
The Hymenochaetales are an order of fungi in the class Agaricomycetes. The order in its current sense is based on molecular research and not on any unifying morphological characteristics. According to one 2008 estimate, the Hymenochaetales contain around 600 species worldwide, mostly corticioid fungi and poroid fungi, but also including several clavarioid fungi and agarics. Species of economic importance include wood decay fungi in the genera Phellinus and Inonotus sensu lato, some of which may cause losses in forestry. Therapeutic properties are claimed for Inonotus obliquus ("chaga") and Phellinus linteus, both of which are now commercially marketed.

Betulin is an abundant, naturally occurring triterpene. It is commonly isolated from the bark of birch trees. It forms up to 30% of the dry weight of silver birch bark. It is also found in birch sap. Inonotus obliquus and red alder also contain betulin.

Inonotus obliquus, commonly known as chaga, is a fungus in the family Hymenochaetaceae. It is parasitic on birch and other trees. The sterile conk is irregularly formed and has the appearance of burnt charcoal. It is not the fruiting body of the fungus, but a sclerotium or mass of mycelium, mostly black because of the presence of massive amounts of melanin. Some people consider chaga to be medicinal.

Inonotus hispidus, commonly known as shaggy bracket, is a fungus and a plant pathogen.
Inonotus ludovicianus is a species of fungus in the family Hymenochaetaceae. A plant pathogen, it is found in the southwestern United States and Louisiana.

Inonotus is a genus of fungi in the family Hymenochaetaceae. The genus, described by Petter Karsten in 1879, is estimated to contain about 80 species sensu lato and 30 species sensu stricto.

Inonotus dryadeus, commonly known as oak bracket, warted oak polypore, weeping polypore or weeping conk, is an inedible species of fungus belonging to the genus Inonotus, which consists of bracket fungi with fibrous flesh. Most often found growing at the base of oak trees, it causes white rot and decay of the trunks. It secretes an amber liquid which weeps from tubes in its upper surface.
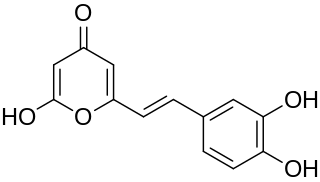
Hispidin is a natural substance. It can also be synthesized.

Inonotus tamaricis is a species of fungus in the family Hymenochaetaceae. A plant pathogen, it grows on dead and living Tamarix species, and is found in Southern Europe, North Africa, Syria and Senegal, Southern Asia and east to China.

Inonotus nothofagi is a species of fungus in the family Hymenochaetaceae. It is parasitic, and causes a white rot in the wood it infects. First described scientifically by mycologist George Herriot Cunningham, it is found in Australia and New Zealand where it infects Nothofagus cunninghamii, and India, where it grows on oak.
Methanobrevibacter cuticularis is a species of methanogen archaeon. It was first isolated from the hindgut of the termite Reticulitermes flavipes. It is rod-shaped, ranging in size from 0.34 to 1.6 µm and possesses polar fibers. Its morphology, gram-positive staining reaction, resistance to cell lysis by chemical agents and narrow range of utilizable substrates are typical of species belonging to the family Methanobacteriaceae. It habitates on or near the hindgut epithelium and also attached to filamentous prokaryotes associated with the gut wall. It is one of the predominant gut biota.
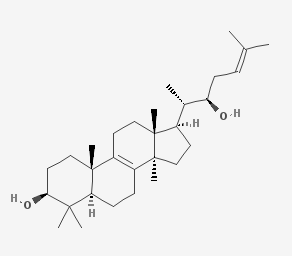
Inotodiol is an anti-inflammatory sterol isolated from Inonotus obliquus.

Trametenolic acid is an anti-inflammatory sterol isolated from Inonotus obliquus.
Tropicoporus is a genus of fungi in the family Hymenochaetaceae. It was circumscribed in 2015 with Tropicoporus excentrodendri as the type species, and six additional species transferred from Inonotus.
Tropicoporus tropicalis is part of the family Hymenochaetaceae, and was recently renamed to Tropicoporus tropicalis from Inonotus tropicalis, which is part of the Inonotus clade B. Tropicoporus tropicalis is a wood-decaying basidiomycetes that rarely causes disease in animals and human, and is commonly found in humid climate such as Brazil. In its natural environment, the fungus is associated with white rot woody angiosperms, and has its annual fruiting body on tree trunks and branches. Tropicoporus tropicalis has two kinds of hyphae, generative and skeletal, that lack clamp connections.
Inonotus rigidus is a species of fungus in the family Hymenochaetaceae. It is distinguished by its resupinate and rigid basidiocarps, its yellow pore surface, being microscopically ellipsoid and yellowish brown, its thick-walled basidiospores, and by lacking both setal hyphae and hymenial setae.
Inonotus chrysomarginatus is a species of fungus in the family Hymenochaetaceae. It is distinguished by having an annual to perennial growth habit, pileate basidiocarps, setal hyphae and hooked hymenial setae, and sublobose, yellowish, thick-walled cyanophilous basidiospores.
Inonotus acutus is a species of fungus in the family Hymenochaetaceae. It is characterized by having small and thin basidiocarps, a sharp pileus margin, ventricose hymenial setae, and ellipsoid, yellowish and thick-walled basidiospores.

Inocutis is a genus of nine species of polypore fungi in the family Hymenochaetaceae.
Philotheca cuticularis is a species of flowering plant in the family Rutaceae and is endemic to Queensland. It is a rounded shrub with small, crowded leaves and small white flowers arranged singly on the ends of branchlets.










