
Cyprinidae is a family of freshwater fish commonly called the carp or minnow family, including the carps, the true minnows, and their relatives the barbs and barbels, among others. Cyprinidae is the largest and most diverse fish family, and the largest vertebrate animal family overall, with about 3,000 species; only 1,270 of these remain extant, divided into about 200 valid genera. Cyprinids range from about 12 mm (0.5 in) in size to the 3 m (9.8 ft) giant barb. By genus and species count, the family makes up more than two-thirds of the ostariophysian order Cypriniformes. The family name is derived from the Greek word kyprînos.

A tuna is a saltwater fish that belongs to the tribe Thunnini, a subgrouping of the Scombridae (mackerel) family. The Thunnini comprise 17 species across five genera, the sizes of which vary greatly, ranging from the bullet tuna up to the Atlantic bluefin tuna, which averages 2 m (6.6 ft) and is believed to live up to 50 years.
Bass is a generic common name shared by many species of ray-finned fish from the large clade Percomorpha, mainly belonging to the orders Perciformes and Moroniformes, encompassing both freshwater and marine species. The word bass comes from Middle English bars, meaning "perch", despite that none of the commonly referred bass species belong to the perch family Percidae.

The ricefishes are a family (Adrianichthyidae) of small ray-finned fish that are found in fresh and brackish waters from India to Japan and out into the Malay Archipelago, most notably Sulawesi. The common name ricefish derives from the fact that some species are found in rice paddies. This family consists of about 37 species in two genera. Several species are rare and threatened, and some 2–4 may already be extinct.
Squalidae, more commonly known as dogfish, dog sharks, or spiny dogfish, are one of several families of sharks categorized under Squaliformes, making it the second largest order of sharks, numbering 119 species across 7 families. Having earned their name after a group of fishermen reportedly observed the species chasing down smaller fish in dog-like packs, dogfish have slender, streamlined bodies, usually more compact in comparison to other species, and a pointed snout. Dogfish likewise have two dorsal fins, each with smooth spines, but no anal fin, and their skin is generally rough to the touch. As the species reaches adulthood, males usually measure a maximum of 100 cm, while females typically measure 125 cm long. The species therefore exhibits female-dominant sexual dimorphism.

Hijiki, sometimes called hiziki, is a brown sea vegetable that grows wild on the rocky coastlines of East Asia.

The sandperches are a family, Pinguipedidae, of ray-finned fishes in the percomorph order Labriformes. Sandperches are benthic fish which normally occur over sand or rubble substrates in shallow seas. They are found off the coasts of South America, South Africa and in the Indo-Pacific as far east as Japan. The family contains a few species which are used by humans for food.

Onychostoma is a genus of cyprinid fish found in eastern Asia.
Auxis is a genus of ocean-dwelling ray-finned bony fish in the family Scombridae, and tribe Thunnini, also known as the tunas. Auxis, commonly and collectively called the frigate tunas, is one of five genera of tunas which comprise the Thunnini tribe.

Eels are ray-finned fish belonging to the order Anguilliformes, which consists of eight suborders, 20 families, 164 genera, and about 1000 species. Eels undergo considerable development from the early larval stage to the eventual adult stage and are usually predators.

Amyzon is an extinct genus belonging to the sucker family Catostomidae first described in 1872 by E. D. Cope. There are six valid species in the genus. Amyzon are found in North American fossil sites dated from the Early Eocene in Montana and Washington USA, as well as the British Columbian sites at McAbee Fossil Beds, Driftwood Canyon, and the "Horsefly shale", as well as Early Oligocene sites in Nevada USA. One Middle Eocene species is known from the Xiawanpu Formation of China. The Ypresian species A. brevipinne of the Allenby Formation was redescribed in 2021 and moved to a separate monotypic genus Wilsonium.

An anchovy is a small, common forage fish of the family Engraulidae. Most species are found in marine waters, but several will enter brackish water, and some in South America are restricted to fresh water.
Canarium fusiforme is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Strombidae, the true conchs.
Coptodon fusiforme is a species of fish in the cichlid family, endemic to Lake Ejagham in western Cameroon. It was only scientifically described in 2010, so has not been rated by the IUCN, but it likely faces the same risks as the critically endangered C. deckerti, which is threatened by pollution and sedimentation from human activities, a catfish from the genus Parauchenoglanis that has been introduced to the lake, and potentially also by large emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2) from the lake's bottom (compare Lake Nyos), although Ejagham is too shallow to contain very high amounts of this gas.

The swamp darter is a species of freshwater ray-finned fish, a darter from the subfamily Etheostomatinae, part of the family Percidae, which also contains the perches, ruffes and pikeperches. It is endemic to the Eastern United States.

Sebastiscus is a genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the subfamily Sebastinae part of the family Scorpaenidae. These fishes are native to the western Pacific Ocean. They are collectively called sea ruffes and resemble the rockfishes in the genus Sebastes, but are usually smaller and have a different pattern.

Opecoelidae is a family of trematodes. It is the largest digenean family with over 90 genera and nearly 900 species, almost solely found in marine and freshwater teleost fishes. It was considered by Bray et al. to belong in the superfamily Opecoeloidea Ozaki, 1925 or the Brachycladioidea Odhner, 1905.

Coptodon is a genus of cichlids native to fresh, brackish and coastal marine waters in Africa with C. zillii also found in the Middle East. It is the only genus in the tribe Coptodonini. Formerly included in Tilapia, this genus and tribe was separated in 2013. Despite the change in genus, Coptodon spp. are still referred to by the common name tilapia. Several species are important in local fisheries and a few are aquacultured.
Microcotyle polymixiae is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae. It was first described and illustrated based on 82 whole mounts, from the gills of the silver eye, Polymixia japonica (Polymixiidae) off Hawaii.
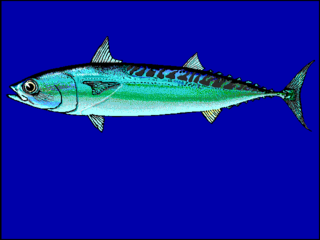
Onychostoma fusiforme is a species of cyprinid in the genus Onychostoma. It inhabits inland wetlands in Asia and has a maximum length of 23.0 centimetres (9.1 in). It is used for food locally.













