The Cambrian Period was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 55.6 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 541 million years ago (mya) to the beginning of the Ordovician Period 485.4 mya. Its subdivisions, and its base, are somewhat in flux. The period was established as "Cambrian series" by Adam Sedgwick, who named it after Cambria, the Latin name for 'Cymru' (Wales), where Britain's Cambrian rocks are best exposed. The Cambrian is unique in its unusually high proportion of lagerstätte sedimentary deposits, sites of exceptional preservation where "soft" parts of organisms are preserved as well as their more resistant shells. As a result, our understanding of the Cambrian biology surpasses that of some later periods.

The Ordovician is a geologic period and system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period 485.4 million years ago (Mya) to the start of the Silurian Period 443.8 Mya.

The halkieriids are a group of fossil organisms from the Lower to Middle Cambrian. Their eponymous genus is Halkieria, which has been found on almost every continent in Lower to Mid Cambrian deposits, forming a large component of the small shelly fossil assemblages. The best known species is Halkieria evangelista, from the North Greenland Sirius Passet Lagerstätte, in which complete specimens were collected on an expedition in 1989. The fossils were described by Simon Conway Morris and John Peel in a short paper in 1990 in the journal Nature. Later a more thorough description was undertaken in 1995 in the journal Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London and wider evolutionary implications were posed.
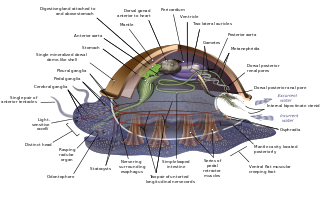
The evolution of the molluscs is the way in which the Mollusca, one of the largest groups of invertebrate animals, evolved. This phylum includes gastropods, bivalves, scaphopods, cephalopods, and several other groups. The fossil record of mollusks is relatively complete, and they are well represented in most fossil-bearing marine strata. Very early organisms which have dubiously been compared to molluscs include Kimberella and Odontogriphus.

Scenella is an extinct genus of fossil invertebrate animal which is generally considered to be a mollusc; at various times it has been suggested that this genus belongs with the gastropods, the monoplacophorans, or the helcionellids, although no firm association with any of these classes has been established. An affinity with the hydrozoa has been considered, although some authors oppose this hypothesis. A gastropod affinity is defended on the basis of six pairs of internal muscle scars, whilst the serially-repeated nature of these scars suggests to other authors a monoplacophoran affinity. However the specimens showing this scarring have not been convincingly shown to belong to the genus Scenella. A similarity to the Ediacaran Ovatoscutum has also been drawn.

Helcionellid or Helcionelliformes is an order of small fossil shells that are universally interpreted as molluscs, though no sources spell out why this taxonomic interpretation is preferred. These animals are first found about 540 to 530 million years ago in the late Nemakit-Daldynian age, which is the earliest part of the Cambrian period. A single species persisted to the Early Ordovician. These fossils are component of the small shelly fossils (SSF) assemblages.

Matthevia is a genus of Cambrian molluscs, perhaps related to the chitons. It consists of repeated monoplacophoran-like shells; according to one hypothesis, chitons arose when these tall shells began to overlap over the generations. The tall element of the shell was retained and forms the tips of modern chiton plates. There are distinct head, 'centre', and tail valves, which occur approximately in the ratio 1:5:1 — suggesting a seven-plated configuration.
Robustum nodum is the one species of a problematic genus of Ordovician hemithecellid mollusc proposed by Stinchcomb and Darrough in 1995. Its similarities to Matthevia were outlined by Vendrasco & Runnegar.
The Kirengellids are a group of problematic Cambrian fossil shells of marine organisms. The shells bear a number of paired muscle scars on the inner surface of the valve.
The cephalopods have a long geological history, with the first nautiloids found in late Cambrian strata, and purported stem-group representatives present in the earliest Cambrian lagerstätten.
Paradycheia is a genus of polyplacophoran known from the Upper Cambrian Eminence Dolomite, Missouri, USA.
Dycheiidae is a wastebasket taxon containing problematic polyplacophora from Upper Cambrian strata in the USA.
Allochiton is a genus of upper Cambrian chitons with a circular head valve.
The Paleoloricata are valved polyplacophora without sutural laminae or insertion plates. The "order" probably represents a paraphyletic grouping.

Mattheviidae is an extinct taxonomic family of fossil chitons, marine polyplacophoran mollusks that are found in Cambrian-Silurian deposits.
Multiplacophora is a stem-group of chitons with a number of plates arranged in 7 rows along the body. They date to at least the Upper Cambrian, but two lower Cambrian fossils- Ocruranus and Trachyplax - may extend the range downwards.

The Roubidoux Formation is a geologic formation in the Ozarks of Missouri and in Virginia. It preserves fossils dating back to the Ordovician period.

The Bonneterre Formation is an Upper Cambrian geologic formation which outcrops in the St. Francois Mountains of the Missouri Ozarks. The Bonneterre is a major host rock for the lead ores of the Missouri Lead Belt.

The Potosi Formation is a geologic formation in Missouri and Indiana. It preserves fossils dating back to the Cambrian period.

The Gasconade Formation is a geologic formation in the Ozarks of Missouri. It preserves fossils dating back to the Ordovician Period.








