
Schist is a medium-grained metamorphic rock showing pronounced schistosity. This means that the rock is composed of mineral grains easily seen with a low-power hand lens, oriented in such a way that the rock is easily split into thin flakes or plates. This texture reflects a high content of platy minerals, such as mica, talc, chlorite, or graphite. These are often interleaved with more granular minerals, such as feldspar or quartz.

Metamorphism is the transformation of existing rock to rock with a different mineral composition or texture. Metamorphism takes place at temperatures in excess of 150 °C (300 °F), and often also at elevated pressure or in the presence of chemically active fluids, but the rock remains mostly solid during the transformation. Metamorphism is distinct from weathering or diagenesis, which are changes that take place at or just beneath Earth's surface.

Blueschist, also called glaucophane schist, is a metavolcanic rock that forms by the metamorphism of basalt and rocks with similar composition at high pressures and low temperatures, approximately corresponding to a depth of 15–30 km (9.3–18.6 mi). The blue color of the rock comes from the presence of the predominant minerals glaucophane and lawsonite.

The Alpine Fault is a geological fault that runs almost the entire length of New Zealand's South Island, being about 600 km (370 mi). long, and forms the boundary between the Pacific Plate and the Australian Plate. The Southern Alps have been uplifted on the fault over the last 12 million years in a series of earthquakes. However, most of the motion on the fault is strike-slip, with the Tasman district and West Coast moving north and Canterbury and Otago moving south. The average slip rates in the fault's central region are about 38 mm (1.5 in) a year, very fast by global standards. The last major earthquake on the Alpine Fault was in about 1717 AD with a great earthquake magnitude of 8.1± 0.1. The probability of another one occurring before 2068 was estimated at 75 percent in 2021.

The Franciscan Complex or Franciscan Assemblage is a geologic term for a late Mesozoic terrane of heterogeneous rocks found throughout the California Coast Ranges, and particularly on the San Francisco Peninsula. It was named by geologist Andrew Lawson, who also named the San Andreas fault that defines the western extent of the assemblage.
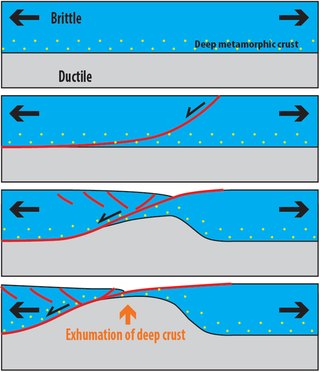
Metamorphic core complexes are exposed areas of deep crust brought to the surface by crustal extension (stretching). They form, and are exhumed, through relatively fast transport of middle and lower continental crust to the Earth's surface in the form of uplifting welts of hot rock and magma. The resulting doming causes the overlying rock to gravitationally collapse, sliding down and usually away from the uplift along low-angle detachment faults. Brittle, faulted cover rock above the detachment surface lies in direct contact with the ductile middle-lower crust below.
An isograd is a concept used in the study of metamorphic rocks. The metamorphic grade of such a rock is a rough measure of the degree of metamorphism it has undergone, as characterised by the presence of certain index minerals. An isograd is a theoretical surface comprising points all at the same metamorphic grade, and thus separates metamorphic zones whose rocks contain different index minerals.

The Torlesse Composite Terrane is a plate tectonic terrane forming part of the South Island of New Zealand. It contains the Rakaia, Aspiring and Pahau Terranes and the Esk Head Belt. Greywacke is the dominant rock type of the composite terrane; argillite is less common and there are minor basalt occurrences. The Torlesse Composite Terrane is found east of the Alpine Fault in the Southern Alps of New Zealand. Its southern extent is a cryptic boundary with the Caples Terrane within the Haast Schists in Central Otago. It is named for the Torlesse Range in Canterbury.

The geology of New Zealand is noted for its volcanic activity, earthquakes and geothermal areas because of its position on the boundary of the Australian Plate and Pacific Plates. New Zealand is part of Zealandia, a microcontinent nearly half the size of Australia that broke away from the Gondwanan supercontinent about 83 million years ago. New Zealand's early separation from other landmasses and subsequent evolution have created a unique fossil record and modern ecology.

The Tasman Region, and the small adjoining Nelson Region, form one of the more geologically interesting regions of New Zealand. It contains the oldest rocks of anywhere on New Zealand's main islands. It contains all the main terranes that make up New Zealand's basement. These basement rocks include Ultramafic rocks, such as Serpentine and Dunite, and valuable minerals, such as Gold. The Nelson Region is bordered to the south by the Alpine Fault, the main fault forming the boundary between the Pacific Plate and the Indo-Australian Plate, that generated the Southern Alps.

High pressure terranes along the ~1200 km long east-west trending Bangong-Nujiang suture zone (BNS) on the Tibetan Plateau have been extensively mapped and studied. Understanding the geodynamic processes in which these terranes are created is key to understanding the development and subsequent deformation of the BNS and Eurasian deformation as a whole.
The geology of Alaska includes Precambrian igneous and metamorphic rocks formed in offshore terranes and added to the western margin of North America from the Paleozoic through modern times. The region was submerged for much of the Paleozoic and Mesozoic and formed extensive oil and gas reserves due to tectonic activity in the Arctic Ocean. Alaska was largely ice free during the Pleistocene, allowing humans to migrate into the Americas.

The Dun Mountain-Maitai Terrane comprises the Dun Mountain Ophiolite Belt, Maitai Group and Patuki Mélange. The Dun Mountain Ophiolite is an ophiolite of Permian age located in New Zealand's South Island. Prehistorically this ophiolite was quarried by Māori for both metasomatized argillite and pounamu (jade) which was used in the production of tools and jewellery.
The geology of Ecuador includes ancient Precambrian basement rock and a complex tectonic assembly of new sections of crust from formerly separate landmasses, often uplifted as the Andes or transformed into basins.

This is a list of the units into which the rock succession of New Zealand is formally divided. As new geological relationships have been discovered new names have been proposed and others are made obsolete. Not all these changes have been universally adopted. This table is based on the 2014 New Zealand Stratigraphic Lexicon (Litho2014). However, obsolete names that are still in use and names postdating the lexicon are included if it aids in understanding.

The geology of the West Coast of New Zealand's South Island is divided in two by the Alpine Fault, which runs through the Region in a North-East direction. To the West of the fault Paleozoic basement rocks are interluded by plutones and both are unconformably covered in a sedimentary sequence. To the East of the Alpine Fault are the Mesozoic Alpine Schist and Greywacke of the Southern Alps. There are numerous active faults throughout the region.

The geology of New Caledonia includes all major rock types, which here range in age from ~290 million years old (Ma) to recent. Their formation is driven by alternate plate collisions and rifting. The mantle-derived Eocene Peridotite Nappe is the most significant and widespread unit. The igneous unit consists of ore-rich ultramafic rocks thrust onto the main island. Mining of valuable metals from this unit has been an economical pillar of New Caledonia for more than a century.
The volcanic activity in the South Island of New Zealand terminated 5 million years ago as the more northern parts of the North Island became extremely volcanically active. The South Islands surface geology reflects the uplift of the Pacific Plate as it collides with the Indo-Australian Plate along the Alpine Fault over the last 12 million years and the termination of subduction, about 100 to 105 million years ago. There is a very small chance of reactivation of volcanism in the Dunedin Volcano. This chance is made slightly higher by the observation that Southland's Solander Islands / Hautere just off the coast of the South Island were active as recently as 50,000 years old, and on a larger scale 150,000 years old.

The Dunstan Mountains are a mountain range in Central Otago, in the South Island of New Zealand. The mountains lie on the eastern shore of the man-made Lake Dunstan and overlook the towns of Cromwell to the west, Clyde to the south and Omakau to the east. The highest named peak on the mountain range, a rocky knoll simply called Dunstan, is 1,667 m.
Nick Mortimer is a New Zealand geologist, who has made a name for himself with his work on Zealandia.














