
The Aders's duiker, also known as nunga in Swahili, kunga marara in Kipokomo and harake in Giriama, is a small, forest-dwelling duiker found only in Zanzibar and Kenya. It may be a subspecies of the red, Harvey's, or Peters's duiker or a hybrid of a combination of these. It is named after W. Mansfield Aders, a zoologist with the Zanzibar Government Service.

The Coastal forests of eastern Africa, also known as the East African Coastal Forests, is a tropical moist forest region along the east coast of Africa. The region was designated a biodiversity hotspot by Conservation International.

The Eastern Arc Mountains is a chain of mountains found in Kenya and Tanzania. The chain runs from northeast to southwest, with the Taita Hills being in Kenya and the other ranges being in Tanzania. They are delimited on the southwest by the fault complex represented by the Makambako Gap that separates them from the Kipengere Range. To the northeast, they are delimited by more recent volcanism represented by Mount Kilimanjaro. The chain is considered a Tentative World Heritage Site.

Hildegarde's tomb bat is a species of sac-winged bat in the family Emballonuridae. It is found near the coast in Kenya and Tanzania where it feeds in tropical dry forests and roosts in caves. It is a diurnal species and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has assessed its conservation status as "endangered". The specific name hildegardeae was given in honour of anthropologist Hildegarde Beatrice Hinde.
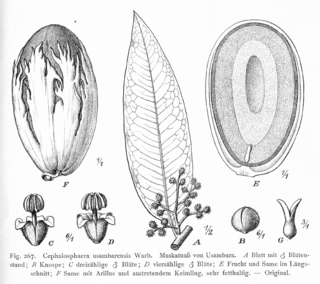
Cephalosphaera is a monotypic genus of flowering plants in the nutmeg family, Myristicaceae. The only species is Cephalosphaera usambarensis, a tree native to the moist evergreen forests of Kenya and Tanzania.
Kraussia speciosa is a species of plant in the family Rubiaceae. It is found in coastal Kenya and Tanzania, where it is associated with the Zanzibar-Inhambane regional mosaic.
The Boni National Reserve is a national reserve for conservation and lies in the Garissa County, Kenya. The reserve covers an area of 1,339 km2 (517 sq mi) and is managed by Kenya Wildlife Service. It was gazetted in 1976 as a dry season sanctuary for elephants in the former Kenyan Ijara, and Lamu districts and Somalia. The elephant population has been greatly reduced by poaching.

The Jozani Chwaka Bay National Park is a 50 km2 (19 sq mi) national park in Tanzania located on the island of Zanzibar. It is the only national park in Zanzibar.

The Southern Zanzibar–Inhambane coastal forest mosaic, also known as the Southern Swahili coastal forests and woodlands, is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion of eastern Africa. It is a southern variation of Northern Zanzibar-Inhambane coastal forest mosaic. The ecoregion supports habitats of forest, savanna and swamps. The southern portion of the ecoregion is not as well studied due to the 1977-1992 civil war in Mozambique.
Michelsonia is a genus of tree in the legume family, Fabaceae, where it is classified in the subfamily Detarioideae. It is a monotypic genus, the only species being Michelsonia microphylla. It is native to the tropical rain forests of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The wood is used locally for construction work.

Nuxia floribunda, the forest elder, forest nuxia or wild elder, is a species of tree in the Stilbaceae family, that is native to moist regions of southern Africa, East Africa and central tropical Africa.

The wildlife of Zanzibar consists of terrestrial and marine flora and fauna in the archipelago of Zanzibar, an autonomous region of Tanzania. Its floral vegetation is categorized among the coastal forests of eastern Africa as the Southern Zanzibar-Inhambane coastal forest mosaic and the Northern Zanzibar-Inhambane coastal forest mosaic. Its faunal species are mostly small animals, birds, and butterflies.

Northern Zanzibar–Inhambane coastal forest mosaic, also known as the Northern Swahili coastal forests and woodlands, is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion of coastal East Africa. The ecoregion includes a variety of habitats, including forest, savanna and swamps.

Vachellia robusta, the splendid thorn, is an Afrotropical tree species.

The Eastern Arc forests is a montane tropical moist forest ecoregion of eastern Africa. The ecoregion comprises several separate highland areas above 800 meters in Kenya, and (mostly) Tanzania.

The eastern tree hyrax is a species of mammal within the family Procaviidae. The eastern tree hyrax is the most localized of the tree hyrax species, distributed patchily in a narrow band of lowland and montane forests in Kenya and Tanzania and adjacent islands.
The Mueda Plateau, also known as the Maconde Plateau, is a plateau in Cabo Delgado Province of northeastern Mozambique.

The Northern Acacia–Commiphora bushlands and thickets are a tropical grasslands, savannas and shrublands ecoregion in eastern Africa. The ecoregion is mostly located in Kenya, extending north into southeastern South Sudan, northeastern Uganda and southwestern Ethiopia and south into Tanzania along the Kenya-Tanzania border.

The Southern miombo woodlands is a tropical grasslands and woodlands ecoregion extending across portions of Malawi, Mozambique, Zambia, and Zimbabwe.















