
Vitellaria paradoxa, commonly known as shea tree, shi tree, or vitellaria, is a tree of the family Sapotaceae. It is the only species in the genus Vitellaria, and is indigenous to Africa.

The South American lungfish is the single species of lungfish found in swamps and slow-moving waters of the Amazon, Paraguay, and lower Paraná River basins in South America. Notable as an obligate air-breather, it is the sole member of its family Lepidosirenidae. Relatively little is known about the South American lungfish. Additional common names include American mud-fish and scaly salamanderfish. The South American Lungfish have adapted to cope with both droughts and floods. This is normal due to the South American Lungfish adapting pulmonary mechanoreceptors. In Brazil, it is known by the indigenous language Tupi name piramboia, which means "snake-fish", and synonyms pirarucu-bóia, traíra-bóia, and caramuru.

Pseudis paradoxa, known as the paradoxical frog or shrinking frog, is a species of hylid frog from South America. Its name refers to the very large—up to 27 cm (11 in) long—tadpole, which in turn "shrinks" during metamorphosis into an ordinary-sized frog, only about a quarter or third of its former length. Although the recordholder was a tadpole in Amapá that belonged to this species, others in the genus Pseudis also have large tadpoles and ordinary-sized adults.

Nolana is a genus of hard annual or perennial plants in the nightshade family. The genus is mostly native to Chile and Peru. Species in this genus, especially N. paradoxa, serve as a model system for studies on flower color.
The Heterogynidae are a family of insects in the order Lepidoptera. Only two genera are currently recognized: Heterogynis and Janseola.

The yellow wattlebird is a species of bird in the honeyeater family Meliphagidae. Other names include the long wattlebird or Tasmanian wattlebird.
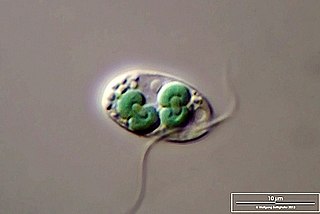
Cyanophora paradoxa is a freshwater species of Glaucophyte that is used as a model organism. C. paradoxa has two cyanelles or chloroplasts where photosynthesis occurs. Cyanelles are unusual organelles in that they retain a rudimentary peptidoglycan wall. The cyanelle genome of C. paradoxa strain LB 555 was sequenced and published in 1995. The nuclear genome was also sequenced and published in 2012.
Heterogynis is a genus of moths of the Heterogynidae family.
Charaxes paradoxa is a butterfly in the family Nymphalidae. It is found on Grande Comore. The habitat consists of forests.
Nosphidia is a monotypic moth genus in the family Carposinidae. It contains the single species Nosphidia paradoxa, which is found in Sri Lanka. Both the genus and species were first described by Alexey Diakonoff in 1982.

The Paradoxa Stoicorum is a work by the academic skeptic philosopher Cicero in which he attempts to explain six famous Stoic sayings that appear to go against common understanding: (1) virtue is the sole good; (2) virtue is the sole requisite for happiness; (3) all good deeds are equally virtuous and all bad deeds equally vicious; (4) all fools are mad; (5) only the wise are free, whereas all fools are enslaved; and (6) only the wise are rich.

Iris paradoxa is a species of flowering plant native to western Asia. It has large upright petals and smaller lower petals, which is unique amongst most iris forms. They come in various shades from white, lavender, mauve, medium purple, violet, dark purple to black. It has a black or purplish black beard on the lower petals. It comes from the region of Transcaucasia, and is found in the countries of Iran,, Turkey, Armenia and in Azerbaijan.
Heterogynis canalensis is a moth in the Heterogynidae family. It was described by Thomas Algernon Chapman in 1904. The Global Lepidoptera Names Index reports it as a synonym of Heterogynis penella.
Heterogynis eremita is a moth in the Heterogynidae family. It was described by Alberto Zilli, R. Cianchi, T. Racheli and L. Bullini in 1988.
Heterogynis andalusica is a moth in the Heterogynidae family. It was described by Franz Daniel in 1966.
Heterogynis thomas is a moth in the Heterogynidae family. It was described by Alberto Zilli in 1987.
Heterogynis jellaba is a moth in the Heterogynidae family. It was described by Josef J. de Freina in 2003.
Heterogynis rifensis is a moth in the Heterogynidae family. It was described by Josef J. de Freina in 2003.

Bartheletia paradoxa is a species of dimorphic fungus and is the only member of the genus Bartheletia. Bartheletia is the only genus in the family Bartheletiaceae, which is the only family in Bartheletiales, which in turn is the only order in the class Bartheletiomycetes.








