A request that this article title be changed to Index of British Columbia–related articles is under discussion. Please do not move this article until the discussion is closed. |
Articles related to British Columbia include:
A request that this article title be changed to Index of British Columbia–related articles is under discussion. Please do not move this article until the discussion is closed. |
Articles related to British Columbia include:
This section is empty.You can help by adding to it.(July 2010) |
This section is empty.You can help by adding to it.(January 2018) |
This section is empty.You can help by adding to it.(July 2010) |
This section is empty.You can help by adding to it.(July 2010) |
This section is empty.You can help by adding to it.(July 2010) |
This section is empty.You can help by adding to it.(July 2010) |
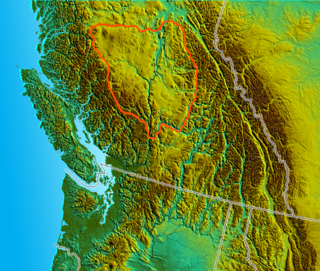
The Cariboo is an intermontane region of British Columbia along a plateau stretching from the Fraser Canyon to the Cariboo Mountains. The name is a reference to the caribou that were once abundant in the region. The Cariboo was the first region of the Interior north of the lower Fraser and its canyon to be settled by non-indigenous people, and played an important part in the early history of the colony and province. The boundaries of the Cariboo proper in its historical sense are debatable, but its original meaning was the region north of the forks of the Quesnel River and the low mountainous basins between the mouth of that river on the Fraser at the city of Quesnel and the northward end of the Cariboo Mountains - an area that is mostly in the Quesnel Highland and focused on several now-famous gold-bearing creeks near the head of the Willow River, the richest of them all, Williams Creek, the location of Barkerville, which was the capital of the Cariboo Gold Rush and also of government officialdom for decades afterwards. This area, the Cariboo goldfields, is underpopulated today but was once the most settled and most powerful of the regions of the province's Interior. As settlement spread southwards of this area, flanking the route of the Cariboo Road and spreading out through the rolling plateaus and benchlands of the Cariboo Plateau and lands adjoining it along the Fraser and Thompson, the meaning changed to include a wider area than the goldfields.
Cariboo was a federal electoral district in British Columbia, Canada, that was represented in the House of Commons of Canada from 1871 to 1892.
British Columbia gold rushes were important episodes in the history and settlement of European, Canadian and Chinese peoples in western Canada.
The Chilcotin region of British Columbia is usually known simply as "the Chilcotin", and also in speech commonly as "the Chilcotin Country" or simply Chilcotin. It is a plateau and mountain region in British Columbia on the inland lee of the Coast Mountains on the west side of the Fraser River. Chilcotin is also the name of the river draining that region. In the language of the Chilcotin people their name and the name of the river means "people of the red ochre river"
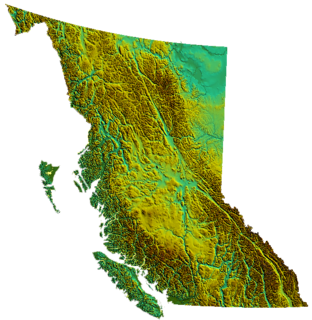
British Columbia is the westernmost province of Canada, bordered by the Pacific Ocean. With an area of 944,735 square kilometres (364,764 sq mi) it is Canada's third-largest province. The province is almost four times the size of United Kingdom and larger than every U.S. state except Alaska. It is bounded on the northwest by the U.S. state of Alaska, directly north by Yukon and the Northwest Territories, on the east by Alberta, and on the south by the U.S. states of Washington, Idaho, and Montana. Formerly part of the British Empire, the southern border of British Columbia was established by the 1846 Oregon Treaty. The province is dominated by mountain ranges, among them the Canadian Rockies but dominantly the Coast Mountains, Cassiar Mountains, and the Columbia Mountains. Most of the population is concentrated on the Pacific coast, notably in the area of Vancouver, located on the southwestern tip of the mainland, which is known as the Lower Mainland. It is the most mountainous province of Canada.
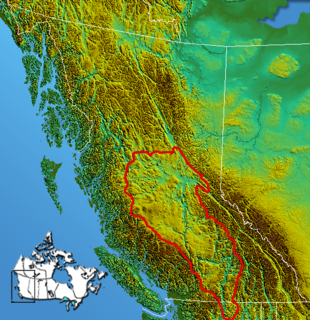
The Interior Plateau comprises a large region of the Interior of British Columbia, and lies between the Cariboo and Monashee Mountains on the east, and the Hazelton Mountains, Coast Mountains and Cascade Range on the west. The continuation of the plateau into the United States is known there as the Columbia Plateau.

The Camelsfoot Range is a sub-range of the Chilcotin Ranges subdivision of the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains in British Columbia. The Fraser River forms its eastern boundary. The range is approximately 90 km at its maximum length and less than 30 km wide at its widest.

Bute Inlet is one of the principal inlets of the British Columbia Coast. It is 80 km (50 mi) long from the estuaries of the Homathko and Southgate Rivers at the head of the inlet, to the mouth, where it is nearly blocked by Stuart Island, and it averages about 4 km (2.5 mi) in width. Bute Inlet is in a spectacular wilderness setting and is one of the most scenic waterways in the world. In the upper reaches of the inlet mountains rise 2,700 m (9,000 ft) feet above sea level. Bute Inlet is a spectacular wilderness that is visited by very few people. In more recent years tourists are travelling from around the world to view grizzly bears in a natural setting and explore the wilderness of Bute Inlet.

The Cariboo Plateau is a volcanic plateau in south-central British Columbia, Canada. It is part of the Fraser Plateau that itself is a northward extension of the North American Plateau. The southern limit of the plateau is the Bonaparte River although some definitions include the Bonaparte Plateau between that river and the Thompson, but it properly is a subdivision of the Thompson Plateau. The portion of the Fraser Plateau west of the Fraser River is properly known as the Chilcotin Plateau but is often mistakenly considered to be part of the Cariboo Plateau, which is east of the Fraser.
Paul St. Pierre was a journalist and author in British Columbia, Canada. He was the Member of Parliament for the riding of Coast Chilcotin from 1968-1972. He was defeated in the 1972 election by New Democratic Party candidate Harry Olaussen in a tight three-way race. He was especially known for his popular fiction recounting adventures and quirks of life in the Chilcotin-Cariboo, and for a regular column that appeared for many years in the Vancouver Sun.
Cariboo was one of the twelve original electoral districts created when British Columbia became a Canadian province in 1871. Roughly corresponding to the old colonial electoral administrative district of the same name, it was a three-member riding until the 1894 election, when it was reduced through reapportionment and became a two-member riding until the 1916 election, after which it has been a single-member riding. It produced many notable Members of the Legislative Assembly (MLAs), including George Anthony Boomer Walkem, third and fifth holder of the office of Premier of British Columbia and who was one of the first representatives elected from the riding; John Robson, ninth Premier of British Columbia; and Robert Bonner, a powerful minister in the W.A.C. Bennett cabinet, and later CEO of MacMillan Bloedel and BC Hydro.

Ten Mile Lake Provincial Park is a provincial park in the Cariboo Land District of British Columbia, Canada, ten miles (16 km) north of the city of Quesnel. The park is situated within the Fraser Plateau and Basin complex, in a transition area between the wetter Quesnel Highland to the east, and the dry Chilcotin Plateau to the west.
The Nechako Plateau is the northernmost subdivision of the Interior Plateau, one of the main geographic regions of the Canadian province of British Columbia. It spans the basin of the Nechako River and its tributaries the Stuart River and Endako Rivers, and is bounded on the south by the West Road River, south of which is the Chilcotin Plateau and on the north by the Nation River and the valleys of Babine and Takla Lakes, beyond which are the Omineca Mountains (N) and Skeena Mountains (NW). To the west, it abuts the various ranges of the Hazelton Mountains while on its east it is bounded by the pass between Prince George, British Columbia and the Parsnip Arm of Williston Lake, beyond which is the McGregor Plateau, which skirts the Northern Rockies. Some classification systems include the plateau area on the east bank of the Fraser River beyond the city of Prince George; this area neighbours the northernmost reaches of the Quesnel Highland and Cariboo Mountains.
The British Columbia Interior, BC Interior or Interior of British Columbia, usually referred to only as the Interior, is one of the three main regions of the Canadian province of British Columbia, the other two being the Lower Mainland, which comprises the overlapping areas of Greater Vancouver and the Fraser Valley, and the Coast, which includes Vancouver Island and also including the Lower Mainland.
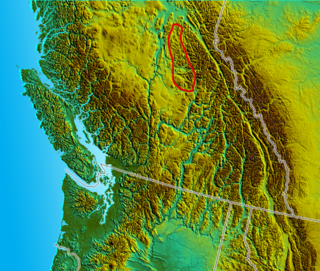
The Quesnel Highland is a geographic area in the Central Interior of the Canadian province of British Columbia. As defined by BC government geographer in Landforms of British Columbia, an account and analysis of British Columbia geography that is often cited as authoritative, the Highland is a complex of upland hill and plateau areas forming and defined as being the buffer between the Cariboo Plateau and the Cariboo Mountains, as a sort of highland foothills along the eastern edge of the Interior Plateau running southeast from a certain point southeast of the city of Prince George to the Mahood Lake area at the southeast corner of the Cariboo. Beyond Mahood Lake lies another separately classified area dubbed by Holland the Shuswap Highland which spans similar terrain across the North Thompson and Shuswap Lake-Adams River drainage basins, forming a similar upland-area buffer between the Thompson Plateau and the Monashee Mountains. A third area, the Okanagan Highland, extends from the southern end of the Shuswap Highland in the area of Vernon and Enderby in the northern Okanagan region into Washington State, and also abuts the Monashee Mountains.

Alexandria or Fort Alexandria is a National Historic Site of Canada on the Fraser River in British Columbia, and was the end of the Old Cariboo Road and the Cariboo Wagon Road. It is located on Highway 97, 103 miles (166 km) north of 100 Mile House and 28 miles (45 km) south of Quesnel.

Thomas Elwyn was a British soldier, police officer and gold commissioner in colonial British Columbia.
The British Columbia electoral redistribution of 2008 was undertaken over a lengthy period that began in late 2005 and was completed with the passage of the Electoral Districts Act, 2008 on April 10, 2008. The redistribution modified most electoral boundaries in the province, and increased the number of MLAs from 79 to 85. The electoral boundaries created by the redistribution were first used in the 2009 provincial election.
Coralee Oakes is a Canadian politician, who was elected to the Legislative Assembly of British Columbia in the 2013 provincial election. She represents the electoral district of Cariboo North as a member of the British Columbia Liberal Party and was appointed Minister of Community, Sport and Cultural Development on June 10, 2013.