
Plasmodium is a genus of unicellular eukaryotes that are obligate parasites of vertebrates and insects. The life cycles of Plasmodium species involve development in a blood-feeding insect host which then injects parasites into a vertebrate host during a blood meal. Parasites grow within a vertebrate body tissue before entering the bloodstream to infect red blood cells. The ensuing destruction of host red blood cells can result in malaria. During this infection, some parasites are picked up by a blood-feeding insect, continuing the life cycle.

Balantidium is a genus of ciliates. It contains the parasitic species Balantidium coli, the only known cause of balantidiasis.
Isospora is a genus of internal parasites in the subclass Coccidia.

Gongylonema is a genus of thread-like nematode that was described by Molin in 1857. It is the only currently valid genus in the family Gongylonematidae, though the mysterious Spiruroides – usually placed in the Subuluridae, which are not closely related to Gongylonema among the Spiruria – might actually belong here. They are parasites of birds and mammals, transmitted by insects. Some 38 species are known, about 12 of which have been recorded in Europe.

Mesostigmata is an order of mites belonging to the Parasitiformes. They are by far the largest group of Parasitiformes, with over 8,000 species in 130 families. Mesostigmata includes parasitic as well as free-living and predatory forms. They can be recognized by the single pair of spiracles positioned laterally on the body.

Rouget's rail is a species of bird in the family Rallidae. It is the only member of the genus Rougetius. It is found in Eritrea and Ethiopia.

Adeleorina is a suborder of parasites in the phylum Apicomplexa.

Leucostele chiloensis is a species of cactus native to South America; genus members are known as hedgehog cacti, sea-urchin cactus or Easter lily cactus.
Defretinella is a genus of parasitic alveolates of the phylum Apicomplexa.
Pseudoklossia is a genus in the phylum Apicomplexa. Species in this genus infect marine molluscs, although one species infects in an ascidian worm. The life cycle is heteroxenous.

Opecoelidae is a family of trematodes. It is the largest digenean family with over 90 genera and nearly 900 species, almost solely found in marine and freshwater teleost fishes. It was considered by Bray et al. to belong in the superfamily Opecoeloidea Ozaki, 1925 or the Brachycladioidea Odhner, 1905.
Schizocystidae is a genus of parasitic alveolates in the phylum Apicomplexa.
Lipotropha is a genus of parasitic alveolates of the phylum Apicomplexa.
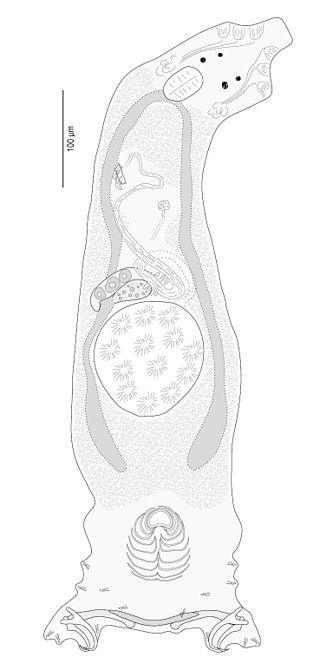
Lamellodiscus is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans in the family Diplectanidae; all species of Lamellodiscus are small worms, parasitic on the gills of teleost fish.

Camallanus is a genus of parasitic roundworms in the family Camallanidae.

Cystidicolidae is a family of spirurian nematodes. It was described by Skrjabin in 1946. All members of the family are parasites of fish.

Ascarophis is a genus of parasitic nematodes, belonging to the family Cystidicolidae. Species of Ascarophis are parasitic as adults in the gastrointestinal tract of marine and estuarine fishes.
Rhabdochonidae is a family of nematodes belonging to the order Rhabditida.
Spinitectus is a genus of nematodes belonging to the family Cystidicolidae.

Procamallanus is a genus of nematodes belonging to the family Camallanidae.











