
Alberta is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is a part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta borders British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Territories to the north, and the U.S. state of Montana to the south. It is one of the only two landlocked provinces in Canada, with Saskatchewan being the other. The eastern part of the province is occupied by the Great Plains, while the western part borders the Rocky Mountains. The province has a predominantly continental climate but experiences quick temperature changes due to air aridity. Seasonal temperature swings are less pronounced in western Alberta due to occasional Chinook winds.

Jasper National Park, in Alberta, Canada, is the largest national park within Alberta's Rocky Mountains, spanning 11,000 km2 (4,200 sq mi). It was established as Jasper Forest Park in 1907, renamed as a national park in 1930, and declared a UNESCO world heritage site in 1984. Its location is north of Banff National Park and west of Edmonton. The park contains the glaciers of the Columbia Icefield, springs, lakes, waterfalls and mountains.
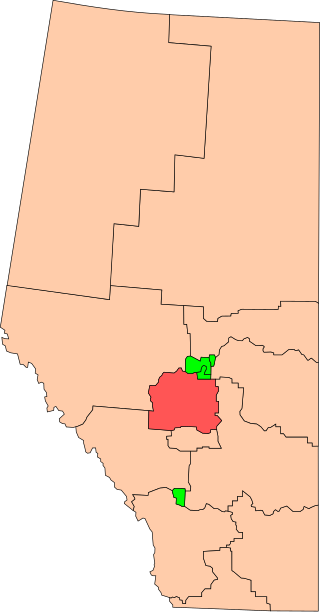
Wetaskiwin was a federal electoral district in Alberta, Canada, that was represented in the House of Commons of Canada from 1925 to 2015.
Highway 2 is a major highway in Alberta that stretches from the Canada–United States border through Calgary and Edmonton to Grande Prairie. Running primarily north to south for approximately 1,273 kilometres (791 mi), it is the longest and busiest highway in the province carrying more than 170,000 vehicles per day near Downtown Calgary. The Fort Macleod—Edmonton section forms a portion of the CANAMEX Corridor that links Alaska to Mexico. More than half of Alberta's 4 million residents live in the Calgary–Edmonton Corridor created by Highway 2.
Alberta Provincial Highway No. 16, commonly referred to as Highway 16, is a major east–west highway in central Alberta, Canada, connecting Jasper to Lloydminster via Edmonton. It forms a portion of the Yellowhead Highway, a major interprovincial route of the Trans-Canada Highway system that stretches from Masset, British Columbia, to Portage la Prairie, Manitoba, near Winnipeg. Highway 16 spans approximately 634 km (394 mi) from Alberta's border with British Columbia in the west to its border with Saskatchewan in the east. As of 2010, all but less than 96 km (60 mi) of the route was divided, with a minimum of two lanes in each direction. It is designated a core route in Canada's National Highway System.

Alberta Provincial Highway No. 11, commonly referred to as Highway 11 and officially named the David Thompson Highway, is a provincial highway in central Alberta, Canada. It runs for 318 km (198 mi) from Highway 93 at Saskatchewan River Crossing near Mount Sarbach in Banff National Park east to Highway 12 near Nevis. It passes by Nordegg and through Rocky Mountain House, Sylvan Lake and Red Deer along its course. The highway is named after David Thompson, a British-Canadian fur trader, surveyor, and map-maker who explored the area between Rocky Mountain House and Kootenae House through Howse Pass.
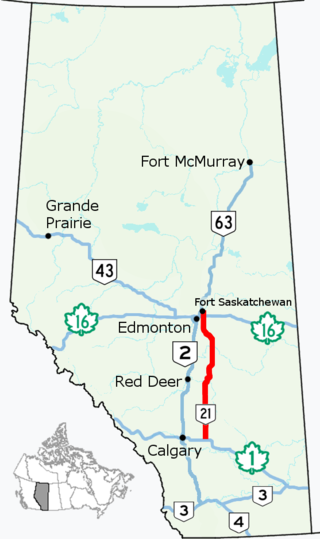
Highway 21 is a north–south highway in Alberta, Canada that parallels Highway 2 between Calgary and Edmonton. It is approximately 328 kilometres (204 mi) in length. It begins at the Trans-Canada Highway east of Strathmore, and ends at Fort Saskatchewan where it is succeeded by Highway 15. The northernmost 25 kilometres (16 mi) of the highway are twinned. Highway 21 runs roughly parallel to the main north–south CN rail line between Calgary and Edmonton between Three Hills and Looma.

Highway 11A is the designation of two routes that connect to Highway 11 in Alberta, Canada. The Rocky Mountain House section is referred to as 11A:02 by Alberta Transportation, while 11A:06 runs from Sylvan Lake to Red Deer.

Highway 16 is a provincial highway in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan. It is the Saskatchewan section of the Yellowhead Highway, and also the Trans-Canada Highway Yellowhead section. The main purpose of this highway is to connect Saskatchewan with Canadian cities such as Edmonton and Winnipeg. The highway runs from the Alberta boundary in Lloydminster to the Manitoba boundary near Marchwell. Major cities it passes through are Saskatoon, North Battleford in the central part of the province, Yorkton in the far east and Lloydminster to the far west.

Alberta has been a tourist destination since the early days of the 20th Century, with attractions including national parks, National Historic Sites of Canada, urban arts and cultural facilities, outdoor locales for skiing, hiking and camping, shopping locales such as West Edmonton Mall, outdoor festivals, professional athletic events, international sporting competitions such as the Commonwealth Games and Olympic Winter Games, as well as more eclectic attractions.

Southern Alberta is a region located in the Canadian province of Alberta. In 2016, the region's population was approximately 291,112. The primary cities are Lethbridge and Medicine Hat. The region is known mostly for agricultural production, but other sectors, such as alternative energy, film production and tourism, are emerging.
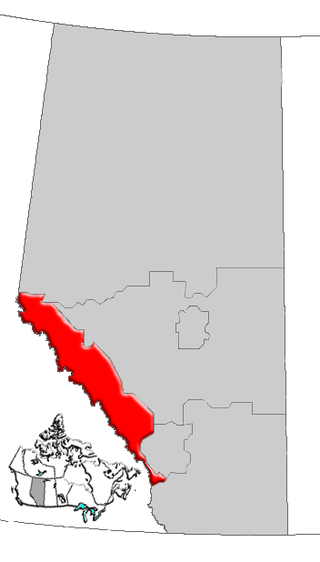
Alberta's Rockies comprise the Canadian Rocky Mountains in Alberta, Canada. On the southwestern part of the province along the British Columbia border, the region covers all but the south of Census Division 15.
Transport in Edmonton is fairly typical for a Canadian city of its size, involving air, rail, road and public transit. With very few natural barriers to growth and largely flat to gently rolling terrain bisected by a deep river valley, the city of Edmonton has expanded to cover an area of nearly 768 km2 (297 sq mi), of which only two-thirds is built-up, while the metropolitan area covers around 9,430 km2 (3,640 sq mi).
Alberta Health Services (AHS) is the single health authority for the Canadian province of Alberta and the "largest integrated provincial health care system" in Canada. Headquartered in Edmonton, AHS delivers medical care on behalf of the Government of Alberta's Ministry of Health. It operates 850 facilities throughout the province, including hospitals, clinics, continuing care facilities, mental health facilities and community health sites, that provide a variety of programs and services. AHS is the largest employer in the province of Alberta. In 2019, AHS served 4.3 million Albertans with a staff of 125,000 staff and 10,000 physicians, and an annual budget of $15.365 billion. Sean Chilton is the Acting President and CEO of AHS and reports to Dr. John Cowell, the AHS Official Administrator. The Official Administrator is accountable to the Minister of Health and the Premier.

Value Drug Mart is a Western Canada drug store serving over 36 locations throughout Alberta and British Columbia.











