This article explains terms used for the British Armed Forces' ordnance and also ammunition. The terms may have slightly different meanings in the military of other countries.
HMCS Vegreville was a Bangor-class minesweeper that served in the Royal Canadian Navy during the Second World War. She saw action in the Battle of the St. Lawrence, Battle of the Atlantic and the Invasion of Normandy. She was broken up after the war in 1947. She was named for Vegreville, Alberta.

The Eclipse-class cruisers were a class of nine second-class protected cruisers constructed for the Royal Navy in the mid-1890s.

HMS Andromeda was one of eight Diadem-class protected cruisers built for the Royal Navy in the 1890s. Upon completion in 1899, the ship was assigned to the Mediterranean Fleet where she helped to escort a royal yacht during its cruise through the Mediterranean Sea. After a refit, she was assigned to the China Station in 1904 and returned home three years later to be reduced to reserve. Andromeda was converted into a training ship in 1913 and remained in that role under various names until 1956. That year she was sold for scrap and broken up in Belgium, the last Pembroke-built ship still afloat.

The QF 3 inch 20 cwt anti-aircraft gun became the standard anti-aircraft gun used in the home defence of the United Kingdom against German airships and bombers and on the Western Front in World War I. It was also common on British warships in World War I and submarines in World War II. 20 cwt referred to the weight of the barrel and breech, to differentiate it from other 3 inch guns. While other AA guns also had a bore of 3 inches (76 mm), the term 3 inch was only ever used to identify this gun in the World War I era, and hence this is what writers are usually referring to by 3 inch AA gun.

The Pathfinder-class cruisers were a pair of scout cruisers built for the Royal Navy in the first decade of the 20th century. The sister ships spent much of the first decade of their careers in reserve. When the First World War began in August 1914 they were given coastal defence missions, Pathfinder on the coast of Scotland and Patrol on the coast of Yorkshire. The latter ship was badly damaged when the Germans bombarded Hartlepool in December. She spent the rest of the war in British waters. The ship was paid off in 1919 and sold for scrap the following year. Pathfinder was sunk by a German submarine shortly after the war began, the first sinking of a British warship during the war by a German submarine.

The Forward-class cruisers were a pair of scout cruisers built for the Royal Navy in the first decade of the 20th century. The sister ships spent much of the first decade of their careers in reserve. When the First World War began in August 1914 they were given coastal defence missions, Foresight in the English Channel and Forward on the coast of Yorkshire. The latter ship was in Hartlepool when the German bombarded it in December, but never fired a shot. The ships were transferred to the Mediterranean in 1915 and then to the Aegean in mid-1916 where they remained until 1918. They survived the war, but were scrapped shortly afterwards.

The Adventure-class cruisers were a pair of scout cruisers built for the Royal Navy in the first decade of the 20th century. The sister ships spent about half of the first decade of their careers in reserve and were based in home waters when on active duty. During this time Attentive was involved in two collisions. When the First World War began in August 1914 the ships were given coastal defence missions on the English Channel. Attentive was transferred to Ireland in mid-1915, but Adventure remained with the Dover Patrol for another three years. They were assigned convoy escort duties in the Atlantic Ocean in 1918 before being separated when Attentive was transferred to the Mediterranean and Adventure was tasked to support the British intervention in North Russia. The sisters returned home a few months after the end of the war in November 1918 and were sold for scrap in 1920.
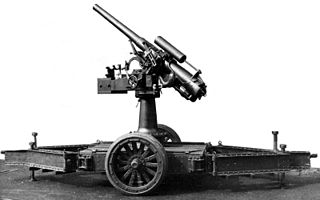
The 12 pounder 12 cwt anti-aircraft gun was borrowed for AA use from the QF 12 pounder 12 cwt coast defence gun with the addition of a modified cradle for higher elevation, a retaining catch for the cartridge, and an additional spring recuperator above the barrel and high-angle sights. Writers commonly refer to it simply as "12 pounder anti-aircraft gun". 12 cwt referred to the weight of the barrel and breech to differentiate it from other "12 pounder" guns.

The QF 12-pounder 12-cwt gun was a common, versatile 3-inch (76.2 mm) calibre naval gun introduced in 1894 and used until the middle of the 20th century. It was produced by Armstrong Whitworth, Elswick and used on Royal Navy warships, exported to allied countries, and used for land service. In British service "12-pounder" was the rounded value of the projectile weight, and "12 cwt (hundredweight)" was the weight of the barrel and breech, to differentiate it from other "12-pounder" guns.
12-pounder gun or 12-pdr, usually denotes a gun which fired a projectile of approximately 12 pounds.

The QF 12 pounder 18 cwt gun was a 3-inch high-velocity naval gun used to equip larger British warships such as battleships for defence against torpedo boats. 18 cwt referred to the weight of gun and breech, to differentiate the gun from others that also fired the "12 pound" shell.

The QF 14-pounder was a 3-inch medium-velocity naval gun used to equip warships for defence against torpedo boats. It was produced for export by Maxim-Nordenfelt in competition with the Elswick QF 12-pounder 12 cwt and QF 12-pounder 18 cwt guns.
The BL 6-inch gun Marks II, III, IV and VI were the second and subsequent generations of British 6-inch rifled breechloading naval guns, designed by the Royal Gun Factory in the 1880s following the first 6-inch breechloader, the relatively unsuccessful BL 6-inch 80-pounder gun designed by Elswick Ordnance. They were originally designed to use the old gunpowder propellants but from the mid-1890s onwards were adapted to use the new cordite propellant. They were superseded on new warships by the QF 6-inch gun from 1891.

The Challenger-class cruisers were a pair of second-class protected cruisers built for the Royal Navy in the first decade of the 20th century. One ship, HMS Encounter, was later transferred to the Royal Australian Navy.

Devil's Gap Battery is a coastal battery in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar, overlooking the Bay of Gibraltar near the westernmost limits of the Upper Rock Nature Reserve.
HMCS Lachine was a Bangor-class minesweeper of the Royal Canadian Navy that served during the Second World War. Following the war a proposed transfer to the Royal Canadian Mounted Police as Starnes was cancelled, and the ship was instead sold for conversion to a salvage tug in 1945. The ship was broken up in the United Kingdom in 1955.