
Telangana is a state in India situated in the southern-central part of the Indian peninsula on the high Deccan Plateau. It was the eleventh largest state and the twelfth most populated state in India as per the 2011 census. On 2 June 2014, the area was separated from the northwestern part of United Andhra Pradesh as the newly formed state of Telangana, with Hyderabad as its capital. Telugu, one of the classical languages of India, is the most widely spoken and the primary official language of the state.
The Politics of Andhra Pradesh take place in the context of a bicameral parliamentary system within the Constitutional framework of India. The main parties in the state are the Telugu Desam Party (TDP), Jana Sena Party (JSP) and YSR Congress Party (YSRCP). Other parties that have small presence in the state include the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP), Indian National Congress (INC) and Left parties.
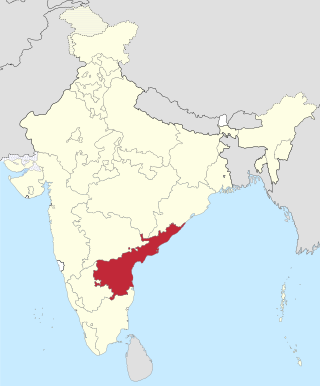
Andhra State was a state in India created in 1953 from the Telugu-speaking northern districts of Madras State. The state was made up of this two distinct cultural regions – Rayalaseema and Coastal Andhra. Andhra State did not include all Telugu-speaking areas, as it excluded some in Hyderabad State. Under the State Reorganisation Act of 1956, Andhra State was merged with the Telugu-speaking regions of Hyderabad State to form Andhra Pradesh.

The recorded history of Andhra Pradesh, one of the 28 states of 21st-century India, begins in the Vedic period. It is mentioned in Sanskrit epics such as the Aitareya Brahmana. Its sixth-century BCE incarnation Assaka lay between the Godavari and Krishna Rivers, one of sixteen mahajanapadas. The Satavahanas succeeded them, built Amaravati, and reached a zenith under Gautamiputra Satakarni.

The Gentlemen's agreement of Andhra Pradesh was signed between Telangana and Andhra leaders before the formation of the state of Andhra Pradesh of India on 20 February 1956. The agreement provided safeguards with the purpose of preventing discrimination against Telangana by the government of Andhra Pradesh. The violations of this agreement are cited as one of the reasons for formation of separate statehood for Telangana.
The States Reorganisation Commission of India (SRC) constituted by the Central Government of India in December 1953 to recommend the reorganization of state boundaries. In September 1955, after two years of study, the Commission, comprising Justice Fazal Ali, K. M. Panikkar and H. N. Kunzru, submitted its report. The commission's recommendations were accepted with some modifications and implemented in the States Reorganisation Act in November, 1956. The act provided that India's state boundaries should be reorganized to form 14 states and 6 centrally administered territories. On December 10, 1948, the report of Dar Commission was published but the issue remained unsolved.

The Visalandhra,VishalandhraorVishala Andhra was a movement in post-independence India for a united state for all Telugu speakers, a Greater Andhra. This movement was led by the Communist Party of India under the banner of Andhra Mahasabha with a demand to merge all the Telugu-speaking areas into one state.. The movement succeeded and a separate state of Andhra Pradesh was formed by merging Telugu-speaking areas of Hyderabad State with Andhra State on 1 November 1956 as part of the States Reorganisation Act.. However, on 2 June 2014, Telangana State was separated back out of Andhra Pradesh and the Vishalandhra experiment came to an end. The residual Andhra Pradesh now has approximately the same borders as the old Andhra State of 1956.
The Telangana movement refers to a movement for the creation of a separate state, Telangana, from the pre-existing state of Andhra Pradesh in India. The new state corresponds to the Telugu-speaking portions of the erstwhile princely state of Hyderabad, which were merged with Andhra Pradesh in 1956, leading to the Mulki Agitations.

Samaikya Andhra Movement was a movement organized to keep the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh united, and to prevent the division of the state - separating the Telangana districts of the state into a separate Telangana state. The movement was supported by government employees, advocates in Coastal Andhra & Rayalaseema regions along with students from 14 universities, various occupational, caste & religious groups of Coastal Andhra & Rayalaseema regions. The last set of protests were triggered after the Congress Working Committee decision to divide the state came to an end after President of India gave nod to Telangana Bill which would make the latter to come into existence from 2 June 2014.

1969 Telangana Agitation was a political movement for the statehood for Telangana region. The first person to raise the issue of Telangana happened in 1968 during October or November timeframe. A hunger strike was being carried on by a person named Ravindranath on 1969/January/08 in Khammam near the Railway Station. He was on an indefinite fast and his prime demand was to implement Telangana safeguards. One other demand was his insistence on implementation of the Gentleman's agreement. It is a major event in Telangana movement. In the indiscriminate police firing, 369 Telangana students were killed.

The Pre-2004 Telangana protests refers to the movements and agitations related to the Telangana movement that took place before the year 2004. Andhra state and Telangana was merged to form Andhra Pradesh state on 1 November 1956 after providing safeguards to Telangana in the form of Gentlemen's agreement. Soon after the formation of Andhra Pradesh, people of Telangana expressed dissatisfaction over how the agreements and guarantees were implemented. Protests initially led by students later under the leadership of newly formed political party Telangana Praja Samithi, led by M. Chenna Reddy and Konda Lakshman Bapuji, a minister who resigned from the cabinet led by then Chief Minister Kasu Brahmananda Reddy, demanding the formation of a separate state of Telangana. More than three hundred people died in police firing. Under the Mulki rules in force at the time, anyone who had lived in Hyderabad for 15 years was considered a local, and was thus eligible for certain government posts. When the Supreme Court upheld the Mulki rules at the end of 1972, the Jai Andhra movement, with the aim of re-forming a separate state of Andhra, was started in Coastal Andhra and Rayalaseema regions.
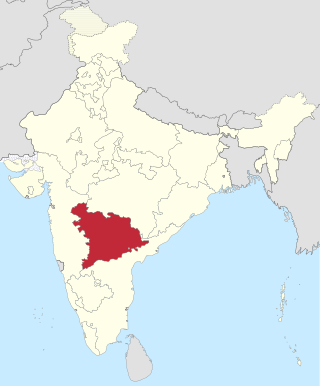
Hyderabad State was a state in Dominion and later Republic of India, formed after the accession of the State of Hyderabad into the Union on 17 September 1948. It existed from 1948 to 1956. Hyderabad State comprised present day Telangana, Marathwada and Hyderabad-Karnataka

The Andhra movement or Andhrodyamam was a campaign for recognition of Telugu-speaking part of the Madras Presidency as a separate political unit in British India. The Andhra movement leaders alleged that the Telugu people were being suppressed by the Tamils, who dominated politics and government jobs. A similar movement was started by the Telangana people living in the Hyderabad State under Nizam's rule. Lead by Andhra Mahasabha

Elections to the Legislative Assembly of the Indian state of Hyderabad were held and Sri Burgula Rama Krishna Rao took oath as First Chief Minister of Hyderabad State on 6 March 1952. 564 candidates competed for the 175 seats in the Assembly. There were 33 two-member constituencies and 109 constituencies single-member constituencies.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Telangana:
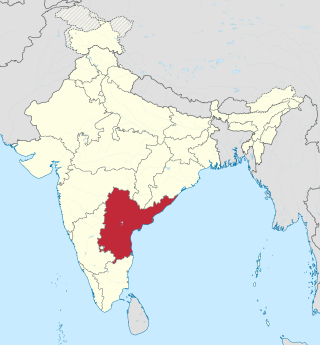
Andhra Pradesh, retrospectively referred to as United Andhra Pradesh, Undivided Andhra Pradesh, Combined Andhra Pradesh and Ummadi Andhra Pradesh, was a state in India formed by States Reorganisation Act, 1956 with Hyderabad as its capital and was reorganised by Andhra Pradesh Reorganisation Act, 2014. The state was made up of three distinct cultural regions of Telangana, Rayalaseema, and Coastal Andhra. Before the 1956 reorganisation, Telangana had been part of Hyderabad State, whereas Rayalaseema and Coastal Andhra had been part of Andhra State, formerly a part of Madras Presidency ruled by British India.
The Andhra Pradesh Decentralisation and Inclusive Development of All Regions Act, 2020 is an act of Andhra Pradesh Legislature aimed at the decentralisation of governance in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. The bill was proposed by the Government of Andhra Pradesh to establish three capitals at different places in the state namely Visakhapatnam, Amaravati, and Kurnool, which will serve as executive, legislative and judicial capitals respectively.














