Related Research Articles
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to health sciences:

Medicine is the science and practice of caring for patients, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness. Contemporary medicine applies biomedical sciences, biomedical research, genetics, and medical technology to diagnose, treat, and prevent injury and disease, typically through pharmaceuticals or surgery, but also through therapies as diverse as psychotherapy, external splints and traction, medical devices, biologics, and ionizing radiation, amongst others.
Medical psychology or medico-psychology is the application of psychological principles to the practice of medicine, sometimes using drugs for both physical and mental disorders.

Health care, or healthcare, is the improvement of health via the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other physical and mental impairments in people. Health care is delivered by health professionals and allied health fields. Medicine, dentistry, pharmacy, midwifery, nursing, optometry, audiology, psychology, occupational therapy, physical therapy, athletic training, and other health professions all constitute health care. The term includes work done in providing primary care, secondary care, tertiary care, and public health.

William Cullen was a Scottish physician, chemist and agriculturalist, and professor at the Edinburgh Medical School. Cullen was a central figure in the Scottish Enlightenment: He was David Hume's physician, and was friends with Joseph Black, Henry Home, Adam Ferguson, John Millar, and Adam Smith, among others.

Primary care is a model of health care that supports first-contact, accessible, continuous, comprehensive and coordinated person-focused care. It aims to optimise population health and reduce disparities across the population by ensuring that subgroups have equal access to services.

In a physical examination, medical examination, clinical examination, or medical checkup, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a medical condition. It generally consists of a series of questions about the patient's medical history followed by an examination based on the reported symptoms. Together, the medical history and the physical examination help to determine a diagnosis and devise the treatment plan. These data then become part of the medical record.

Telehealth is the distribution of health-related services and information via electronic information and telecommunication technologies. It allows long-distance patient and clinician contact, care, advice, reminders, education, intervention, monitoring, and remote admissions. Telemedicine is sometimes used as a synonym, or is used in a more limited sense to describe remote clinical services, such as diagnosis and monitoring. When rural settings, lack of transport, a lack of mobility, conditions due to outbreaks, epidemics or pandemics, decreased funding, or a lack of staff restrict access to care, telehealth may bridge the gap as well as provide distance-learning; meetings, supervision, and presentations between practitioners; online information and health data management and healthcare system integration. Telehealth could include two clinicians discussing a case over video conference; a robotic surgery occurring through remote access; physical therapy done via digital monitoring instruments, live feed and application combinations; tests being forwarded between facilities for interpretation by a higher specialist; home monitoring through continuous sending of patient health data; client to practitioner online conference; or even videophone interpretation during a consult.

Family medicine is a medical specialty within primary care that provides continuing and comprehensive health care for the individual and family across all ages, genders, diseases, and parts of the body. The specialist, who is usually a primary care physician, is named a family physician. It is often referred to as general practice and a practitioner as a general practitioner. Historically, their role was once performed by any doctor with qualifications from a medical school and who works in the community. However, since the 1950s, family medicine / general practice has become a specialty in its own right, with specific training requirements tailored to each country. The names of the specialty emphasize its holistic nature and/or its roots in the family. It is based on knowledge of the patient in the context of the family and the community, focusing on disease prevention and health promotion. According to the World Organization of Family Doctors (WONCA), the aim of family medicine is "promoting personal, comprehensive and continuing care for the individual in the context of the family and the community". The issues of values underlying this practice are usually known as primary care ethics.
Athletic training is an allied health care profession recognized by the American Medical Association (AMA) that "encompasses the prevention, examination, diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation of emergent, acute, or chronic injuries and medical conditions." There are five areas of athletic training listed in the seventh edition (2015) of the Athletic Training Practice Analysis: injury and illness prevention and wellness promotion; examination, assessment, diagnosis; immediate and emergency care; therapeutic intervention; and healthcare administration and professional responsibility.
A medical specialty is a branch of medical practice that is focused on a defined group of patients, diseases, skills, or philosophy. Examples include those branches of medicine that deal exclusively with children (pediatrics), cancer (oncology), laboratory medicine (pathology), or primary care. After completing medical school or other basic training, physicians or surgeons and other clinicians usually further their medical education in a specific specialty of medicine by completing a multiple-year residency to become a specialist.
Medical model is the term coined by psychiatrist R. D. Laing in his The Politics of the Family and Other Essays (1971), for the "set of procedures in which all doctors are trained". It includes complaint, history, physical examination, ancillary tests if needed, diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis with and without treatment.

Medicine in ancient Rome was highly influenced by ancient Greek medicine, but also developed new practices through knowledge of the Hippocratic Corpus combined with use of the treatment of diet, regimen, along with surgical procedures. This was most notably seen through the works of two of the prominent Greek physicians, Dioscorides and Galen, who practiced medicine and recorded their discoveries. This is contrary to two other physicians like Soranus of Ephesus and Asclepiades of Bithynia, who practiced medicine both in outside territories and in ancient Roman territory, subsequently. Dioscorides was a Roman army physician, Soranus was a representative for the Methodic school of medicine, Galen performed public demonstrations, and Asclepiades was a leading Roman physician. These four physicians all had knowledge of medicine, ailments, and treatments that were healing, long lasting and influential to human history.
The doctor–patient relationship is a central part of health care and the practice of medicine. A doctor–patient relationship is formed when a doctor attends to a patient's medical needs and is usually through consent. This relationship is built on trust, respect, communication, and a common understanding of both the doctor and patients' sides. The trust aspect of this relationship goes is mutual: the doctor trusts the patient to reveal any information that may be relevant to the case, and in turn, the patient trusts the doctor to respect their privacy and not disclose this information to outside parties.
Health is the state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being and a positive concept emphasizing social and personal resources, as well as physical capacities. This article lists major topics related to personal health.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to medicine:

A hospital is a healthcare institution providing patient treatment with specialized health science and auxiliary healthcare staff and medical equipment. The best-known type of hospital is the general hospital, which typically has an emergency department to treat urgent health problems ranging from fire and accident victims to a sudden illness. A district hospital typically is the major health care facility in its region, with many beds for intensive care and additional beds for patients who need long-term care.
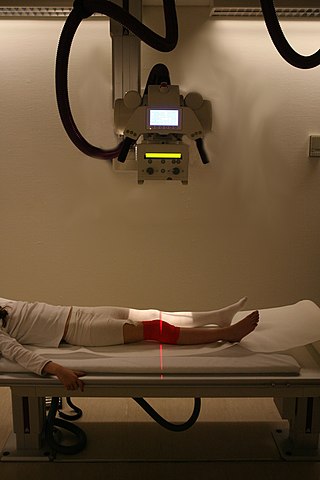
Medical diagnosis is the process of determining which disease or condition explains a person's symptoms and signs. It is most often referred to as a diagnosis with the medical context being implicit. The information required for a diagnosis is typically collected from a history and physical examination of the person seeking medical care. Often, one or more diagnostic procedures, such as medical tests, are also done during the process. Sometimes the posthumous diagnosis is considered a kind of medical diagnosis.

A doctor's visit, also known as a physician office visit or a consultation, or a ward round in an inpatient care context, is a meeting between a patient with a physician to get health advice or treatment plan for a symptom or condition, most often at a professional health facility such as a doctor's office, clinic or hospital. According to a survey in the United States, a physician typically sees between 50 and 100 patients per week, but it may vary with medical specialty, but differs only little by community size such as metropolitan versus rural areas.
Online doctor is a term that emerged during the 2000s, used by both the media and academics, to describe a generation of physicians and health practitioners who deliver healthcare, including drug prescription, over the internet.
References
- 1 2 Miller TE, Derse AR. Between strangers: the practice of medicine online. Health Aff (Millwood) 2002;21(4):168-79.
- 1 2 3 4 Amara R, Robert Wood Johnson Foundation., Institute for the Future. Health and health care 2010 : the forecast, the challenge. Second ed. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass; 2003.
- ↑ Weisbord SD, Soule JB, Kimmel PL. Poison on line—acute renal failure caused by oil of wormwood purchased through the Internet. N Engl J Med 1997;337(12):825-7.
- 1 2 3 Fung CH, Woo HE, Asch SM. Controversies and legal issues of prescribing and dispensing medications using the Internet. Mayo Clin Proc 2004;79(2):188-94.
- ↑ Jensen JA, Hickman NJ, 3rd, Landrine H, Klonoff EA. Availability of tobacco to youth via the Internet. Jama 2004;291(15):1837.
- ↑ Nunn JF. Ancient Egyptian medicine. Norman: University of Oklahoma Press; 1996.
- ↑ Kleisiaris, Christos F.; Sfakianakis, Chrisanthos; Papathanasiou, Ioanna V. (2014-03-15). "Health care practices in ancient Greece: The Hippocratic ideal". Journal of Medical Ethics and History of Medicine. 7: 6. ISSN 2008-0387. PMC 4263393 . PMID 25512827.
- ↑ Garrison FH. An introduction to the history of medicine : with medical chronology, suggestions for study and bibliographic data. 4th ed. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders; 1929.
- ↑ Thorndike L. A history of magic and experimental science. New York,: Macmillan; 1923.
- 1 2 Friedlèander L, Magnus LA, Freese JH, Gough AB. Roman life and manners under the early empire. London, New York,: G. Routledge & sons limited; E. P. Dutton & co.; 1908.
- ↑ Durant W, Durant A. Chapter XXIV. The Hellenistic Revival in The story of civilization. New York,: Simon and Schuster; 1935.
- ↑ Scarborough J. Roman medicine. Ithaca, N.Y.,: Cornell University Press; 1969.
- 1 2 Porter R. The greatest benefit to mankind : a medical history of humanity. 1st American ed. New York: W. W. Norton; 1998.
- 1 2 3 Porter D, Porter R. Patient's progress : doctors and doctoring in eighteenth- century England. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press; 1989.
- ↑ Porter R, Porter D. In sickness and in health : the British experience, 1650-1850. New York, NY: B. Blackwell; 1989.
- 1 2 3 Reiser SJ. Medicine and the reign of technology. Cambridge; New York: Cambridge University Press; 1978.
- ↑ King LS. The medical world of the eighteenth century. [Chicago]: University of Chicago Press; 1958.
- 1 2 3 Risse G. Cullen as clinician: organisation and strategies of an eighteenth century medical practice. In: Doig A, Ferguson J, Milne I, Passmore R, eds. William Cullen and the eighteenth century medical world : a bicentenary exhibition and symposium arranged by the Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh in 1990. Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press; 1993:133-51.
- ↑ Oakley AF. Letters to a 17th Century Yorkshire Physician. History of Medicine 1970;2:24-8.
- 1 2 Carson G. The roguish world of Doctor Brinkley. New York,: Rinehart; 1960.
- ↑ Pruitt V. John R. Brinkley, Kansas physician, and the goat gland rejuvenation fad. Pharos Alpha Omega Alpha Honor Med Soc 2002;65(3):33-9.
- 1 2 Lee RA. The bizarre careers of John R. Brinkley. Lexington, Ky.: University Press of Kentucky; 2002.