Lasiocroton is a plant genus of the family Euphorbiaceae first described as a genus in 1859. The genus is endemic to the West Indies. It is a member of the Leucocroton alliance, which also includes Leucocroton and Garciadelia. Species in this alliance are dioecious.
- Lasiocroton bahamensisPax & K.Hoffm. - Bahamas, Cuba, Haiti
- Lasiocroton fawcettiiUrb. - Jamaica
- Lasiocroton gracilisBritton & P.Wilson - SE Cuba
- Lasiocroton gutierreziiJestrow - Cuba
- Lasiocroton harrisiiBritton - Jamaica
- Lasiocroton macrophyllus(Sw.) Griseb. - Jamaica
- Lasiocroton microphyllus(A.Rich.) Jestrow - Cuba
- moved to other genera (Bernardia Croton Leucocroton)
- Lasiocroton cordifoliusBritton & P.Wilson - Leucocroton cordifolius (Britton & P.Wilson) Alain
- Lasiocroton prunifoliusGriseb. - Croton punctatusJacq.
- Lasiocroton subpeltatusUrb. - Leucocroton subpeltatus(Urb.) Alain
- Lasiocroton trelawniensisC.D.Adams - Bernardia trelawniensis(C.D.Adams) Jestrow & Proctor

The Tropidophiidae, common name dwarf boas or thunder snakes, are a family of nonvenomous snakes found from Mexico and the West Indies south to southeastern Brazil. These are small to medium-sized fossorial snakes, some with beautiful and striking color patterns. Currently, two living genera, containing 34 species, are recognized. Two other genera were once considered to be tropidophiids but are now known to be more closely related to boids, and are classified in the subfamily Ungaliophiinae. There are a relatively large number of fossil snakes that have been described as tropidophiids, but which of these are more closely related to Tropidophis and Trachyboa and which are more closely related to Ungaliophis and Exiliboa is unknown.
Picrodendron is a genus of plant belonging to the family Picrodendraceae described as a genus in 1859.

Pimenta is a genus of flowering plants in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae described as a genus in 1821. It is native to Central and South America, Mexico, and the West Indies.

The Caribbean pine is a hard pine species native to Central America and the northern West Indies. It belongs to subsection Australes in subgenus Pinus. It inhabits tropical and subtropical coniferous forests such as Bahamian pineyards, in both lowland savannas and montane forests.

Uniola is a genus of New World plants in the grass family.

Swietenia mahagoni, commonly known as American mahogany, Cuban mahogany, small-leaved mahogany, and West Indian mahogany, is a species of Swietenia native to South Florida in the United States and islands in the Caribbean including the Bahamas, Cuba, Jamaica, and Hispaniola. It is the species from which the original mahogany wood was produced. Mahogany is grown as a plantation tree and sold in timber markets in Kerala, India. Swietenia mahagoni is listed as "Threatened" in the Preservation of Native Flora of Florida Act. It is the national tree of the Dominican Republic.
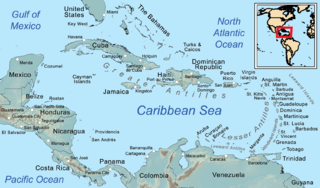
The Caribbean is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands and the surrounding coasts. The region is southeast of the Gulf of Mexico and the North American mainland, east of Central America and north of South America islets, reefs and cays. Island arcs delineate the eastern and northern edges of the Caribbean Sea: the Greater Antilles and the Lucayan Archipelago on the north and the Lesser Antilles on the south and east. They form the West Indies with the nearby Lucayan Archipelago, which are considered to be part of the Caribbean despite not bordering the Caribbean Sea. On the mainland, Belize, Nicaragua, the Caribbean region of Colombia, Cozumel, the Yucatán Peninsula, Margarita Island, and the Guianas are often included due to their political and cultural ties with the region.

Eleocharis parvula is a species of spikesedge known by the common names dwarf spikerush, small spikerush and hairgrass in aquaria. It is a plant of brackish and saltwater habitat, such as marshes and mudflats. It is a perennial herb growing tufts of spongy, compressible stems not more than 10 centimeters tall. The plant grows from a tuber which is J-shaped or horseshoe-shaped, a characteristic that helps in the identification of the species. The inflorescence is an oval-shaped spikelet just 2 or 3 millimeters long, made up of several tiny flowers.

Clusia rosea, the autograph tree, copey, cupey, balsam apple, pitch-apple, and Scotch attorney, is a tropical and sub-tropical flowering plant species in the family Clusiaceae. The name Clusia major is sometimes misapplied to this species.
Halophila engelmannii is a species of seagrass in the Hydrocharitaceae family. It is referred to by the common names star grass and Engelmann's seagrass and grows underwater on shallow sandy or muddy sea floors. It is native to the Bahamas, the Cayman Islands, Costa Rica, Cuba, the Gulf Coast of the United States, the Gulf Coast of Mexico, Puerto Rico, and Trinidad and Tobago.
Basiphyllaea corallicola is a species of orchid native to Florida, Bahamas, Cuba, Hispaniola, and Puerto Rico.

Macradenia lutescens is a species of epiphytic orchid known by the common name longgland orchid. It is native to South America, the West Indies, and southern Florida.

Petitia, called the bastard stopper, is a genus of flowering plants in the mint family, Lamiaceae, first described in 1760. It contains two known species, native to Florida and the West Indies.

Piloblephis is a monotypic genus of flowering plant in the family Lamiaceae, first described in 1838. It contains only one known species, Piloblephis rigida, the wild pennyroyal, or pennyroyal native to Florida, southern Georgia, and the Bahamas.
Pseudocarpidium is a genus of flowering plants in the family Lamiaceae first described in 1906. It is native the West Indies.
- Pseudocarpidium avicennioides(A.Rich.) Millsp. - eastern Cuba
- Pseudocarpidium domingense(Urb. & Ekman) Moldenke - Hispaniola
- Pseudocarpidium ilicifolium (A.Rich.) Millsp. - Cuba
- Pseudocarpidium multidens(Urb.) Moldenke - eastern Cuba
- Pseudocarpidium neglectaBisse - Cuba
- Pseudocarpidium pungensBritton - eastern Cuba
- Pseudocarpidium rigens(Griseb.) Britton - eastern Cuba
- Pseudocarpidium shaferiBritton - eastern Cuba
- Pseudocarpidium wrightiiMillsp. - Bahamas, Cuba
Neobracea is a genus of plant in the family Apocynaceae first described as a genus in 1905. It was first given the name Bracea, but this turned out to be an illegitimate homonym. In other words, somebody else had already used it for another plant. Neobracea is native to Cuba and the Bahamas.
- Neobracea acunanaLippold - E Cuba
- Neobracea angustifoliaBritton - W Cuba
- Neobracea bahamensis(Britton) Britton - Bahamas, Cuba
- Neobracea ekmaniiUrb. - E Cuba
- Neobracea howardiiWoodson - EC Cuba
- Neobracea martianaBorhidi & O.Muñiz - E Cuba
- Neobracea susanninaBorhidi - E Cuba
- Neobracea valenzuelana(A.Rich.) Urb. - Cuba

Angadenia berteroi, the pineland golden trumpet, is a plant species in the family Apocynaceae, first described in 1844. It is native to Florida, North Carolina, Bahamas, Cuba, Hispaniola, and the Turks & Caicos Islands.
Smilax havanensis is a plant species native to Cuba, the Cayman Islands, Bahamas, Turks & Caicos, and southern Florida.












