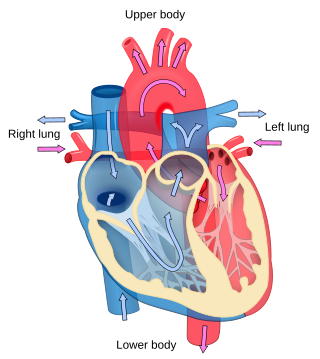
Cardiology is the study of the heart. Cardiology is a branch of medicine that deals with disorders of the heart and the cardiovascular system. The field includes medical diagnosis and treatment of congenital heart defects, coronary artery disease, heart failure, valvular heart disease, and electrophysiology. Physicians who specialize in this field of medicine are called cardiologists, a specialty of internal medicine. Pediatric cardiologists are pediatricians who specialize in cardiology. Physicians who specialize in cardiac surgery are called cardiothoracic surgeons or cardiac surgeons, a specialty of general surgery.

Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF), formerly known as Steno-Fallot tetralogy, is a congenital heart defect characterized by four specific cardiac defects. Classically, the four defects are:

Atrial septal defect (ASD) is a congenital heart defect in which blood flows between the atria of the heart. Some flow is a normal condition both pre-birth and immediately post-birth via the foramen ovale; however, when this does not naturally close after birth it is referred to as a patent (open) foramen ovale (PFO). It is common in patients with a congenital atrial septal aneurysm (ASA).

The ostium primum atrial septal defect is a defect in the atrial septum at the level of the tricuspid and mitral valves. This is sometimes known as an endocardial cushion defect because it often involves the endocardial cushion, which is the portion of the heart where the atrial septum meets the ventricular septum and the mitral valve meets the tricuspid valve.

A congenital heart defect (CHD), also known as a congenital heart anomaly, congenital cardiovascular malformation, and congenital heart disease, is a defect in the structure of the heart or great vessels that is present at birth. A congenital heart defect is classed as a cardiovascular disease. Signs and symptoms depend on the specific type of defect. Symptoms can vary from none to life-threatening. When present, symptoms are variable and may include rapid breathing, bluish skin (cyanosis), poor weight gain, and feeling tired. CHD does not cause chest pain. Most congenital heart defects are not associated with other diseases. A complication of CHD is heart failure.

An acyanotic heart defect, is a class of congenital heart defects. In these, blood is shunted (flows) from the left side of the heart to the right side of the heart, most often due to a structural defect (hole) in the interventricular septum. People often retain normal levels of oxyhemoglobin saturation in systemic circulation.

A ventricular septal defect (VSD) is a defect in the ventricular septum, the wall dividing the left and right ventricles of the heart. The extent of the opening may vary from pin size to complete absence of the ventricular septum, creating one common ventricle. The ventricular septum consists of an inferior muscular and superior membranous portion and is extensively innervated with conducting cardiomyocytes.

Ebstein's anomaly is a congenital heart defect in which the septal and posterior leaflets of the tricuspid valve are displaced downwards towards the apex of the right ventricle of the heart. EA has great anatomical heterogeneity that generates a wide spectrum of clinical features at presentation and is complicated by the fact that the lesion is often accompanied by other congenital cardiac lesions. It is classified as a critical congenital heart defect accounting for less than 1% of all congenital heart defects presenting in around 1 per 200,000 live births. Ebstein's anomaly usually presents with a systolic murmur and frequently with a gallop rhythm.

Transposition of the great vessels (TGV) is a group of congenital heart defects involving an abnormal spatial arrangement of any of the great vessels: superior and/or inferior venae cavae, pulmonary artery, pulmonary veins, and aorta. Congenital heart diseases involving only the primary arteries belong to a sub-group called transposition of the great arteries (TGA), which is considered the most common congenital heart lesion that presents in neonates.

Pulmonary atresia is a congenital malformation of the pulmonary valve in which the valve orifice fails to develop. The valve is completely closed thereby obstructing the outflow of blood from the heart to the lungs. The pulmonary valve is located on the right side of the heart between the right ventricle and pulmonary artery. In a normal functioning heart, the opening to the pulmonary valve has three flaps that open and close.

Tricuspid atresia is a form of congenital heart disease whereby there is a complete absence of the tricuspid valve. Therefore, there is an absence of right atrioventricular connection. This leads to a hypoplastic (undersized) or absent right ventricle. This defect is contracted during prenatal development, when the heart does not finish developing. It causes the systemic circulation to be filled with relatively deoxygenated blood. The causes of tricuspid atresia are unknown.

Atrioventricular septal defect (AVSD) or atrioventricular canal defect (AVCD), also known as "common atrioventricular canal" or "endocardial cushion defect" (ECD), is characterized by a deficiency of the atrioventricular septum of the heart that creates connections between all four of its chambers. It is a very specific combination of 3 defects:

The interventricular septum is the stout wall separating the ventricles, the lower chambers of the heart, from one another.
Double outlet right ventricle (DORV) is a form of congenital heart disease where both of the great arteries connect to the right ventricle (RV). In some cases it is found that this occurs on the left side of the heart rather than the right side.

A sinus venosus atrial septal defect is a type of atrial septal defect primarily associated with the sinus venosus.

Pentalogy of Cantrell is an extremely rare congenital syndrome that causes defects involving the diaphragm, abdominal wall, pericardium, heart and lower sternum.
The Trilogy of Fallot also called Fallot's trilogy is a rare congenital heart disease consisting of the following defects: pulmonary valve stenosis, right ventricular hypertrophy and atrial septal defect. It occurs in 1.2% of all congenital heart defects.
Aortopulmonary septal defect is a rare congenital heart disorder accounting for only 0.1-0.3% of congenital heart defects worldwide. It is characterized by a communication between the aortic and pulmonary arteries, with preservation of two normal semilunar valves. It is the result of an incomplete separation of the aorticopulmonary trunk that normally occurs in early fetal development with formation of the spiral septum. Aortopulmonary septal defects occur in isolation in about half of cases, the remainder are associated with more complex heart abnormalities.

The atrioventricular septum is a septum of the heart between the right atrium (RA) and the left ventricle (LV).

Pulmonary atresia with ventricular septal defect is a rare birth defect characterized by pulmonary valve atresia occurring alongside a defect on the right ventricular outflow tract.














