Related Research Articles

In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm is a finite sequence of mathematically rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specifications for performing calculations and data processing. More advanced algorithms can use conditionals to divert the code execution through various routes and deduce valid inferences.
Complexity characterizes the behavior of a system or model whose components interact in multiple ways and follow local rules, leading to non-linearity, randomness, collective dynamics, hierarchy, and emergence.
In theoretical computer science and mathematics, computational complexity theory focuses on classifying computational problems according to their resource usage, and explores the relationships between these classifications. A computational problem is a task solved by a computer. A computation problem is solvable by mechanical application of mathematical steps, such as an algorithm.
Quadratic programming (QP) is the process of solving certain mathematical optimization problems involving quadratic functions. Specifically, one seeks to optimize a multivariate quadratic function subject to linear constraints on the variables. Quadratic programming is a type of nonlinear programming.
Software design is the process of conceptualizing how a software system will work before it is implemented or modified. Software design also refers to the direct result of the design process – the concepts of how the software will work which consists of both design documentation and undocumented concepts.
Critical thinking is the analysis of available facts, evidence, observations, and arguments in order to form a judgement by the application of rational, skeptical, and unbiased analyses and evaluation. In modern times, the use of the phrase critical thinking can be traced to John Dewey, who used the phrase reflective thinking. The application of critical thinking includes self-directed, self-disciplined, self-monitored, and self-corrective habits of the mind; thus, a critical thinker is a person who practices the skills of critical thinking or has been trained and educated in its disciplines. Philosopher Richard W. Paul said that the mind of a critical thinker engages the person's intellectual abilities and personality traits. Critical thinking presupposes assent to rigorous standards of excellence and mindful command of their use in effective communication and problem solving, and a commitment to overcome egocentrism and sociocentrism.
TRIZ combines an organized, systematic method of problem-solving with analysis and forecasting techniques derived from the study of patterns of invention in global patent literature. The development and improvement of products and technologies in accordance with TRIZ are guided by the laws of technical systems evolution. Its development, by Soviet inventor and science-fiction author Genrich Altshuller and his colleagues, began in 1946. In English, TRIZ is typically rendered as the theory of inventive problem solving.

In the philosophy of mind, the hard problem of consciousness is to explain why and how humans and other organisms have qualia, phenomenal consciousness, or subjective experience. It is contrasted with the "easy problems" of explaining why and how physical systems give a (healthy) human being the ability to discriminate, to integrate information, and to perform behavioral functions such as watching, listening, speaking, and so forth. The easy problems are amenable to functional explanation—that is, explanations that are mechanistic or behavioral—since each physical system can be explained purely by reference to the "structure and dynamics" that underpin the phenomenon.
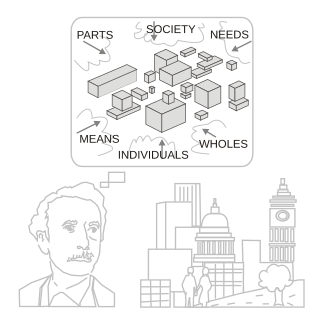
Systems science, also referred to as systems research, or, simply, systems, is a transdisciplinary field that is concerned with understanding simple and complex systems in nature and society, which leads to the advancements of formal, natural, social, and applied attributions throughout engineering, technology and science, itself.

Russell Lincoln Ackoff was an American organizational theorist, consultant, and Anheuser-Busch Professor Emeritus of Management Science at the Wharton School, University of Pennsylvania. Ackoff was a pioneer in the field of operations research, systems thinking and management science.
Soft systems methodology (SSM) is an organised way of thinking that's applicable to problematic social situations and in the management of change by using action. It was developed in England by academics at the Lancaster Systems Department on the basis of a ten-year action research programme.
In planning and policy, a wicked problem is a problem that is difficult or impossible to solve because of incomplete, contradictory, and changing requirements that are often difficult to recognize. It refers to an idea or problem that cannot be fixed, where there is no single solution to the problem; and "wicked" denotes resistance to resolution, rather than evil. Another definition is "a problem whose social complexity means that it has no determinable stopping point". Moreover, because of complex interdependencies, the effort to solve one aspect of a wicked problem may reveal or create other problems. Due to their complexity, wicked problems are often characterized by organized irresponsibility.

Problem solving is the process of achieving a goal by overcoming obstacles, a frequent part of most activities. Problems in need of solutions range from simple personal tasks to complex issues in business and technical fields. The former is an example of simple problem solving (SPS) addressing one issue, whereas the latter is complex problem solving (CPS) with multiple interrelated obstacles. Another classification of problem-solving tasks is into well-defined problems with specific obstacles and goals, and ill-defined problems in which the current situation is troublesome but it is not clear what kind of resolution to aim for. Similarly, one may distinguish formal or fact-based problems requiring psychometric intelligence, versus socio-emotional problems which depend on the changeable emotions of individuals or groups, such as tactful behavior, fashion, or gift choices.
Design thinking refers to the set of cognitive, strategic and practical procedures used by designers in the process of designing, and to the body of knowledge that has been developed about how people reason when engaging with design problems.
Michael Christopher Jackson OBE is a British systems scientist, consultant and Emeritus Professor of Management Systems and former Dean of Hull University Business School, known for his work in the field of systems thinking and management.
Robert Louis (Bob) Flood is a British organizational scientist, former Professor of Management Sciences at the University of Hull, specialized in applied systemic thinking, particularly in the areas of strategic management, organizational behavior and organizational improvement.
Critical systems thinking (CST) is a systems approach designed to aid decision-makers, and other stakeholders, improve complex problem situations that cross departmental and, often, organizational boundaries. CST sees systems thinking as essential to managing multidimensional 'messes' in which technical, economic, organizational, human, cultural and political elements interact. It is critical in a positive manner because it seeks to capitalize on the strengths of existing approaches while also calling attention to their limitations. CST seeks to allow systems approaches such as systems engineering, system dynamics, organizational cybernetics, soft systems methodology, critical systems heuristics, and others, to be used together, in a responsive and flexible way, to maximize the benefits they can bring.

Systems modeling or system modeling is the interdisciplinary study of the use of models to conceptualize and construct systems in business and IT development.

Problem structuring methods (PSMs) are a group of techniques used to model or to map the nature or structure of a situation or state of affairs that some people want to change. PSMs are usually used by a group of people in collaboration to create a consensus about, or at least to facilitate negotiations about, what needs to change. Some widely adopted PSMs include
References
This article needs additional citations for verification .(January 2017) |