Related Research Articles

Ariane 5 is a retired European heavy-lift space launch vehicle developed and operated by Arianespace for the European Space Agency (ESA). It was launched from the Centre Spatial Guyanais (CSG) in French Guiana. It was used to deliver payloads into geostationary transfer orbit (GTO),low Earth orbit (LEO) or further into space. The launch vehicle had a streak of 82 consecutive successful launches between 9 April 2003 and 12 December 2017. Since 2014,Ariane 6,a direct successor system,is in development.
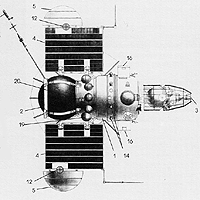
Venera 2MV-1 No.1,also known as Sputnik 19 in the West,was a Soviet spacecraft,which was launched in 1962 as part of the Venera programme.
Venera 2MV-1 No.2,also known as Sputnik 20 in the Western world,was a Soviet spacecraft,which was launched in 1962 as part of the Venera programme. Due to a problem with its upper stage it failed to leave low Earth orbit,and reentered the atmosphere a few days later. It was the second of two Venera 2MV-1 spacecraft,both of which failed to leave Earth orbit. The previous mission,Venera 2MV-1 No.1,was launched several days earlier.

The Scout family of rockets were American launch vehicles designed to place small satellites into orbit around the Earth. The Scout multistage rocket was the first orbital launch vehicle to be entirely composed of solid fuel stages. It was also the only vehicle of that type until the successful launch of the Japanese Lambda 4S in 1970.

The Thor-Burner was an American expendable launch system,a member of the Thor rocket family. It consisted of a Thor missile,with one or two Burner upper stages. It was used between 1965 and 1976 to orbit a number of satellites,most commonly Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP) weather satellites. Twenty-four were launched,of which two failed. It weighed 51,810 kg and was 24 metres tall.

This article lists all active and upcoming orbital launch systems. For retired launch vehicles,see Comparison of retired orbital launch systems.
The Broadcasting Satellite System Corporation (B-SAT) is a Japanese corporation established in April 1993 to procure,manage and lease transponders on communications satellites. Its largest stockholder,owning 49.9%,is NHK,the Japan Broadcasting Corporation. In 1994,it was ranked by Space News as the world's 19th largest fixed satellite operator.
Scout X-2 was an American expendable launch system and sounding rocket which was flown twice in 1962. It was a four-stage rocket,based on the earlier Scout X-1,uprated first and third stages. It was a member of the Scout family of rockets.

The Altair was a solid-fuel rocket with a fiberglass casing,initially developed for use as the third stage of Vanguard rockets in 1959. It was manufactured by Allegany Ballistics Laboratory (ABL) as the X-248. It was also sometimes called the Burner 1.

The Atlas E/F was an American expendable launch system and sounding rocket built using parts of decommissioned SM-65 Atlas missiles. It was a member of the Atlas family of rockets.

The Thor-Delta,also known as Delta DM-19 or just Delta was an early American expendable launch system used for 12 orbital launches in the early 1960s. A derivative of the Thor-Able,it was a member of the Thor family of rockets,and the first member of the Delta family.

The Delta C,or Thor-Delta C was an American expendable launch system used for thirteen orbital launches between 1963 and 1969. It was a member of the Delta family of rockets.

The Delta D,Thrust Augmented Delta or Thor-Delta D was an American expendable launch system used to launch two communications satellites in 1964 and 1965. It was derived from the Delta C,and was a member of the Delta family of rockets.
Scout X,also known as Cub Scout,was an American rocket which served as a prototype of the Scout,which was launched on a single test flight in 1960. It was used to test the configuration that later Scout rockets would use as well as two of the solid rocket motors that would be used on them.
Scout X-1 was an American expendable launch system and sounding rocket which was flown seven times between August 1960 and October 1961. Four orbital and three suborbital launches were made,with four of the launches resulting in failures.

The RM-90 Blue Scout II was an American sounding rocket and expendable launch system which was flown three times during 1961. It was used for two HETS test flights,and the launch of the Mercury-Scout 1 satellite for NASA. It was a member of the Scout family of rockets.

The RM-89 Blue Scout I was an American sounding rocket which was flown four times between January 1961 and April 1962. It was used for two HETS test flights,and a flight to investigate atmospheric re-entry. It was a member of the Scout family of rockets.
Scout X-1A was an American sounding rocket which was flown in 1962. It was a five-stage derivative of the earlier Scout X-1,with an uprated first stage,and a NOTS-17 upper stage.

Scout X-2M was an American expendable launch system which was flown three times between May 1962 and April 1963. It was a four-stage rocket,based on the earlier Scout X-2,but with an MG-18 upper stage instead of the Altair used on the X-2. It was a member of the Scout family of rockets.
Kuaizhou is a family of Chinese "quick-reaction" orbital launch vehicles. Flying since 2013,Kuaizhou 1 and 1A consist of three solid-fueled rocket stages,with a liquid-fueled fourth stage as part of the satellite system. Kuaizhou 11,which flew an unsuccessful maiden flight in July 2020,is a larger model able to launch a 1,500 kg (3,300 lb) payload into low Earth orbit. Heavy-lift models KZ-21 and KZ-31 are in development. The Kuaizhou series of rockets is manufactured by ExPace,a subsidiary of China Aerospace Science and Industry Corporation (CASIC),as their commercial launch vehicles.
References
- Wade, Mark. "Scout". Encyclopedia Astronautica. Archived from the original on September 17, 2008. Retrieved 2009-07-03.
- Krebs, Gunter. "Scout". Gunter's Space Page. Retrieved 2009-07-03.
- McDowell, Jonathan. "Scout". Orbital & Suborbital Launch Database. Jonathan's Space Page. Archived from the original on 2020-08-11. Retrieved 2009-07-03.
- Heyman, Jos; Parsch, Andreas (2007-07-09). "LTV SLV-1 Scout". Appendix 3: Space Vehicles. Directory of U.S. Military Rockets and Missiles. Retrieved 2009-07-03.
