A seahorse is any of 46 species of small marine bony fish in the genus Hippocampus. "Hippocampus" comes from the Ancient Greek hippókampos (ἱππόκαμπος), itself from híppos (ἵππος) meaning "horse" and kámpos (κάμπος) meaning "sea monster" or "sea animal". Having a head and neck suggestive of a horse, seahorses also feature segmented bony armour, an upright posture and a curled prehensile tail. Along with the pipefishes and seadragons they form the family Syngnathidae.

The Syngnathidae is a family of fish which includes seahorses, pipefishes, and seadragons. The name is derived from Ancient Greek: σύν, meaning "together", and γνάθος, meaning "jaw". The fused jaw is one of the traits that the entire family have in common.

The big-belly seahorse or pot-bellied seahorse is one of the largest seahorse species in the world, with a length of up to 35 cm (14 in), and is the largest in Australia. Seahorses are members of the family Syngnathidae, and are teleost fishes. They are found in southeast Australia and New Zealand, and are listed on Appendix II of CITES.
The pygmy seahorses comprise several species of tiny seahorse in the syngnathid family or Syngnathidae. Family Syngnathidae is part of order Syngnathiformes, which contains fishes with fused jaws that suck food into tubular mouths. They are found in Southeast Asia in the Coral Triangle area. They are some of the smallest seahorse species in the world, typically measuring less than 2 centimetres (0.79 in) in height.

Hippocampus bargibanti, also known as Bargibant's seahorse or the pygmy seahorse, is a seahorse of the family Syngnathidae found in the central Indo-Pacific area.

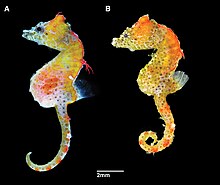
The knobby seahorse, also known as the short-headed seahorse or short-snouted seahorse, is a species of marine fish of the family Syngnathidae. It inhabits coastal waters in southwestern and southeastern Australia, from Gregory to Bremer Bay, and from Denial Bay to Newcastle.

The tiger tail seahorse is a species of fish in the family Syngnathidae. The species was first described by Theodore Cantor in 1850. It is found in India, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand and Vietnam. Its natural habitats are subtidal aquatic beds and coral reefs. It is threatened by habitat loss.

Hippocampus coronatus, commonly known as the high-crowned seahorse or crowned seahorse, is a species of fish of the family Syngnathidae. It is endemic to the Pacific coastal waters of Japan, where it lives among Zostera seagrasses. It can grow to lengths of 10.8 centimetres (4.3 in), but is more commonly 6 centimetres (2.4 in). Individuals feed mainly on small crustaceans such as gammarid amphipods and copepods, although this can vary by size, with smaller individuals consuming copepods while larger individuals feed on amphipods and mysids. This species is ovoviviparous, with males brooding eggs in a brood pouch before giving birth to live young. Breeding season occurs from June to November, with females and males reaching sexual maturity at 6.9 centimetres (2.7 in) and 7.3 centimetres (2.9 in) respectively. Male brood size ranges from 12–46. The International trade in this species has been monitored through Appendix II of the CITES licensing system since 2004 and a minimum size of 10 centimetres (3.9 in) applies to traded specimens.

Hippocampus denise, also known as Denise's pygmy seahorse or the yellow pygmy seahorse, is a seahorse of the family Syngnathidae native to the western Pacific.

The Japanese seahorse or lemur-tail seahorse is a species of fish in the family Syngnathidae. The Japanese seahorse reaches a maximum length of 8.0 cm, is usually dark brown and has a relatively long tail, a ridgelike coronet and flattened spines. Many seahorse species look similar, so in addition to any distinguishing features, individual specimens are identified using a series of specific measurements and counts of anatomical features such as spines and tail rings.

The short-snouted seahorse is a species of seahorse in the family Syngnathidae. It is endemic to the Mediterranean Sea and parts of the North Atlantic, particularly around Italy and the Canary Islands. In 2007, colonies of the species were discovered in the River Thames around London and Southend-on-Sea.

The spiny seahorse, also referred to as the thorny seahorse, is a small marine fish in the family Syngnathidae, native to the Indo-Pacific area. It is classified as a Vulnerable species by the IUCN.

The Hippocampinae are a subfamily of small marine fishes in the family Syngnathidae. Depending on the classification system used, it comprises either seahorses and pygmy pipehorses, or only seahorses.

Acentronura is a genus of pygmy pipehorse native to the Indian and Pacific oceans. The name is derived from the Greek ακεντρονουρα, or a-kentron-oura, and refers to the lack of a sting on the tail.

Hippocampus waleananus, the Walea pygmy seahorse, is a species of seahorse endemic to the Togian Islands in Indonesia, and is associated with specific soft corals. The species was described in 2009 from a single specimen which was found close to the island Walea. A 2016 classification considered it a synonym of Hippocampus satomiae, Lourie & Kuiter, 2008 due to lack of sufficient morphological differences, but following a reevaluation it is now recognised as a distinct species.

Hippocampus pontohi, also known as Pontoh's pygmy seahorse or the weedy pygmy seahorse, is a seahorse of the family Syngnathidae native to the central Indo-pacific. Named after Hentje Pontoh, the Indonesian dive guide from Bunaken (Manado) who first brought these pygmy seahorses to attention.
Hippocampus debelius, commonly known as the softcoral seahorse, is a species of marine fish of the family Syngnathidae. It is known from only two specimens collected from the Gulf of Suez in the Red Sea, at depths of 15–30 metres (49–98 ft). Individuals were found associated with soft corals. Although little is known of this species, it is expected to feed on crustaceans, similar to other seahorses. It is also expected to be ovoviviparous, with males carrying eggs in a brood pouch before giving birth to live young.

The paradoxical seahorse is a small seahorse in the genus Hippocampus. The only known specimen was captured in 1995 and remained unnoticed in a museum until 2006.

Hippocampus haema, the Korean seahorse, is a seahorse of the family Syngnathidae native to the northern Pacific Ocean, and it usually lives in Sargassum and weeds on shallow soft bottom habitats from 0 to 18 m depth. The Korean seahorse is the most common seahorse in Korean waters so that the scientific name 'haema' is named from 'seahorse' in Korean. The Japanese name 'Himetatsu' is derived from its smaller shape such as body and coronet rather than the shape of a sister species, crowned seahorse. This species had been repeatedly misidentified as crowned seahorse and Shiho's seahorse before a taxonomic review. However, the two genuine species do not live in Korean waters, therefore this species was handled by naming a new scientific name, Hippocampus haema. It can grow to lengths of 11 centimeters, but more commonly 6 to 8 centimeters as adult. Namely, the length of juvenile is 1 to 5 centimeters, whereas and the lengths of males and females reaching sexual maturity are considered as ca. 5 centimeters with or without male brood pouch. However, sex determination of this species is considered as ca. 2 centimeters from anatomic examination of gonad. This species has sexual dimorphism, the difference is male has a longer tail, while female has a longer trunk for same size. Breeding season of this species is from April to October or May to November, relating to warm water temperature. The number of fertilized egg or larvae inside the male brood pouch were 38.3±14.8 (20-76), and the number of fecundity identified from female were 47.2±8.6 (31-59). The female-to-male ratio was 1:1.7, indicating the dominance of males.

Hippocampus nalu, the Sodwana pygmy seahorse, African pygmy seahorse or Honeypot seahorse, is a South African species of pygmy seahorse in the family Syngnathidae.