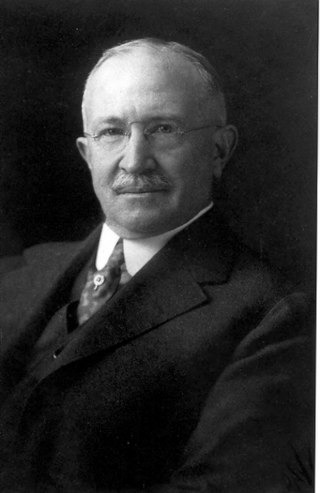The Jordan River or River Jordan, also known as Nahr Al-Sharieat, is a 251-kilometre-long (156 mi) river in the Levant that flows roughly north to south through the Sea of Galilee and drains to the Dead Sea. The river passes by or through Jordan, Syria, Israel, and the Palestinian territories.

The Percidae are a family of ray-finned fish, part of the order Perciformes, which are found in fresh and brackish waters of the Northern Hemisphere. The majority are Nearctic, but there are also Palearctic species. The family contains more than 200 species in 11 genera. The perches and their relatives are in this family; well-known species include the walleye, sauger, ruffe, and three species of perch. However, small fish known as darters are also a part of this family.

Sciaenidae is a family of ray-finned fishes belonging to the order Acanthuriformes. They are commonly called drums or croakers in reference to the repetitive throbbing or drumming sounds they make. The family consists of about 293 to 298 species in about 66 or 67 genera.

A sculpin is a type of fish that belongs to the superfamily Cottoidea in the order Scorpaeniformes. As of 2006, this superfamily contains 7 families, 94 genera, and 387 species.

The Scorpaeniformes are a diverse order of ray-finned fish, including the lionfishes and sculpins, but have also been called the Scleroparei. It is one of the five largest orders of bony fishes by number of species, with over 1,320.

Myliobatiformes is one of the four orders of batoids, cartilaginous fishes related to sharks. They were formerly included in the order Rajiformes, but more recent phylogenetic studies have shown the myliobatiforms to be a monophyletic group, and its more derived members evolved their highly flattened shapes independently of the skates.

The Cottidae are a family of fish in the superfamily Cottoidea, the sculpins. It is the largest sculpin family, with about 275 species in 70 genera. They are referred to simply as cottids to avoid confusion with sculpins of other families.

David Starr Jordan was the founding president of Stanford University, serving from 1891 to 1913. He was an ichthyologist during his research career. Prior to serving as president of Stanford University, he served as president of Indiana University from 1884 to 1891.

The Carangidae are a family of ray-finned fish that includes the jacks, pompanos, jack mackerels, runners, trevallies, and scads. It is the largest of the six families included within the order Carangiformes. Some authorities classify it as the only family within that order but molecular and anatomical studies indicate that there is a close relationship between this family and the five former Perciform families which make up the Carangiformes.

Ophichthidae is a family of fish in the order Anguilliformes, commonly known as the snake eels. The term "Ophichthidae" comes from Greek ophis ("serpent") and ichthys ("fish"). Snake eels are also burrowing eels. They are named for their physical appearance, as they have long, cylindrical, snake-like bodies. This family is found worldwide in tropical to warm temperate waters. They inhabit a wide range of habitats, from coastal shallows and even rivers, to depths below 800 m (2,600 ft). Most species are bottom dwellers, hiding in mud or sand to capture their prey of crustaceans and small fish, but some are pelagic.

Sebastes is a genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the subfamily Sebastinae part of the family Scorpaenidae, most of which have the common name of rockfish. A few are called ocean perch, sea perch or redfish instead. They are found in the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans.

The superorder Elopomorpha contains a variety of types of fishes that range from typical silvery-colored species, such as the tarpons and ladyfishes of the Elopiformes and the bonefishes of the Albuliformes, to the long and slender, smooth-bodied eels of the Anguilliformes. The one characteristic uniting this group of fishes is they all have leptocephalus larvae, which are unique to the Elopomorpha. No other fishes have this type of larvae.

Stichaeidae, the pricklebacks or shannies, are a family of marine ray-finned fishes in the suborder Zoarcoidei of the order Scorpaeniformes. Most species are found in the North Pacific Ocean with a few in the North Atlantic Ocean.

Carl Henry Eigenmann was a German-American ichthyologist of the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, who, along with his wife Rosa Smith Eigenmann, and his zoology students is credited with identifying and describing for the first time 195 genera containing nearly 600 species of fishes of North America and South America. Especially notable among his published papers are his studies of the freshwater fishes of South America, the evolution and systematics of South American fishes, and for his analysis of degenerative evolution based on his studies of blind cave fishes found in parts of North America and in Cuba. His most notable works are The American Characidae (1917–1929) and A revision of the South American Nematognathi or cat-fishes (1890), in addition to numerous published papers such as "Cave Vertebrates of North America, a study of degenerative evolution" (1909) and "The fresh-water fishes of Patagonia and an examination of the Archiplata-Archelenis theory" (1909).
"Saturday Night Fish Fry" is a jump blues song written by Louis Jordan and Ellis Lawrence Walsh, best known through the version recorded by Louis Jordan and His Tympany Five. The recording is considered to be one of the "excellent and commercially successful" examples of the jump blues genre.
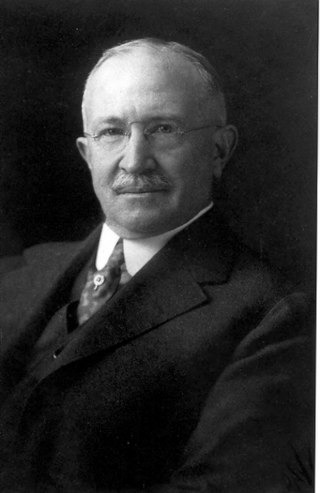
Charles Henry Gilbert was a pioneer ichthyologist and fishery biologist of particular significance to natural history of the western United States. He collected and studied fishes from Central America north to Alaska and described many new species. Later he became an expert on Pacific salmon and was a noted conservationist of the Pacific Northwest. He is considered by many as the intellectual founder of American fisheries biology. He was one of the 22 "pioneer professors" of Stanford University.

The Atka mackerel is a mackerel in the family Hexagrammidae. Atka mackerel are common in the northern Pacific Ocean, and are one of only two members of the genus Pleurogrammus – the other being the Arabesque greenling. The Atka mackerel was named for Atka Island, the largest island of the Andreanof islands, a branch of the Aleutians.

Cottoidei is a suborder of ray-finned fishes which, according to the 5th edition of Fishes of the World, is placed within the order Scorpaeniformes, alongside the scorpionfishes, flatheads, eelpouts, sticklebacks and related fishes.

Cichliformes is an order of fishes. Its members were previously classified under the order Perciformes, but now many authorities consider it to be an independent order within the subseries Ovalentaria.

Sakha cuisine encompasses the customary and traditional cooking techniques and culinary arts of Sakha.