Related Research Articles

A diode is a two-terminal electronic component that conducts current primarily in one direction ; it has low resistance in one direction, and high resistance in the other.

The field of electronics is a branch of physics and electrical engineering that deals with the emission, behaviour and effects of electrons using electronic devices. Electronics uses active devices to control electron flow by amplification and rectification, which distinguishes it from classical electrical engineering, which only uses passive effects such as resistance, capacitance and inductance to control electric current flow.

A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify or switch electrical signals and power. The transistor is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semiconductor material, usually with at least three terminals for connection to an electronic circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals controls the current through another pair of terminals. Because the controlled (output) power can be higher than the controlling (input) power, a transistor can amplify a signal. Some transistors are packaged individually, but many more are found embedded in integrated circuits.

A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve, or tube, is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric potential difference has been applied.
A semiconductor device is an electronic component that relies on the electronic properties of a semiconductor material for its function. Its conductivity lies between conductors and insulators. Semiconductor devices have replaced vacuum tubes in most applications. They conduct electric current in the solid state, rather than as free electrons across a vacuum or as free electrons and ions through an ionized gas.
The JEDEC Solid State Technology Association is an independent semiconductor engineering trade organization and standardization body headquartered in Arlington County, Virginia, United States.
A thin-film transistor (TFT) is a special type of field-effect transistor (FET) where the transistor is thin relative to the plane of the device. TFTs are grown on a supporting substrate. A common substrate is glass, because the traditional application of TFTs is in liquid-crystal displays (LCDs). This differs from the conventional bulk metal oxide field effect transistor (MOSFET), where the semiconductor material typically is the substrate, such as a silicon wafer.
The tilde˜ or ~, is a grapheme with several uses. The name of the character came into English from Spanish and Portuguese, which in turn came from the Latin titulus, meaning "title" or "superscription". Its primary use is as a diacritic (accent) in combination with a base letter; but for historical reasons, it is also used in standalone form within a variety of contexts.

The 7400 series of integrated circuits (ICs) are a popular logic family of transistor–transistor logic (TTL) logic chips.
Pro Electron or EECA is the European type designation and registration system for active components.

A television set or television receiver, more commonly called the television, TV, TV set, telly, tele, or tube, is a device that combines a tuner, display, and loudspeakers, for the purpose of viewing and hearing television broadcasts, or using it as a computer monitor. Introduced in the late 1920s in mechanical form, television sets became a popular consumer product after World War II in electronic form, using cathode ray tube (CRT) technology. The addition of color to broadcast television after 1953 further increased the popularity of television sets in the 1960s, and an outdoor antenna became a common feature of suburban homes. The ubiquitous television set became the display device for the first recorded media in the 1970s, such as Betamax, VHS and later DVD. It has been used as a display device since the first generation of home computers and dedicated video game consoles in the 1980s. By the early 2010s, flat-panel television incorporating liquid-crystal display (LCD) technology, especially LED-backlit LCD technology, largely replaced CRT and other display technologies. Modern flat panel TVs are typically capable of high-definition display and can also play content from a USB device. Starting in the late 2010s, most flat panel TVs began to offer 4K and 8K resolutions.
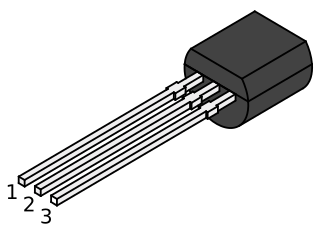
The TO-92 is a widely used style of semiconductor package mainly used for transistors. The case is often made of epoxy or plastic, and offers compact size at a very low cost.

An electronic symbol is a pictogram used to represent various electrical and electronic devices or functions, such as wires, batteries, resistors, and transistors, in a schematic diagram of an electrical or electronic circuit. These symbols are largely standardized internationally today, but may vary from country to country, or engineering discipline, based on traditional conventions.
In Europe, the principal method of numbering vacuum tubes was the nomenclature used by the Philips company and its subsidiaries Mullard in the UK, Valvo(de, it) in Germany, Radiotechnique (Miniwatt-Dario brand) in France, and Amperex in the United States, from 1934 on. Adhering manufacturers include AEG (de), CdL (1921, French Mazda brand), CIFTE (fr, Mazda-Belvu brand), EdiSwan (British Mazda brand), Lorenz (de), MBLE(fr, nl), RCA (us), RFT(de, sv) (de), Siemens (de), Telefunken (de), Tesla (cz), Toshiba (ja), Tungsram (hu), and Unitra. This system allocated meaningful codes to tubes based on their function and became the starting point for the Pro Electron naming scheme for active devices.

Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS) are the standards used for industrial activities in Japan, coordinated by the Japanese Industrial Standards Committee (JISC) and published by the Japanese Standards Association (JSA). The JISC is composed of many nationwide committees and plays a vital role in standardizing activities across Japan.
Founded in 1948, the Electronic Industries Association of Japan (EIAJ) was one of two Japanese electronics trade organizations that were merged into the Japan Electronics and Information Technology Industries Association (JEITA).
A transistor is a semiconductor device with at least three terminals for connection to an electric circuit. In the common case, the third terminal controls the flow of current between the other two terminals. This can be used for amplification, as in the case of a radio receiver, or for rapid switching, as in the case of digital circuits. The transistor replaced the vacuum-tube triode, also called a (thermionic) valve, which was much larger in size and used significantly more power to operate.The first transistor was successfully demonstrated on December 23, 1947, at Bell Laboratories in Murray Hill, New Jersey. Bell Labs is the research arm of American Telephone and Telegraph (AT&T). The three individuals credited with the invention of the transistor were William Shockley, John Bardeen and Walter Brattain. The introduction of the transistor is often considered one of the most important inventions in history.
A reference designator unambiguously identifies the location of an component within an electrical schematic or on a printed circuit board. The reference designator usually consists of one or two letters followed by a number, e.g. R13, C1002. The number is sometimes followed by a letter, indicating that components are grouped or matched with each other, e.g. R17A, R17B. IEEE 315 contains a list of Class Designation Letters to use for electrical and electronic assemblies. For example, the letter R is a reference prefix for the resistors of an assembly, C for capacitors, K for relays.

Random-access memory is a form of computer memory that can be read and changed in any order, typically used to store working data and machine code. A random-access memory device allows data items to be read or written in almost the same amount of time irrespective of the physical location of data inside the memory, in contrast with other direct-access data storage media, where the time required to read and write data items varies significantly depending on their physical locations on the recording medium, due to mechanical limitations such as media rotation speeds and arm movement.

The BC548 is a general-purpose NPN bipolar junction transistor commonly used in European and American electronic equipment. It is notably often the first type of bipolar transistor hobbyists encounter and is often featured in designs in hobby electronics magazines where a general-purpose transistor is required. The BC548 is low in cost and widely available.
References
- ↑ Renesas Electronics Corporation (June 2004). "Small Signal Transistor Type Designation" (PDF). Retrieved June 24, 2012.
- ↑ CliveTEC Electronic resources (September 9, 2004). "Transistor Data" . Retrieved June 24, 2012.