
A, or a, is the first letter and the first vowel of the modern English alphabet and the ISO basic Latin alphabet. Its name in English is a, plural aes. It is similar in shape to the Ancient Greek letter alpha, from which it derives. The uppercase version consists of the two slanting sides of a triangle, crossed in the middle by a horizontal bar. The lowercase version can be written in two forms: the double-storey a and single-storey ɑ. The latter is commonly used in handwriting and fonts based on it, especially fonts intended to be read by children, and is also found in italic type.

Economics is a social science that studies the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services.
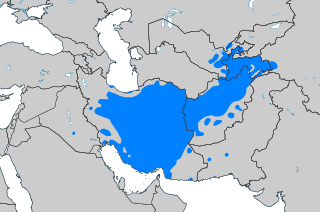
Persian, also known by its endonym Farsi, is a Western Iranian language belonging to the Iranian branch of the Indo-Iranian subdivision of the Indo-European languages. Persian is a pluricentric language predominantly spoken and used officially within Iran, Afghanistan and Tajikistan in three mutually intelligible standard varieties, namely Iranian Persian, Afghan Persian and Tajiki Persian. It is also spoken natively in the Tajik variety by a significant population within Uzbekistan, as well as within other regions with a Persianate history in the cultural sphere of Greater Iran. It is written officially within Iran and Afghanistan in the Persian alphabet, a derivation of the Arabic script, and within Tajikistan in the Tajik alphabet, a derivation of the Cyrillic script.

Erectile dysfunction (ED), also called impotence, is the type of sexual dysfunction in which the penis fails to become or stay erect during sexual activity. It is the most common sexual problem in men. Through its connection to self-image and to problems in sexual relationships, erectile dysfunction can cause psychological harm.

Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Psychology includes the study of conscious and unconscious phenomena, including feelings and thoughts. It is an academic discipline of immense scope, crossing the boundaries between the natural and social sciences. Psychologists seek an understanding of the emergent properties of brains, linking the discipline to neuroscience. As a social science, psychologists aim to understand the behavior of individuals and groups. Ψ is a Greek letter which is commonly associated with the science of psychology.

Science is a systematic enterprise that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe.

Yahweh was the national god of ancient Israel and Judah. His origins reach at least to the early Iron Age, and likely to the Late Bronze Age. In the oldest biblical literature, he is a storm-and-warrior deity who leads the heavenly army against Israel's enemies; at that time the Israelites worshipped him alongside a variety of Canaanite gods and goddesses, including El, Asherah and Baal; in later centuries, El and Yahweh became conflated and El-linked epithets such as El Shaddai came to be applied to Yahweh alone, and other gods and goddesses such as Baal and Asherah were absorbed into the Yahwist religion.

Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severity of the condition is variable.

Newton's laws of motion are three laws of classical mechanics that describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting on it. These laws can be paraphrased as follows:

Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek, Dark Ages, the Archaic period, and the Classical period.

In statistics, the standard score is the number of standard deviations by which the value of a raw score is above or below the mean value of what is being observed or measured. Raw scores above the mean have positive standard scores, while those below the mean have negative standard scores.
Islam is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion teaching that Muhammad is a messenger of God. It is the world's second-largest religion with 1.9 billion followers, or 24.9% of the world's population, known as Muslims. Muslims make up a majority of the population in 47 countries. Islam teaches that God is merciful, all-powerful, and unique, and has guided humanity through prophets, revealed scriptures, and natural signs. The primary scriptures of Islam are the Quran, believed to be the verbatim word of God, as well as the teachings and normative examples of Muhammad.
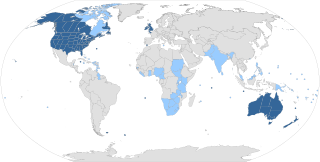
English is a West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, originally spoken by the inhabitants of early medieval England. It is named after Anglia, a peninsula on the Baltic Sea, and the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to the area of Great Britain that later took their name: England. Living languages most closely related to English include the Low Saxon and Frisian languages, while English's vocabulary has been significantly influenced by Old Norman French and Latin, as well as by other Germanic languages, particularly Old Norse.

Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditary information encoded in genes, which can be transmitted to future generations. Another major theme is evolution, which explains the unity and diversity of life. Energy processing is also important to life as it allows organisms to move, grow, and reproduce. Finally, all organisms are able to regulate their own internal environments.
Far-left politics are politics further to the left of the left–right political spectrum than the standard political left. There are different definitions of the far-left. Some scholars define it as representing the left of social democracy, while others limit it to the left of communist parties. In certain instances, especially in the news media, far-left has been associated with some forms of anarchism and communism, or it characterizes groups that advocate for revolutionary anti-capitalism and anti-globalization.

Socrates was a Greek philosopher from Athens who is credited as a founder of Western philosophy and the first moral philosopher of the ethical tradition of thought. An enigmatic figure, Socrates authored no texts and is known mainly through the posthumous accounts of classical writers, particularly his students Plato and Xenophon. These accounts are written as dialogues, in which Socrates and his interlocutors examine a subject in the style of question and answer; they gave rise to the Socratic dialogue literary genre. Contradictory accounts of Socrates make a reconstruction of the history of his life nearly impossible, a situation known as the Socratic problem. Socrates was a polarizing figure in Athenian society. In 399 BC, he was accused of corrupting the youth and failing to acknowledge the city's official gods. After a trial that lasted a day, he was sentenced to death. He spent his last day in prison, refusing to escape.

Edward Christopher Sheeran is an English singer-songwriter. Born in Halifax, West Yorkshire, he was brought up in Framlingham, Suffolk where he began writing songs while in high school. In early 2011, Sheeran independently released the extended play, No. 5 Collaborations Project. He signed with Asylum Records the same year.
















