt end to require a heat shield for atmospheric entry. A crewed capsule contains the spacecraft's instrument panel, limited storage space, and seats for crew members. Because a capsule shape has little aerodynamic lift, the final descent is via parachute, either coming to rest on land, at sea, or by active capture by an aircraft. In contrast, the development of spaceplane reentry vehicles attempts to provide a more flexible reentry profile.

The Advanced Reentry Demonstrator (ARD) was a European Space Agency (ESA) suborbital reentry vehicle. It was developed and operated for experimental purposes, specifically to validate the multiple reentry technologies integrated upon it and the vehicle's overall design, as well as to gain greater insight into the various phenomenon encountered during reentry.

The Intermediate eXperimental Vehicle (IXV) is a European Space Agency (ESA) experimental suborbital re-entry vehicle. It was developed to serve as a prototype lifting body orbital return vehicle to validate the ESA's work in the field of reusable orbital return vehicles.
The J-I was a Solid-fuel rocket expendable launch vehicle developed by the National Space Development Agency of Japan and the Institute of Space and Astronautical Science. In an attempt to reduce development costs, it used the solid rocket booster from the H-II as the first stage, and the upper stages of the M-3SII. It flew only once on a suborbital flight taking place 11 February 1996 UTC from Tanegashima Space Center pad LA-N, in a partial configuration, to launch the demonstrator HYFLEX. The vehicle never flew in the final orbital capability configuration, which should have launched the OICETS satellite.

The Space Capsule Recovery Experiment is an Indian experimental spacecraft which was launched at 03:53 UTC on January 10, 2007, from Sriharikota by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). The launch was conducted using the C7 launch of the PSLV rocket, along with three other satellites. It remained in orbit for 12 days before re-entering the Earth's atmosphere and splashing down into the Bay of Bengal at 04:16 UTC on January 22.
Several projects have been planned and undertaken to launch paper planes from the stratosphere or higher.

ALV X-1 was the first and only flight of the ATK Launch Vehicle (ALV) sounding rocket developed by Alliant Techsystems. The launch occurred from LP-0B at the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport (MARS) at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility. This mission carried the SOAREX-VI and Hy-BoLT experiments as payloads when it launched at 09:10 GMT on August 22, 2008. The vehicle was terminated 20 seconds into flight after veering too far off course.

Reusable Launch Vehicle–Technology Demonstration Programme is a series of technology demonstration missions that has been conceived by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) as a first step towards realising a Two Stage To Orbit (TSTO) re-usable launch vehicle, in which the second stage is a spaceplane.

The Alpha Draco missile, also known as Weapons System 199D (WS-199D), was an experimental ballistic missile developed by McDonnell Aircraft in the late 1950s to investigate the aerodynamic physics of the boost-glide reentry trajectory. Three test flights were conducted in 1959, of which two were successful.

Hypersonic Technology Vehicle 2 (HTV-2) is an experimental hypersonic glide vehicle developed as part of the DARPA Falcon Project designed to fly in the Mach 20 range. It is a test bed for technologies to provide the United States with the capability to reach any target in the world within one hour using an unmanned hypersonic bomber aircraft.

Non-ballistic atmospheric entry is a class of atmospheric entry trajectories that follow a non-ballistic trajectory by employing aerodynamic lift in the high upper atmosphere. It includes trajectories such as skip and glide.

Kounotori 7 (こうのとり7号機), also known as HTV-7, was the seventh flight of the H-II Transfer Vehicle (HTV), an uncrewed cargo spacecraft launched on 22 September 2018 to resupply the International Space Station.
WIRES is a Japanese project developing a winged single-stage reusable suborbital rocket as a test bed for a reusable orbital launch system or a crewed suborbital spaceplane. The full-size prototype, called WIRES-X, is expected to be launched in 2020.















