
An expendable launch system is a launch vehicle that can be launched only once, after which its components are either destroyed during reentry or discarded in space. ELVs typically consist of several rocket stages that are discarded sequentially as their fuel is exhausted and the vehicle gains altitude and speed. As of 2022, most satellites and human spacecraft are currently launched on ELVs. ELVs are simpler in design than reusable launch systems and therefore may have a lower production cost. Furthermore, an ELV can use its entire fuel supply to accelerate its payload, offering greater payloads. ELVs are proven technology in widespread use for many decades.

The Brazilian Space Agency is the civilian authority in Brazil responsible for the country's space program. It operates a spaceport at Alcântara, and a rocket launch site at Barreira do Inferno. It is the largest and most prominent space agency in Latin America.

The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) is the Japanese national air and space agency. Through the merger of three previously independent organizations, JAXA was formed on 1 October 2003. JAXA is responsible for research, technology development and launch of satellites into orbit, and is involved in many more advanced missions such as asteroid exploration and possible human exploration of the Moon. Its motto is One JAXA and its corporate slogan is Explore to Realize.

H-IIA (H-2A) is an active expendable launch system operated by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) for the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency. These liquid fuel rockets have been used to launch satellites into geostationary orbit; lunar orbiting spacecraft; Akatsuki, which studied the planet Venus; and the Emirates Mars Mission, which was launched to Mars in July 2020. Launches occur at the Tanegashima Space Center. The H-IIA first flew in 2001. As of December 2021, H-IIA rockets were launched 45 times, including 39 consecutive missions without a failure, dating back to 29 November 2003.

The Mu, also known as M, was a series of Japanese solid-fueled carrier rockets, which were launched from Uchinoura between 1966 and 2006. Originally developed by Japan's Institute of Space and Astronautical Science, Mu rockets were later operated by Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency following ISAS becoming part of it.
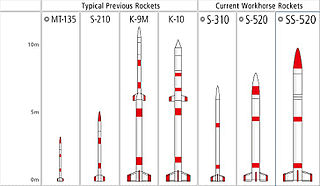
S-Series is a fleet of sounding rockets funded by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) that have been in service since the late 1960s. Manufactured by IHI Aerospace and operated by the Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS). The nomenclature of the S-Series rockets is the number of "S"s indicates the number of stages, and the following number details the diameter of the craft in millimeters. For example, the S-310 is a single stage rocket with a diameter of 310 mm.

The Korea Aerospace Research Institute (KARI), established in 1989, is the aeronautics and space agency of South Korea. Its main laboratories are located in Daejeon, in the Daedeok Science Town. KARI's vision is to continue building upon indigenous launch capabilities, strengthen national safety and public service, industrialize satellite information and applications technology, explore the moon, and develop environmentally-friendly and highly-efficient cutting-edge aircraft and core aerospace technology. Current projects include the KSLV-2 launcher. Past projects include the 1999 Arirang-1 satellite. The agency was founded in 1989. Prior to South Korea's entry into the Institute for Advanced Engineering (IAE) in 1992, it focused primarily on aerospace technology.

Shuttle-derived vehicles (SDV) are space launch vehicles and spacecraft that use components, technology, and infrastructure originally developed for the Space Shuttle program.

H-IIB (H2B) was an expendable space launch system jointly developed by the Japanese government's space agency JAXA and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries. It was used to launch the H-II Transfer Vehicle cargo spacecraft for the International Space Station. The H-IIB was a liquid-fueled rocket, with solid-fuel strap-on boosters and was launched from the Tanegashima Space Center in southern Japan. H-IIB made its first flight in 2009, and had made a total of nine flights through 2020 with no failures.

Commercial Orbital Transportation Services (COTS) was a NASA program to coordinate the development of vehicles for the delivery of crew and cargo to the International Space Station by private companies. The program was announced on January 18, 2006 and successfully flew all cargo demonstration flights by September 2013, when the program ended.

Vulcain is a family of European first stage rocket engines for Ariane 5 and the future Ariane 6. Its development began in 1988 and the first flight was completed in 1996. The updated version of the engine, Vulcain 2, was first successfully flown in 2005. Both members of the family use liquid oxygen/liquid hydrogen cryogenic fuel. The new version under development for Ariane 6 will be called Vulcain 2.1.
The VLS-1 was the Brazilian Space Agency's main satellite launch vehicle. The launch vehicle was to be capable of launching satellites into orbit. The launch site was located at the Alcântara Launch Center due to its proximity to the equator.

The H-II (H2) rocket was a Japanese satellite launch system, which flew seven times between 1994 and 1999, with five successes. It was developed by NASDA in order to give Japan a capability to launch larger satellites in the 1990s. It was the first two-stage liquid-fuelled rocket Japan made using only technologies developed domestically. It was superseded by the H-IIA rocket following reliability and cost issues.

This comparison of orbital launch systems lists the attributes of all individual rocket configurations designed to reach orbit. A first list contains rockets that are operational or in development as of 2022; a second list includes all retired rockets. For the simple list of all conventional launcher families, see: Comparison of orbital launchers families. For the list of predominantly solid-fueled orbital launch systems, see: Comparison of solid-fueled orbital launch systems.
The N-II or N-2 was a derivative of the American Delta rocket, produced under licence in Japan. It replaced the N-I-rocket in Japanese use. It used a Thor-ELT first stage, a Delta-F second stage, nine Castor SRMs, and on most flights either a Star-37E or Burner-2 upper stage, identical to the US Delta 0100 series configurations. Eight were launched between 1981 and 1987, before it was replaced by the H-I, which featured Japanese-produced upper stages. All eight launches were successful.

DIRECT was a late-2000s proposed alternative super heavy lift launch vehicle architecture supporting NASA's Vision for Space Exploration that would replace the space agency's planned Ares I and Ares V rockets with a family of Shuttle-Derived Launch Vehicles named "Jupiter". It was intended to be the alternative to the Ares I and Ares V rockets which were under development for the Constellation program, intended to develop the Orion spacecraft for use in Earth orbit, the Moon, and Mars.

The Japanese space program originated in the mid-1950s as a research group led by Hideo Itokawa at the University of Tokyo. The size of the rockets produced gradually increased from under 30 cm (12 in) at the start of the project, to over 15 m (49 ft) by the mid-1960s. The aim of the original research project was to launch a man-made satellite.

The Epsilon Launch Vehicle, or Epsilon rocket, is a Japanese solid-fuel rocket designed to launch scientific satellites. It is a follow-on project to the larger and more expensive M-V rocket which was retired in 2006. The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) began developing the Epsilon in 2007. It is capable of placing a 590 kg payload into Sun-synchronous orbit.

Hisaki, also known as the Spectroscopic Planet Observatory for Recognition of Interaction of Atmosphere (SPRINT-A) is a Japanese ultraviolet astronomy satellite operated by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). The first mission of the Small Scientific Satellite program, it was launched in September 2013 on the maiden flight of the Epsilon rocket. It remains operational as of 2022 and is used to for extreme ultraviolet observations of the Solar System planets.

Liquid Fly-back Booster (LFBB) was a German Aerospace Center's (DLR's) project concept to develop a liquid rocket booster capable of reusing for Ariane 5 in order to significantly reduce the high cost of space transportation and increase environmental friendliness. LFBB would replace the existing solid rocket boosters, providing main thrust during the liftoff. Once separated, two winged boosters would perform an atmospheric entry, fly back autonomously to the French Guiana, and land horizontally on the airport like an aeroplane.


















