
Ficinia spiralis is a coastal sedge endemic to New Zealand. Originally widespread, it has suffered severely from competition with introduced marram grass and animal grazing and now has only a patchy distribution.

Pleurophyllum speciosum, also known as the giant emperor daisy or Campbell Island daisy, is a megaherb native to the Auckland and Campbell Islands of New Zealand. A false colour image is depicted on the lower left corner on the reverse of the current five dollar New Zealand banknote. The Campbell Island daisy was first described by Joseph Dalton Hooker in Flora Antarctica of 1844, after he had collected it during the Ross expedition.

Gentianella concinna is a flowering plant species, endemic to the Auckland Islands of New Zealand.

Carex capillacea, common name yellowleaf sedge in Tasmania, is a species of sedge found in Assam, the far east of Russia, New Guinea, south east Australia, New Zealand, Malesia, China, Japan and India.

Carex solandri is a species of sedge that was first described by Francis Boott in 1853.

Isolepis prolifera is a species of flowering plant in the family Cyperaceae that grows in temperate regions of the Southern Hemisphere. It has leafless stems up to 90 cm (35 in) tall, and clusters of flowers that often proliferate into branches.
Actinoschoenus arthrostyloides, commonly known as hairy actinoschoenus, is flowering plant in the sedge family, Cyperaceae, that is native to Western Australia throughout parts of the Kimberley region.
Cyperus rigidellus is a sedge of the family Cyperaceae that is native to Australia.

Carex albula, common name white sedge, is a species of sedge. It is endemic to the South Island of New Zealand.

Carex berggrenii, common name Berggren's Sedge, is a species of sedge. It is endemic to New Zealand, being found on both the North and the South Islands.

Tupeia is a monotypic genus of semi-parasitic shrubs (mistletoes) which occurs in both the North and South Islands of New Zealand. There is only one species in the genus: Tupeia antarctica. There are no synonyms.

Anisotome antipoda is a species of flowering plant in the family Apiaceae, which is endemic to the Auckland, Campbell and Antipodes Islands.

Plantago aucklandica is a flowering plant in the family Plantaginaceae that is endemic to the Auckland Islands.

Coprosma cuneata, is a shrub in the Rubiaceae family, native to New Zealand.

Gentianella cerina is a plant species in the Gentianaceae family, endemic to the Auckland Islands of New Zealand.

Juncus antarcticus, also known as dwarf rush, is a flowering plant species in the rush family Juncaceae, native to New Zealand and Australia.

Marsippospermum gracile, common name - alpine rush, is a flowering plant species in the rush family Juncaceae which is native to New Zealand.

Oreobolus pectinatus is a species of flowering plant in the sedge family that is native to the subantarctic islands, and to the North and South Islands of New Zealand. The specific epithet derives from the Latin, pectin/pectinis,, and refers to the leaves.
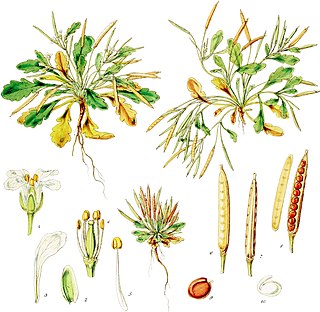
Cardamine depressa is a plant in the Brassicaceae family, found in the Antipodean Islands.
Eleocharis confervoides is a species of plant in the sedge family (Cyperaceae). It is a perennial, submerged, aquatic and deeply rooted herb. It is known by its common name Algal bulrush and has lots of synonyms. The species has worldwide but very spotty distribution and is native in many tropical and subtropical regions in America, Asia and Africa. It inhabits in water, usually in shallow or deep lakes and ponds. The plant has slender stem with many branches, the leaves float in the water and flowers are usually emergent over the water surface. Fruiting occurs in fall. The most occurrences of plant appear in April and frequency of occurrences is increasing the last years

















