
Acetophenone is the organic compound with the formula C6H5C(O)CH3. It is the simplest aromatic ketone. This colorless, viscous liquid is a precursor to useful resins and fragrances.

Azo compounds are organic compounds bearing the functional group diazenyl.
In chemistry, radical initiators are substances that can produce radical species under mild conditions and promote radical reactions. These substances generally possess weak bonds—bonds that have small bond dissociation energies. Radical initiators are utilized in industrial processes such as polymer synthesis. Typical examples are molecules with a nitrogen-halogen bond, azo compounds, and organic and inorganic peroxides.

Anisole, or methoxybenzene, is an organic compound with the formula CH3OC6H5. It is a colorless liquid with a smell reminiscent of anise seed, and in fact many of its derivatives are found in natural and artificial fragrances. The compound is mainly made synthetically and is a precursor to other synthetic compounds. Structurally, it is an ether with a methyl and phenyl group attached. Anisole is a standard reagent of both practical and pedagogical value.

Acetylacetone is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3COCH2COCH3. It is a colorless liquid, classified as a 1,3-diketone. It exists in equilibrium with a tautomer CH3C(O)CH=C(OH)CH3. These tautomers interconvert so rapidly under most conditions that they are treated as a single compound in most applications. It is a colorless liquid that is a precursor to acetylacetonate anion, a bidentate ligand. It is also a building block for the synthesis of heterocyclic compounds.

Acetyl chloride is an acyl chloride derived from acetic acid. It belongs to the class of organic compounds called acid halides. It is a colorless, corrosive, volatile liquid. Its formula is commonly abbreviated to AcCl.

A siloxane is a functional group in organosilicon chemistry with the Si−O−Si linkage. The parent siloxanes include the oligomeric and polymeric hydrides with the formulae H(OSiH2)nOH and (OSiH2)n. Siloxanes also include branched compounds, the defining feature of which is that each pair of silicon centres is separated by one oxygen (O) atom. The siloxane functional group forms the backbone of silicones, the premier example of which is polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). The functional group R3SiO− (where the three Rs may be different) is called siloxy. Siloxanes are manmade and have many commercial and industrial applications because of the compounds’ hydrophobicity, low thermal conductivity, and high flexibility.
Chlorosilanes are a group of reactive, chlorine-containing chemical compounds, related to silane and used in many chemical processes. Each such chemical has at least one silicon-chlorine bond. Trichlorosilane is produced on the largest scale. The parent chlorosilane is silicon tetrachloride.

Aluminium isopropoxide is the chemical compound usually described with the formula Al(O-i-Pr)3, where i-Pr is the isopropyl group (–CH(CH3)2). This colourless solid is a useful reagent in organic synthesis.

Rhenium(VII) oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Re2O7. This yellowish solid is the anhydride of HOReO3. Perrhenic acid, Re2O7·2H2O, is closely related to Re2O7. Re2O7 is the raw material for all rhenium compounds, being the volatile fraction obtained upon roasting the host ore.

Decamethylcyclopentasiloxane, also known as D5 and D5, is an organosilicon compound with the formula [(CH3)2SiO]5. It is a colorless and odorless liquid that is slightly volatile.

In organic chemistry, a dithiocarbamate is a functional group with the general formula R2N−C(=S)−S−R and structure >N−C(=S)−S−. It is the analog of a carbamate in which both oxygen atoms are replaced by sulfur atoms.
Dimethyldichlorosilane is a tetrahedral, organosilicon compound with the formula Si(CH3)2Cl2. At room temperature it is a colorless liquid that readily reacts with water to form both linear and cyclic Si-O chains. Dimethyldichlorosilane is made on an industrial scale as the principal precursor to dimethylsilicone and polysilane compounds.
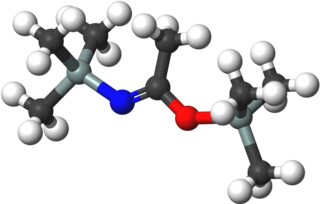
Bis(trimethylsilyl)acetamide (BSA) is an organosilicon compound with the formula MeC(OSiMe3)NSiMe3 (Me = CH3). It is a colorless liquid that is soluble in diverse organic solvents, but reacts rapidly with moisture and solvents containing OH and NH groups. It is used in analytical chemistry to increase the volatility of analytes, e.g., for gas chromatography. It is also used to introduce the trimethylsilyl protecting group in organic synthesis. A related reagent is N,O-bis(trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide (BSTFA).
Silylation is the introduction of one or more (usually) substituted silyl groups (R3Si) to a molecule. Silylations are core methods for production of organosilicon chemistry. Silanization involves similar methods but usually refers to attachment of silyl groups to solids.
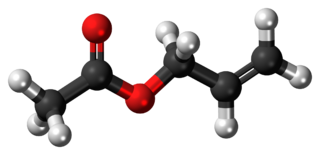
Allyl acetate is an organic compound with formula C3H5OC(O)CH3. This colourless liquid is a precursor to especially allyl alcohol, which is a useful industrial intermediate. It is the acetate ester of allyl alcohol.
In organic chemistry, ethenolysis is a chemical process in which internal olefins are degraded using ethylene as the reagent. The reaction is an example of cross metathesis. The utility of the reaction is driven by the low cost of ethylene as a reagent and its selectivity. It produces compounds with terminal alkene functional groups (α-olefins), which are more amenable to other reactions such as polymerization and hydroformylation.

1-Octanol, also known as octan-1-ol, is the organic compound with the molecular formula CH3(CH2)7OH. It is a fatty alcohol. Many other isomers are also known generically as octanols. 1-Octanol is manufactured for the synthesis of esters for use in perfumes and flavorings. It has a pungent odor. Esters of octanol, such as octyl acetate, occur as components of essential oils. It is used to evaluate the lipophilicity of pharmaceutical products.

Octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane, also called D4, is an organosilicon compound with the formula [(CH3)2SiO]4. It is a colorless viscous liquid. It is a common cyclomethicone. It is widely used in cosmetics.
Silanes refers to diverse organosilicon charge-neutral compounds with the formula SiR
4. The R substituents can any combination of organic or inorganic groups. Most silanes contain Si-C bonds, and are discussed under organosilicon compounds. Some contain Si-H bonds and are discussed under hydrosilanes.
















