Related Research Articles

The John F. Kennedy Space Center, located on Merritt Island, Florida, is one of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) ten field centers. Since 1968, KSC has been NASA's primary launch center of American spaceflight, research, and technology. Launch operations for the Apollo, Skylab and Space Shuttle programs were carried out from Kennedy Space Center Launch Complex 39 and managed by KSC. Located on the east coast of Florida, KSC is adjacent to Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS). The management of the two entities work very closely together, share resources, and operate facilities on each other's property.

Space Shuttle Endeavour is a retired orbiter from NASA's Space Shuttle program and the fifth and final operational Shuttle built. It embarked on its first mission, STS-49, in May 1992 and its 25th and final mission, STS-134, in May 2011. STS-134 was expected to be the final mission of the Space Shuttle program, but with the authorization of STS-135 by the United States Congress, Atlantis became the last shuttle to fly.

North American Aerospace Defense Command, known until March 1981 as the North American Air Defense Command, is a combined organization of the United States and Canada that provides aerospace warning, air sovereignty, and protection for Canada and the continental United States.

The Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center (JSC) is NASA's center for human spaceflight in Houston, Texas, where human spaceflight training, research, and flight control are conducted. It was renamed in honor of the late U.S. president and Texas native, Lyndon B. Johnson, by an act of the United States Senate on February 19, 1973.

The Canadian Space Agency is the national space agency of Canada, established in 1990 by the Canadian Space Agency Act.

The Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) is a major NASA space research laboratory located approximately 6.5 miles (10.5 km) northeast of Washington, D.C., in Greenbelt, Maryland, United States. Established on May 1, 1959, as NASA's first space flight center, GSFC employs about 10,000 civil servants and contractors. Named for American rocket propulsion pioneer Robert H. Goddard, it is one of ten major NASA field centers. GSFC is partially within the former Goddard census-designated place; it has a Greenbelt mailing address.

Canadarm or Canadarm1 is a series of robotic arms that were used on the Space Shuttle orbiters to deploy, manoeuvre, and capture payloads. After the Space Shuttle Columbia disaster, the Canadarm was always paired with the Orbiter Boom Sensor System (OBSS), which was used to inspect the exterior of the shuttle for damage to the thermal protection system.

A mission control center is a facility that manages space flights, usually from the point of launch until landing or the end of the mission. It is part of the ground segment of spacecraft operations. A staff of flight controllers and other support personnel monitor all aspects of the mission using telemetry, and send commands to the vehicle using ground stations. Personnel supporting the mission from an MCC can include representatives of the attitude control system, power, propulsion, thermal, attitude dynamics, orbital operations and other subsystem disciplines. The training for these missions usually falls under the responsibility of the flight controllers, typically including extensive rehearsals in the MCC.
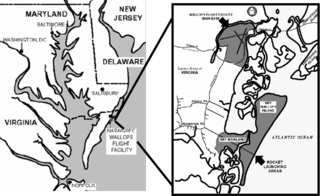
Wallops Flight Facility (WFF) is a rocket launch site on Wallops Island on the Eastern Shore of Virginia, United States, just east of the Delmarva Peninsula and approximately 100 miles (160 km) north-northeast of Norfolk. The facility is operated by the Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, and primarily serves to support science and exploration missions for NASA and other federal agencies. WFF includes an extensively instrumented range to support launches of more than a dozen types of sounding rockets; small expendable suborbital and orbital rockets; high-altitude balloon flights carrying scientific instruments for atmospheric and astronomical research; and, using its Research Airport, flight tests of aeronautical research aircraft, including unmanned aerial vehicles.

Fort McPherson was a U.S. Army military base located in Atlanta, Georgia, bordering the northern edge of the city of East Point, Georgia. It was the headquarters for the U.S. Army Installation Management Command, Southeast Region; the U.S. Army Forces Command; the U.S. Army Reserve Command; the U.S. Army Central. Situated on 487 acres (1.97 km2) and located four miles (6 km) southwest of the center of Atlanta, Fort McPherson has history as an army post dating back to 1867.
Spacecraft call signs are radio call signs used for communication in crewed spaceflight. These are not formalized or regulated to the same degree as other equivalent forms of transportation, like aircraft. The three nations currently launching crewed space missions use different methods to identify the ground and space radio stations; the United States uses either the names given to the space vehicles or else the project name and mission number. Russia traditionally assigns code names as call signs to individual cosmonauts, more in the manner of aviator call signs, rather than to the spacecraft.

Buckley Space Force Base is a United States Space Force base in Aurora, Colorado named after United States Army Air Service First Lieutenant John Harold Buckley. The base is run by Space Base Delta 2, with major units including the U.S. Space Force's Space Delta 4, the Colorado Air National Guard's 140th Wing, the Denver Naval Operations Support Center, and the National Reconnaissance Office's Aerospace Data Facility-Colorado.

A control room or operations room is a central space where a large physical facility or physically dispersed service can be monitored and controlled. It is often part of a larger command center.

A command center is any place that is used to provide centralized command for some purpose.

Flight controllers are personnel who aid space flight by working in such Mission Control Centers as NASA's Mission Control Center or ESA's European Space Operations Centre. Flight controllers work at computer consoles and use telemetry to monitor various technical aspects of a space mission in real-time. Each controller is an expert in a specific area and constantly communicates with additional experts in the "back room". The flight director, who leads the flight controllers, monitors the activities of a team of flight controllers, and has overall responsibility for success and safety.

Located at Kirtland Air Force Base, New Mexico, the Air Force Operational Test and Evaluation Center is a direct reporting unit of Headquarters, United States Air Force. It is the Air Force independent test agency responsible for testing, under operationally realistic conditions, new systems being developed for Air Force and multi-service use.

The Columbus Control Centre also known by its radio callsign, Mission Control Munich, is the mission control centre which is used to control the Columbus research laboratory, which is part of the International Space Station (ISS). The control centre is located at the German Aerospace Center (DLR) facility in Oberpfaffenhofen near Munich, Germany. The centre is operated by the DLR, under contract from the European Space Agency (ESA).

NASA's Christopher C. Kraft Jr. Mission Control Center, also known by its radio callsign, Houston, is the facility at the Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas, that manages flight control for the United States human space program, currently involving astronauts aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The center is in Building 30 at the Johnson Space Center and is named after Christopher C. Kraft Jr., a NASA engineer and manager who was instrumental in establishing the agency's Mission Control operation, and was the first Flight Director.

Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) is NASA's first, and oldest, space center. It is named after Robert H. Goddard, the father of modern rocketry. Throughout its history, the center has managed, developed, and operated many notable missions, including the Cosmic Background Explorer, the Hubble Space Telescope, the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System (TDRSS), the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, and the Solar Dynamics Observatory.
There are NASA facilities across the United States and around the world. NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC provides overall guidance and political leadership to the agency. There are 10 NASA field centers, which provide leadership for and execution of NASA's work. All other facilities fall under the leadership of at least one of these field centers. Some facilities serve more than one application for historic or administrative reasons. NASA has used or supported various observatories and telescopes, and an example of this is the NASA Infrared Telescope Facility. In 2013 a NASA Office of the Inspector General's (OIG) Report recommended a Base Realignment and Closure Commission (BRAC) style organization to consolidate NASA's little used facilities. The OIG determined at least 33 of NASA's 155 facilities were underutilized.
References
- ↑ John H. Chapman Space Center. Treasury Board of Canada Secretariat. Retrieved on April 2016.
- ↑ John Herbert Chapman - Builder of the Canadian space program. Science Canada. Retrieved on April 15, 2016.