
Justo José de Urquiza y García was an Argentine general and politician who served as president of the Argentine Confederation from 1854 to 1860.

The Argentine Confederation was the last predecessor state of modern Argentina; its name is still one of the official names of the country according to the Argentine Constitution, Article 35. It was the name of the country from 1831 to 1852, when the provinces were organized as a confederation without a head of state. The governor of Buenos Aires Province managed foreign relations during this time. Under his rule, the Argentine Confederation engaged in conflicts with Brazil, Bolivia, Uruguay, France and the United Kingdom, as well as other Argentine factions during the Argentine Civil Wars.

Belgrano is a northern and leafy barrio or neighborhood of Buenos Aires, Argentina.

The Buenos Aires Underground, locally known as Subte, is a rapid transit system that serves the area of the city of Buenos Aires, Argentina. The first section of this network opened in 1913, making it the 13th earliest subway network in the world and the first underground railway in Latin America, the Southern Hemisphere, and the Spanish-speaking world, with the Madrid Metro opening nearly six years later, in 1919. As of 2023, Buenos Aires is the only Argentine city with a metro system.

Palermo is a barrio or neighborhood of Buenos Aires, Argentina. It is located in the north of the city, near the Río de la Plata.

Line A is the oldest line of the Buenos Aires Underground. Opened to the public on 1 December 1913, it was the first underground line in South America, the Southern Hemisphere and the Spanish-speaking world. It made Buenos Aires the 13th city in the world to have an underground transport service. The line stretches 9.8 km (6.1 mi) from Plaza de Mayo and San Pedrito and runs under the full length of the Avenida de Mayo and part of the Avenida Rivadavia, and is used by 258,000 people per day.

Line B of the Buenos Aires Underground runs 11.75 kilometres (7.30 mi) from Leandro N. Alem to Juan Manuel de Rosas in Villa Urquiza. Line B opened to the public on 17 October 1930.

Line C of the Buenos Aires Underground, that runs from Retiro to Constitución terminus, opened on 9 November 1934, and it has a length of 4.3 km (2.7 mi). It runs under Lima Sur, Bernardo de Irigoyen, Carlos Pellegrini, Esmeralda, la Plaza San Martín and Avenida Ramos Mejia streets. It not only connects to every other line on the system, but its termini at Retiro and Constitución also connect it to some of the most important commuter rail networks in Buenos Aires, such as the Mitre and Roca lines and also long-distance passenger services. It is thus an important artery in Buenos Aires' transport system. At the same time, it is also the shortest line in both terms of length and number of stations.

Line E of the Buenos Aires Underground runs from Retiro to Plaza de los Virreyes, a total distance of 12 km. Opened in 1944, the Line E was the last completely new line to be added to the Buenos Aires Underground, until 2007 when Line H was opened. The line has a history of being re-routed and extended due to having been historically the line with the lowest passenger numbers on the network.

Federico Lacroze railway station is a passenger railway station in Buenos Aires, Argentina. The station is located in the city's outlying barrio (neighbourhood) of Chacarita in a predominantly residential area. It is just a short distance north of the Cementerio de la Chacarita, the city's largest cemetery. The station is named after Federico Lacroze, a prominent 19th century Argentine railway and transport pioneer who obtained the concession for building the Buenos Aires Central Railway in 1884. When the Argentine railway network was nationalised in 1948 the station became the Buenos Aires terminus for the lines that became part of the General Urquiza Railway (FCGU).

Metrovías S.A. is an Argentine privately held company that operates the Metropolitan services of the Urquiza Line. 90% of Metrovías' shares are held by Grupo Roggio. Metrovías was also operator of the Buenos Aires Underground from 1995 to December 2021, when "Emova Movilidad S.A." took over the concession of the service for 12 years. Emova is also part of the Roggio Group and also associated with Metrovías.

The Belgrano Norte line is a commuter rail service in Buenos Aires, Argentina run by the private company Ferrovías since 1 April 1994. This service had previously been run by the state-owned General Belgrano Railway since nationalisation of the railways in 1948. Ferrovías also formed part of the consortium Unidad de Gestión Operativa Ferroviaria de Emergencia (UGOFE) which operated other commuter rail services in Buenos Aires.
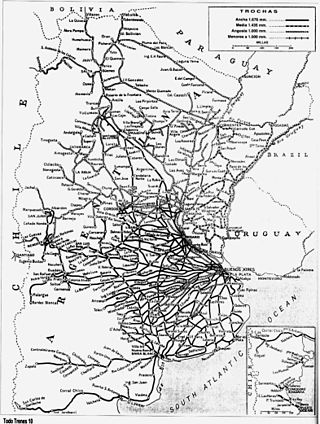
The Argentine railway network consisted of a 47,000 km (29,204 mi) network at the end of the Second World War and was, in its time, one of the most extensive and prosperous in the world. However, with the increase in highway construction, there followed a sharp decline in railway profitability, leading to the break-up in 1993 of Ferrocarriles Argentinos (FA), the state railroad corporation. During the period following privatisation, private and provincial railway companies were created and resurrected some of the major passenger routes that FA once operated.

Federico Lacroze is an underground station on Line B of the Buenos Aires Underground named after the Argentine railway entrepreneur, located at the intersection of Corrientes and Federico Lacroze avenues in the Chacarita neighbourhood and near the La Chacarita Cemetery. The station was opened on 17 October 1930 as the western terminus of the extension of the line from Federico Lacroze to Callao.

Los Incas - Parque Chas is a station on Line B of the Buenos Aires Underground. The station was opened on 9 August 2003 as the western terminus of the extension of the line from Federico Lacroze. It remained the terminus of the line until the opening of Juan Manuel de Rosas station on 26 July 2013.

Dorrego is a station on Line B of the Buenos Aires Underground. The station was opened on 17 October 1930 as part of the inaugural section of the line between Federico Lacroze and Callao.

Scalabrini Ortiz Station is a station on Line D of the Buenos Aires Underground. The station was opened on 23 February 1940 as part of the extension of Line D from Tribunales to Palermo.

General Urquiza is a station on Line E of the Buenos Aires Underground. The station was opened on 20 June 1944 as the eastern terminus of the inaugural section of the line from San José to General Urquiza. On 16 December 1944 the line was extended to Boedo.

The Regional Express Network was a planned commuter network system in Buenos Aires, which consisted in an underground connection among the 3 mainline railway stations of the city: Retiro, Constitucion and Once, in the north, south and west respectively.
The Revolution of 11 September 1852 was a conflict between the Province of Buenos Aires and the government of Justo José de Urquiza after the latter triumphed over Juan Manuel de Rosas at the Battle of Caseros.


















