
Dendrobium teretifolium, commonly known as the thin pencil orchid, rat's tail orchid or bridal veil orchid, is an epiphytic or lithophytic orchid in the family Orchidaceae. It has long, thin hanging stems, pencil-like leaves and rigid flowering stems bearing up to twelve crowded white to cream-coloured flowers. It grows in rainforest and humid open forest mostly in near-coastal districts in New South Wales and Queensland.

Cymbidium canaliculatum, commonly known as the channelled boat-lip orchid, tiger boat-lip orchid, native cymbidium or tiger orchid is a plant in the orchid family and is endemic to Australia. It is a clump-forming epiphyte with large, greyish green pseudobulbs, each with up to six curved, deeply channelled leaves and up to sixty fragrant, variably coloured flowers that often have spots and blotches and a white to cream-coloured labellum with red markings. This orchid usually grows in the forks or hollows of trees and is found from New South Wales to the northern parts of Western Australia.

Sarcochilus falcatus, commonly known as the orange blossom orchid, is a small epiphytic or lithophytic orchid that is endemic to eastern Australia. It has up to eight, leathery leaves with fine teeth on the edges and up to twelve white to cream-coloured flowers with a white labellum that has orange and purple markings.

Lyperanthus, commonly known as beak orchids, is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae, that is endemic to Australia. There are two species, one in Western Australia and the other in four eastern Australian states, distinguished by their single long, narrow, leathery leaf and dull coloured flowers which have prominent short calli on their labellum. Both form loose colonies which reproduce asexually from their tubers, and sexually using their flowers.

Dendrobium aemulum, commonly known as the ironbark feather orchid or white feather orchid, is an epiphytic orchid in the family Orchidaceae and grows on trees that retain their bark, especially ironbarks. It has reddish or purplish pseudobulbs, two to four leathery leaves and up to seven white, feathery flowers. It grows in open forest in Queensland and New South Wales.

Orthoceras strictum, commonly known as the bird's-mouth orchid or horned orchid, is a species of orchid native to eastern and southern Australia, New Zealand and New Caledonia. It has between two and five linear leaves and up to nine yellowish green, brownish or blackish flowers with two long, erect to spreading lateral sepals.

Diuris sulphurea, commonly called the tiger orchid or hornet orchid, is a species of orchid which is endemic to eastern Australia. It has up to three leaves, and a flowering stem with up to seven bright yellow flowers with dark brown markings.
Epiblema grandiflorum, commonly known as babe-in-a-cradle, is the only species in the flowering plant genus Epiblema in the orchid family, Orchidaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is a colony-forming orchid which grows in peaty swamps near the coast. Its flowers are purple with ribbon-like strands attached to its labellum and a broad, petal-like column.

Caladenia congesta, commonly known as black-tongue caladenia, is a plant in the orchid family Orchidaceae and is endemic to Australia. It is a ground orchid with a single, sparsely hairy leaf, and up to three bright pink flowers with the central part of the labellum completely covered with black calli. It is a widespread species but not common in any part of its range.

Caladenia flava subsp. sylvestris, commonly known as the karri cowslip orchid, is a species of orchid endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It has a single, hairy leaf and up to three pale yellow and cream-coloured flowers which are white near the tips of the sepals and petals and marked with bright red or pink.

Caladenia testacea, commonly known as honey caps, or honey caladenia is a plant in the orchid family Orchidaceae and is endemic to New South Wales. It is a ground orchid with a single, sparsely hairy leaf and up to three white to yellowish-green flowers with brownish tips and a darker back.

Pterostylis ophioglossa, commonly known as the snake-tongue greenhood, is a species of orchid endemic to eastern Australia. It has a rosette of leaves at the base and a single dull green, white and brown flower with a deeply notched labellum.

Pterostylis reflexa, commonly known as the dainty greenhood, is a species of orchid endemic to New South Wales. As with similar greenhoods, the flowering plants differ from those which are not flowering. The non-flowering plants have a rosette of leaves flat on the ground but the flowering plants have a single flower with leaves on the flowering stem. This greenhood has a relatively large white, green and light brown flower with a long, curved dorsal sepal and a protruding labellum.
Prasophyllum gibbosum, commonly known as the humped leek orchid, is a species of orchid endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is a late-flowering leek orchid with a single smooth, tubular leaf and up to eighty or more purplish-red and white flowers with a smooth labellum. It is similar to P. cucullatum but that species has a frilly labellum, usually a shorter flowering stem and an earlier flowering period.
Prasophyllum macrostachyum, commonly known as the laughing leek orchid, is a species of orchid endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It has a single smooth, tube-shaped leaf and up to thirty yellowish-green and purple flowers. It is one of the few Western Australian leek orchids which is not stimulated by summer fires and also has an unusually long flowering period.

Prasophyllum striatum, commonly known as the streaked leek orchid or eastern hunchback orchid, is a species of orchid endemic to New South Wales. It has a single thin, tube-shaped leaf and up to ten greenish and whitish flowers with reddish or purplish stripes. It differs from other leek orchids in having a very thin leaf and prominently streaked flowers.

Diuris setacea, commonly called the bristly donkey orchid, is a species of orchid that is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It has a tuft of up to ten twisted leaves at its base and up to seven yellow flowers with a few brown markings. It grows in moist soil on granite outcrops and flowers much more prolifically after fire the previous summer.
Thelymitra angustifolia, commonly known as the long-leaved sun orchid is a species of orchid that is endemic to eastern Australia. It has a single erect, thin, channelled leaf and up to ten purplish blue flowers with white tufts on top of the anther. The flowers are self-pollinating.
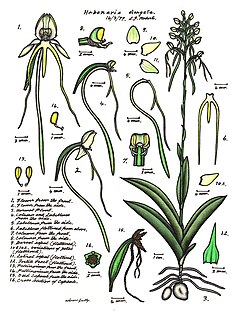
Habenaria elongata, commonly known as the white rein orchid, or Kimberley spider orchid, is a species of orchid that is endemic to northern Australia. It has up to four leaves at its base and up to twenty small white flowers with yellowish tips and thread-like lobes on the labellum.

Dendrobium canaliculatum, commonly known as the brown tea tree orchid or thin tea tree orchid, is an epiphytic or lithophytic orchid in the family Orchidaceae. It has cone-shaped or onion-shaped pseudobulbs, up to six deeply channelled, dark green leaves and up to thirty star-shaped, light brown to caramel-coloured white or greenish to apricot-coloured flowers with darker tips. It grows in tropical North Queensland and New Guinea.















