Related Research Articles

Unaysaurus is a genus of unaysaurid sauropodomorph herbivore dinosaur. Discovered in southern Brazil, in the geopark of Paleorrota, in 1998, and announced in a press conference on Thursday, December 3, 2004, it is one of the oldest dinosaurs known. It is closely related to plateosaurid dinosaurs found in Germany, which indicates that it was relatively easy for species to spread across the giant landmass of the time, the supercontinent of Pangaea.

Guaibasaurus is an extinct genus of basal saurischian dinosaur known from the Late Triassic Caturrita Formation of Rio Grande do Sul, southern Brazil. Most analyses recover it as a sauropodomorph, although there are some suggestions that it was a theropod instead. In 2016 Gregory S. Paul estimated it at 2 meters and 10 kg, whereas in 2020 Molina-Pérez and Larramendi listed it at 3 meters and 35 kg.

Prestosuchus is an extinct genus of pseudosuchian in the group Loricata, which also includes Saurosuchus and Postosuchus. It has historically been referred to as a "rauisuchian", and was the defining member of the family Prestosuchidae, though the validity of both of these groups is questionable: Rauisuchia is now considered paraphyletic and Prestosuchidae is polyphyletic in its widest form.
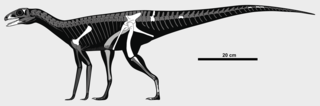
Sacisaurus is a silesaurid dinosauriform from the Late Triassic (Norian) Caturrita Formation of southern Brazil. The scientific name, Sacisaurus agudoensis, refers to the city where the species was found, Agudo in the Rio Grande do Sul state, whereas Sacisaurus refers to Saci, a famous one-legged creature from Brazilian mythology, because among the dozens of fossil material unearthed, 35 right femora were collected whereas only 1 left femur was found.

Procolophon is a genus of lizard-like procolophonid parareptiles that first appeared in the Early Triassic (Induan) of South Africa, Brazil, and Antarctica. It persisted through the Permian–Triassic extinction event, but went extinct in the beginning of the Early Middle Triassic. The type species is P. trigoniceps.

Stahleckeria is an extinct genus of Middle Triassic (Ladinian) dicynodonts. It lived about 240 million years ago in what is now Brazil and Namibia. As a member of the group Kannemeyeriiformes, it was similar to the genus Kannemeyeria. The genus is known from the type species Stahleckeria potens, which was first collected from the Ladinian-age Santa Maria Formation in the Paleorrota fossil site of Brazil. Stahleckeria was named in honor of Rudolf Stahlecker, who discovered the first specimens during a 1935 expedition led by paleontologist Friedrich von Huene to the Chiniquá fossil site.

Prionosuchus is an extinct genus of large temnospondyl. A single species, P. plummeri, is recognized from the Early Permian. Its fossils have been found in what is now northeastern Brazil.

The Caturrita Formation is a rock formation found in Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. Its sediments were deposited in the Paraná Basin. The formation is from the Upper Triassic and forms part of the Santa Maria Supersequence in the upper section of the Rosário do Sul Group.

São Gabriel is a municipality in the state of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil.
Hoplitosuchus is an extinct genus of aetosaur. Fossils have been found from the Santa Maria Formation in Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil that date back to the Late Triassic. At first the genus was named Hoplitosaurus, but this name had previously been assigned to a polacanthine ankylosaurian dinosaur in 1902, thirty-six years before it had been referred to the aetosaur. Thus Hoplitosuchus was constructed as a replacement name for Hoplitosaurus. Because the holotype specimen consists of unidentifiable osteoderms and any other material attributed to the genus may actually be considered a composite of rauisuchian and dinosaurian remains, Hoplitosuchus is now considered to be a nomen dubium. The saurischian dinosaur Teyuwasu was named in 1999 on the basis of material originally attributed to Hoplitosuchus.
Teyumbaita is an extinct genus of hyperodapedontine rhynchosaur from the Upper Triassic epoch of Paleorrota, Rio Grande do Sul, southern Brazil. Its fossils, two nearly complete skulls and a partial skull were discovered in the lower part of the Caturrita Formation and was first assigned to a species of Scaphonyx, Scaphonyx sulcognathus. This species was reassigned to its own genus by Felipe Chinaglia Montefeltro, Max Cardoso Langer and Cesar Leandro Schultz in 2010 and the combinatio nova is Teyumbaita sulcognathus. Fossil material of a second, yet-unnamed species, is known from the Hoyada del Cerro Las Lajas site of the Ischigualasto Formation (Argentina).

Agathoxylon is a form genus of araucarian fossil wood, including massive tree trunks. Although identified from the late Palaeozoic to the end of the Mesozoic, Agathoxylon is common from the Carboniferous to Triassic.

Sommerxylon is a genus described from petrified trunks of Gymnosperms that lived in the Triassic, found in the Caturrita Formation on Linha São Luiz in the municipality of Faxinal do Soturno in the region of Paleorrota. It is named in honor of Dr. Margot Guerra Sommer.

Ginkgoites is a genus that refers to extinct plants belonging to Ginkgoaceae. Fossils of these plants have been found around the globe during the Triassic, Jurassic, Cretaceous, and Paleocene-age Porcupine Hills Formation in Alberta. The name was created as a form genus in 1919 by Albert Seward who stated: "I ... propose to employ the name Ginkgoites for leaves that it is believed belong either to plants generically identical with Ginkgo or to very closely allied types".
Baieroxylon is an extinct prehistoric genus of plants belonging to the Ginkgoaceae family during the Triassic, Jurassic, and Cretaceous Periods.

Brachyphyllum is a form genus of fossil coniferous plant foliage. Plants of the genus have been variously assigned to several different conifer groups including Araucariaceae and Cheirolepidiaceae. They are known from around the globe from the Late Carboniferous to the Late Cretaceous periods.

Pholadomya is a genus of saltwater clams, marine bivalve molluscs in the family Pholadomyidae.

Teyujagua is an extinct genus of small, probably semi-aquatic archosauromorph reptile that lived in Brazil during the Early Triassic period. The genus contains the type and only known species, T. paradoxa. It is known from a well-preserved skull, and probably resembled a crocodile in appearance. It was an intermediary between the primitive archosauromorphs and the more advanced Archosauriformes, revealing the mosaic evolution of how the key features of the archosauriform skull were acquired. Teyujagua also provides additional support for a two-phase model of archosauriform radiation, with an initial diversification in the Permian followed by a second adaptive radiation in the Early Triassic.
Ixalerpeton is a genus of lagerpetid avemetatarsalian containing one species, I. polesinensis. It lived in the Late Triassic of Brazil alongside the sauropodomorph dinosaur Buriolestes.

Aleodon is an extinct genus of cynodonts that lived from the Middle to the Late Triassic. Relatively few analyses have been conducted to identify the phylogenetic placement of Aleodon, however those that have place Aleodon as a sister taxon to Chiniquodon. Two species of Aleodon are recognized: A. brachyramphus which was discovered in Tanzania, and A. cromptoni which was discovered most recently in Brazil.
References
- Kaokoxylon zalesskyi (Sahni) Maheshwari en los niveles superiores de la Secuencia Santa Maria
- O complexo Dadoxylon-Araucarioxylon, Carbonífero e Permiano
- Sommerxylon spiralosus from Upper Triassic in southernmost Paraná Basin (Brazil)
- Técnica de coleta e estabilização de fósseis em pelitos laminados, aplicação em níveis com plantas do Triássico Superior