
Sharpe Field is a private use airport located six nautical miles (11 km) northwest of the central business district of Tuskegee, a city in Macon County, Alabama, United States. This airport is privately owned by the Bradbury Family Partnership.
During World War II, the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) established numerous airfields in Alabama for antisubmarine defense in the Gulf of Mexico and for training pilots and aircrews of AAF fighters and bombers.
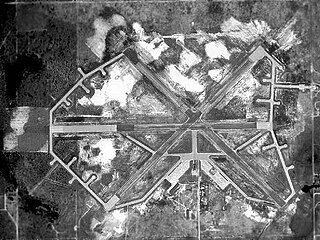
Hillsborough Army Airfield is a former World War II United States Army Air Forces airfield which was located about 7 miles north of Tampa, Florida, near Temple Terrace, Florida. After World War II it served as a civilian airport called Henderson Hillsborough International Airport for several years until it closed.

Stuttgart Army Airfield is a former World War II military airfield, located 7 miles north of Stuttgart, Arkansas. It operated as an advanced pilot training school for the United States Army Air Forces from 1942 until 1945.

Anniston Air Force Base is a former United States Air Force airfield located approximately 10 miles north-northeast of Talladega, Alabama. It was active from 1942 to 1945 and 1949 to 1952. It is currently the site of the Talladega Superspeedway.

Vaughn Airport is an abandoned airport located 9 miles south-southeast of Columbus, Mississippi.

Tallassee Airport is closed airport located 4 miles south of Tallassee, Alabama.
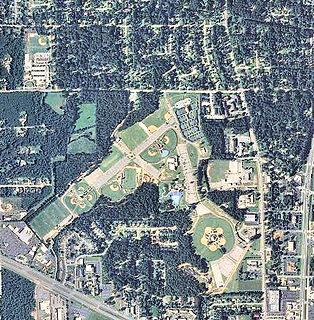
Dothan Municipal Airport is a closed airport located 3 miles (5 km) west-northwest of Dothan, Alabama, United States.
Danville Auxiliary Field is a former facility of the United States Army Air Forces located in Danville, Alabama. Constructed after 1941 as an auxiliary to the nearby Courtland Army Air Field, it was turned into Danville Airport following the war, and was eventually closed between 1986 and 1989. No trace of the airfield remains.
Bay Auxiliary Field is a former facility of the United States Army Air Forces located in Courtland, Alabama. Constructed after 1941 as an auxiliary to the nearby Courtland Army Air Field, it was converted back into farmland after the war.
Leighton Auxiliary Field is a former facility of the United States Army Air Forces located in Leighton, Alabama. Constructed after 1941 as an auxiliary to the nearby Courtland Army Air Field, it was turned back into farmland after the war.

Selma Auxiliary Field was a United States Army facility located 8 kilometres (5.0 mi) east-northeast of Selma, Alabama. Following its closure, it became Selma Municipal Airport.
Furniss Auxiliary Field is a former facility of the United States Army Air Forces located in Orrville, Alabama. Constructed after 1941 as an auxiliary to the nearby Craig Field, it was turned back into farmland after the war.
Mollette Auxiliary Field is a former facility of the United States Army Air Forces located in Orrville, Alabama. Constructed after 1941 as an auxiliary to the nearby Craig Field, it was turned back into farmland after the war.
Autaugaville Auxiliary Field is a former facility of the United States Army Air Forces located in Autaugaville, Alabama. Constructed after 1941 as an auxiliary to the nearby Craig and Maxwell Fields, it was turned back into farmland after the war.
McLemore Auxiliary Field is a former facility of the United States Army Air Forces located in Montgomery, Alabama. Constructed after 1941 as an auxiliary to the nearby Craig Field, it was turned back into farmland after the war.
Elmore Auxiliary Field is a former facility of the United States Army Air Forces located in Montgomery, Alabama. Constructed after 1941 as an auxiliary to the nearby Gunter Field, it was redeveloped into Wetumpka Municipal Airport after the war.
Deatsville Auxiliary Field is a former facility of the United States Army Air Forces located in Montgomery, Alabama. Constructed after 1941 as an auxiliary to the nearby Gunter Field, it was turned back into farmland after the war.
Troy Auxiliary Field is a former facility of the United States Army Air Forces located in Troy, Alabama. Constructed after 1942 as an auxiliary to the nearby Maxwell Field, it was turned into Troy Municipal Airport after the war.













