
Bioterrorism is terrorism involving the intentional release or dissemination of biological agents. These agents include bacteria, viruses, insects, fungi, and/or their toxins, and may be in a naturally occurring or a human-modified form, in much the same way as in biological warfare. Further, modern agribusiness is vulnerable to anti-agricultural attacks by terrorists, and such attacks can seriously damage economy as well as consumer confidence. The latter destructive activity is called agrobioterrorism and is a subtype of agro-terrorism.
Biodefense refers to measures to counter biological threats, reduce biological risks, and prepare for, respond to, and recover from bioincidents, whether naturally occurring, accidental, or deliberate in origin and whether impacting human, animal, plant, or environmental health. Biodefense measures often aim to improve biosecurity or biosafety. Biodefense is frequently discussed in the context of biological warfare or bioterrorism, and is generally considered a military or emergency response term.
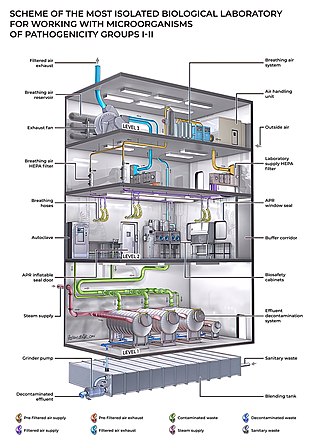
A biosafety level (BSL), or pathogen/protection level, is a set of biocontainment precautions required to isolate dangerous biological agents in an enclosed laboratory facility. The levels of containment range from the lowest biosafety level 1 (BSL-1) to the highest at level 4 (BSL-4). In the United States, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) have specified these levels in a publication referred to as BMBL. In the European Union, the same biosafety levels are defined in a directive. In Canada the four levels are known as Containment Levels. Facilities with these designations are also sometimes given as P1 through P4, as in the term P3 laboratory.

A biological hazard, or biohazard, is a biological substance that poses a threat to the health of living organisms, primarily humans. This could include a sample of a microorganism, virus or toxin that can adversely affect human health. A biohazard could also be a substance harmful to other living beings.
Health Canada is the department of the Government of Canada responsible for national health policy. The department itself is also responsible for numerous federal health-related agencies, including the Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA) and the Public Health Agency of Canada (PHAC), among others. These organizations help to ensure compliance with federal law in a variety of healthcare, agricultural, and pharmaceutical activities. This responsibility also involves extensive collaboration with various other federal- and provincial-level organizations in order to ensure the safety of food, health, and pharmaceutical products—including the regulation of health research and pharmaceutical manufacturing/testing facilities.
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases is one of the 27 institutes and centers that make up the National Institutes of Health (NIH), an agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). NIAID's mission is to conduct basic and applied research to better understand, treat, and prevent infectious, immunologic, and allergic diseases.
The Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) is an executive agency of the Department of Health and Social Care in the United Kingdom which is responsible for ensuring that medicines and medical devices work and are acceptably safe.
The National Microbiology Laboratory (NML) is part of the Public Health Agency of Canada (PHAC), the agency of the Government of Canada that is responsible for public health, health emergency preparedness and response, and infectious and chronic disease control and prevention.

The European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) is an agency of the European Union (EU) whose mission is to strengthen Europe's defences against infectious diseases. It covers a wide spectrum of activities, such as: surveillance, epidemic intelligence, response, scientific advice, microbiology, preparedness, public health training, international relations, health communication, and the scientific journal Eurosurveillance. The centre was established in 2004 and is headquartered in Solna, Sweden.
Infection prevention and control is the discipline concerned with preventing healthcare-associated infections; a practical rather than academic sub-discipline of epidemiology. In Northern Europe, infection prevention and control is expanded from healthcare into a component in public health, known as "infection protection". It is an essential part of the infrastructure of health care. Infection control and hospital epidemiology are akin to public health practice, practiced within the confines of a particular health-care delivery system rather than directed at society as a whole.

One use of the concept of biocontainment is related to laboratory biosafety and pertains to microbiology laboratories in which the physical containment of pathogenic organisms or agents is required, usually by isolation in environmentally and biologically secure cabinets or rooms, to prevent accidental infection of workers or release into the surrounding community during scientific research.

The Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA) is a U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) office responsible for the procurement and development of medical countermeasures, principally against bioterrorism, including chemical, biological, radiological and nuclear (CBRN) threats, as well as pandemic influenza and emerging diseases. BARDA was established in 2006 through the Pandemic and All-Hazards Preparedness Act (PAHPA) and reports to the Office of the Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response (ASPR). The office manages Project BioShield, which funds the research, development and stockpiling of vaccines and treatments that the government could use during public health emergencies such as chemical, biological, radiological or nuclear (CBRN) attacks.
The National Institute for Biological Standards and Control (NIBSC) is a government agency that works in the field of biological standardisation and is part of the United Kingdom's Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA). It is responsible for developing and producing over 90% of the biological international standards in use around the world.
The Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy (CIDRAP) is a center within the University of Minnesota that focuses on addressing public health preparedness and emerging infectious disease response. It was founded in 2001 by Dr. Michael Osterholm, in order to "prevent illness and death from infectious diseases through epidemiological research and rapid translation of scientific information into real-world practical applications and solutions". It is not part of the Center for Disease Control or National Institute of Health.

Biomedical sciences are a set of sciences applying portions of natural science or formal science, or both, to develop knowledge, interventions, or technology that are of use in healthcare or public health. Such disciplines as medical microbiology, clinical virology, clinical epidemiology, genetic epidemiology, and biomedical engineering are medical sciences. In explaining physiological mechanisms operating in pathological processes, however, pathophysiology can be regarded as basic science.

Public Health England (PHE) was an executive agency of the Department of Health and Social Care in England which began operating on 1 April 2013 to protect and improve health and wellbeing and reduce health inequalities. Its formation came as a result of the reorganisation of the National Health Service (NHS) in England outlined in the Health and Social Care Act 2012. It took on the role of the Health Protection Agency, the National Treatment Agency for Substance Misuse and a number of other health bodies. It was an executive agency of the Department of Health and Social Care, and a distinct delivery organisation with operational autonomy.
The United States Biological Defense Program—in recent years also called the National Biodefense Strategy—refers to the collective effort by all levels of government, along with private enterprise and other stakeholders, in the United States to carry out biodefense activities.

Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency, formerly Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, is an organization under the South Korean Ministry of Welfare and Health that is responsible for the advancement of public health by managing prevention, survey, quarantine, trial, and research on infectious diseases, chronic and rare illnesses and injuries. It was founded in December 2003 and is located in Osong Health Technology Administration Complex in Cheongju. The organization is led by the vice-ministerial-level Commissioner of KDCA.

Chikwe Ihekweazu is a Nigerian epidemiologist, public health physician and the World Health Organization's Assistant Director-General for Health Emergency Intelligence and Surveillance Systems.
An occupational infectious disease is an infectious disease that is contracted at the workplace. Biological hazards (biohazards) include infectious microorganisms such as viruses, bacteria and toxins produced by those organisms such as anthrax.










