
Ecuador, officially the Republic of Ecuador, is a country in northwestern South America, bordered by Colombia on the north, Peru on the east and south, and the Pacific Ocean on the west. Ecuador also includes the Galápagos Islands in the Pacific, about 1,000 kilometers (621 mi) west of the mainland. The country's capital is Quito and its largest city is Guayaquil.

The Inca Empire, officially known as the Realm of the Four Parts, was the largest empire in pre-Columbian America. The administrative, political, and military center of the empire was in the city of Cusco. The Inca civilization rose from the Peruvian highlands sometime in the early 13th century. The Spanish began the conquest of the Inca Empire in 1532 and by 1572, the last Inca state was fully conquered.
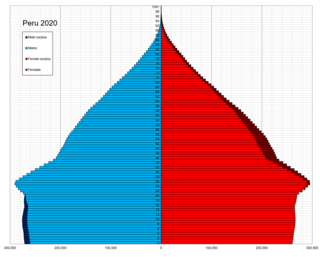
This is a demography of the population of Peru including population density, ethnicity, education level, the health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population.

Quechua, also called Runasimi in Southern Quechua, is an indigenous language family that originated in central Peru and thereafter spread to other countries of the Andes. Derived from a common ancestral "Proto-Quechua" language, it is today the most widely spoken pre-Columbian language family of the Americas, with the number of speakers estimated at 8–10 million speakers in 2004, and just under 7 million from the most recent census data available up to 2011. Approximately 13.9% of Peruvians speak a Quechua language.

Andean music is a group of styles of music from the Andes region in South America.

Wayna Qhapaq was the third Sapa Inca of Tawantinsuyu, the Inca Empire. He was the son of and successor to Túpac Inca Yupanqui., the sixth Sapa Inca of the Hanan dynasty, and eleventh of the Inca civilization. He was born in Tumipampa and tutored to become Sapa Inca from a young age.

Putumayo is a department of Southern Colombia. It is in the south-west of the country, bordering Ecuador and Peru. Its capital is Mocoa.
Ecuador is a multicultural and multiethnic nation, with the majority of its population is descended from a mixture of both European and Amerindian ancestry. The other 10% of Ecuador's population originate east of the Atlantic Ocean, predominantly from Spain, Italy, Lebanon, France and Germany. Around the Esmeraldas and Chota regions, the African influence would be strong among the small population of Afro-Ecuadorians that account for no more than 10%. Close to 80% of Ecuadorians are Roman Catholic, although the indigenous population blend Christian beliefs with ancient indigenous customs. The racial makeup of Ecuador is 70% mestizo, 7% Amerindian, 12% White, and 11% Black.

Tumbes is a coastal department and region in northwestern Peru bordering Ecuador. Due to the region's location near the Equator it has a warm climate, with beaches that are considered among the finest in Peru. Despite its small area, the region contains a wide variety of ecosystems. It is the smallest department in Peru and its third least populous department after Moquegua and Madre de Dios, but it is also its third most densely populated department, after La Libertad and Lambayeque.

Quechua people or Quichua people may refer to any of the indigenous peoples of South America who speak the Quechua languages, which originated among the Indigenous people of Peru. Although most Quechua speakers are native to Peru, there are some significant populations in Ecuador, Bolivia, Chile, Colombia, and Argentina.

Yagua are an indigenous people in Colombia and northeastern Peru, numbering approximately 6,000. Currently, they live near the Amazon, Napo, Putumayo and Yavari rivers and their tributaries. As of 2005, some Yagua have migrated northward to Colombia, near the town of Leticia.

Kichwa is a Quechuan language that includes all Quechua varieties of Ecuador and Colombia (Inga), as well as extensions into Peru. It has an estimated half million speakers.
The High Academy of the Quechua Language, or AMLQ, is a Peruvian organization whose purpose is stated as the teaching, promotion, and dissemination of the Quechua language.

The demographic history of Peru shows the structure of the population in different historical periods. Peru's population drastically increased in the 1900s, with a diverse range of ethnic divisions living in the country. Lima is its capital city situated along the Pacific Ocean coast, where most of its population lives, and its population size is around 9.75 million. Major cities are located near the coastal areas of Peru. In terms of population and area size, it is the fourth and third largest country in South America, a place where the ancestral transcends and all forms of art combine. Peru became an independent country on July 28, 1821. However, Peru did not have a proper national census until 1876, more than a half-century after independence. They took the data before the federal census through different mediums but not on a national level. The significant migration in Peru consisted of Indigenous people, Europeans, enslaved Africans, and Asians; Spaniards were the first European who came to Peru, arrived in 1531, and discovered the Inca culture. The Incas established pre-Columbian America's greatest and most advanced kingdom and monarchy. However, native Americans were still in a larger proportion to total population.

The Cañari are an indigenous ethnic group traditionally inhabiting the territory of the modern provinces of Azuay and Cañar in Ecuador. They are descended from the independent pre-Columbian tribal confederation of the same name. The historic people are particularly noted for their resistance against the Inca Empire. Eventually conquered by the Inca in the early 16th century shortly before the arrival of the Spanish, the Cañari later allied with the Spanish against the Inca. Today, the population of the Cañari, who include many mestizos, numbers in the thousands.

The Jivaroan peoples are the indigenous peoples in the headwaters of the Marañon River and its tributaries, in northern Peru and eastern Ecuador. The tribes speak the Chicham languages.

Amazonian Kichwas are a grouping of indigenous Kichwa peoples in the Ecuadorian Amazon, with minor groups across the borders of Colombia and Peru. Amazonian Kichwas consists of different ethnic peoples, including Napo Kichwa and Canelos Kichwa. There are approximately 419 organized communities of the Amazonian Kichwas. The basic socio-political unit is the ayllu. The ayllus in turn constitute territorial clans, based on common ancestry. Unlike other subgroups, the Napo Kichwa maintain less ethnic duality of acculturated natives or Christians.

The Andean civilizations were South American complex societies of many indigenous people. They stretched down the spine of the Andes for 4,000 km (2,500 mi) from southern Colombia, to Ecuador and Peru, including the deserts of coastal Peru, to north Chile and northwest Argentina. Archaeologists believe that Andean civilizations first developed on the narrow coastal plain of the Pacific Ocean. The Caral or Norte Chico civilization of coastal Peru is the oldest known civilization in the Americas, dating back to 3500 BCE. Andean civilization is one of the six "pristine" civilizations of the world, created independently and without influence by other civilizations.

Spanish is the most-widely spoken language in Ecuador, though great variations are present depending on several factors, the most important one being the geographical region where it is spoken. The three main regional variants are:
The Inca-Caranqui archaeological site is located in the village of Caranqui on the southern outskirts of the city of Ibarra, Ecuador. The ruin is located in a fertile valley at an elevation of 2,299 metres (7,543 ft). The region around Caranqui, extending into the present day country of Colombia, was the northernmost outpost of the Inca Empire and the last to be added to the empire before the Spanish conquest of 1533. The archaeological region is also called the Pais Caranqui.















