Oil sands, tar sands, crude bitumen, or bituminous sands, are a type of unconventional petroleum deposit. Oil sands are either loose sands or partially consolidated sandstone containing a naturally occurring mixture of sand, clay, and water, soaked with bitumen, a dense and extremely viscous form of petroleum.

The Athabasca oil sands, also known as the Athabasca tar sands, are large deposits of bitumen, a heavy and viscous form of petroleum, located in northeastern Alberta, Canada. These reserves are one of the largest sources of unconventional oil in the world, making Canada a significant player in the global energy market.

TotalEnergies SE is a French multinational integrated energy and petroleum company founded in 1924 and is one of the seven supermajor oil companies. Its businesses cover the entire oil and gas chain, from crude oil and natural gas exploration and production to power generation, transportation, refining, petroleum product marketing, and international crude oil and product trading. TotalEnergies is also a large-scale chemicals manufacturer.

Peak oil is the theorized point in time when the maximum rate of global oil production will occur, after which oil production will begin an irreversible decline. The primary concern of peak oil is that global transportation heavily relies upon the use of gasoline and diesel fuel. Switching transportation to electric vehicles, biofuels, or more fuel-efficient forms of travel may help reduce oil demand.

Canadian Utilities Limited, a member of the ATCO Group of companies, is a Canada-based worldwide organization of companies with around $22 billion in assets and more than 8,000 employees.
Enbridge Inc. is a Canadian multinational pipeline and energy company headquartered in Calgary, Alberta, Canada. Enbridge owns and operates pipelines throughout Canada and the United States, transporting crude oil, natural gas, and natural gas liquids, and also generates renewable energy. Enbridge's pipeline system is the longest in North America and the largest oil export pipeline network in the world. Its crude oil system consists of 28,661 kilometres of pipelines. Its 38,300 kilometre natural gas pipeline system connects multiple Canadian provinces, several US states, and the Gulf of Mexico. The company was formed by Imperial Oil in 1949 as the Interprovincial Pipe Line Company Limited to transport Alberta oil to refineries. Over time, it has grown through acquisition of other existing pipeline companies and the expansion of their projects.

China Petroleum and Chemical Corporation, or Sinopec, is a Chinese oil and gas enterprise based in Beijing. It is listed in Hong Kong and also trades in Shanghai.
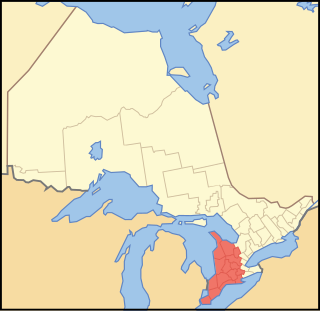
Southwestern Ontario is a secondary region of Southern Ontario in the Canadian province of Ontario. It occupies most of the Ontario Peninsula bounded by Lake Huron, including Georgian Bay, to the north and northwest; the St. Clair River, Lake St. Clair, and Detroit River, to the west; and Lake Erie to the south. To the east, on land, Southwestern Ontario is bounded by Central Ontario and the Golden Horseshoe.
Fort Nelson is a community in northeast British Columbia, Canada, within the Northern Rockies Regional Municipality (NRRM). It held town status prior to 6 February 2009, when it amalgamated with the former Northern Rockies Regional District to form the NRRM, becoming its administrative centre. The NRRM is the first regional municipality in the province.

TC Energy Corporation is a major North American energy company, based in the TC Energy Tower building in Calgary, Alberta, Canada, that develops and operates energy infrastructure in Canada, the United States, and Mexico. The company operates three core businesses: Natural Gas Pipelines, Liquids Pipelines and Energy.

The China National Petroleum Corporation (CNPC) is a major national oil and gas corporation of China and one of the largest integrated energy groups in the world. Its headquarters are in Dongcheng District, Beijing. CNPC was ranked fourth in 2022 Fortune Global 500, a global ranking of the largest corporations by revenue.

Murphy Oil Corporation is a company engaged in hydrocarbon exploration headquartered in Houston, Texas.

Greater Sierra is a large oil and gas field in northeastern British Columbia, Canada. It is east and north from the town of Fort Nelson, extending to the Alberta and Northwest Territories borders.

Brazil is the 7th largest energy consumer in the world and the largest in South America. At the same time, it is an important oil and gas producer in the region and the world's second largest ethanol fuel producer. The government agencies responsible for energy policy are the Ministry of Mines and Energy (MME), the National Council for Energy Policy (CNPE), the National Agency of Petroleum, Natural Gas and Biofuels (ANP) and the National Agency of Electricity (ANEEL). State-owned companies Petrobras and Eletrobras are the major players in Brazil's energy sector, as well as Latin America's.

Although there are numerous oil companies operating in Canada, as of 2009, the majority of production, refining and marketing was done by fewer than 20 of them. According to the 2013 edition of Forbes Global 2000, canoils.com and any other list that emphasizes market capitalization and revenue when sizing up companies, as of March 31, 2014 these are the largest Canada-based oil and gas companies.

Tight oil is light crude oil contained in unconventional petroleum-bearing formations of low permeability, often shale or tight sandstone. Economic production from tight oil formations requires the same hydraulic fracturing and often uses the same horizontal well technology used in the production of shale gas. While sometimes called "shale oil", tight oil should not be confused with oil shale or shale oil. Therefore, the International Energy Agency recommends using the term "light tight oil" for oil produced from shales or other very low permeability formations, while the World Energy Resources 2013 report by the World Energy Council uses the terms "tight oil" and "shale-hosted oil".
Uzbekistan had a total primary energy supply (TPES) of 48.28 Mtoe in 2012. Electricity consumption was 47.80 TWh. The majority of primary energy came from fossil fuels, with natural gas, coal and oil the main sources. Hydroelectricity, the only significant renewable source in the country, accounted for about 2% of the primary energy supply. Natural gas is the source for 73.8% of electricity production, followed by hydroelectricity with 21.4%.

Robert Habeck is a German Green politician and writer who has been serving as Vice Chancellor of Germany, Federal Minister for Economic Affairs and Climate Action in the cabinet of Chancellor Olaf Scholz and as a Member of the German Bundestag for Flensburg – Schleswig since 2021. From 2018 to 2022, he also served as co-leader of Alliance 90/The Greens, alongside Annalena Baerbock. For the 2021 German federal election, he was a member of the leading duo, alongside Baerbock, who ran for chancellor of Germany.
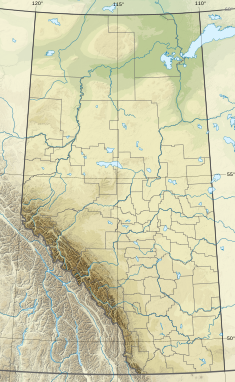
The Canadian province of Alberta faces a number of environmental issues related to natural resource extraction—including oil and gas industry with its oil sands—endangered species, melting glaciers in banff, floods and droughts, wildfires, and global climate change. While the oil and gas industries generates substantial economic wealth, the Athabasca oil sands, which are situated almost entirely in Alberta, are the "fourth most carbon intensive on the planet behind Algeria, Venezuela and Cameroon" according to an August 8, 2018 article in the American Association for the Advancement of Science's journal Science. This article details some of the environmental issues including past ecological disasters in Alberta and describes some of the efforts at the municipal, provincial and federal level to mitigate the risks and impacts.
A global energy crisis began in the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2021, with much of the globe facing shortages and increased prices in oil, gas and electricity markets. The crisis was caused by a variety of economic factors, including the rapid post-pandemic economic rebound that outpaced energy supply, and escalated into a widespread global energy crisis following the Russian invasion of Ukraine. The price of natural gas reached record highs, and as a result, so did electricity in some markets. Oil prices hit their highest level since 2008.