
Fresco is a technique of mural painting executed upon freshly laid ("wet") lime plaster. Water is used as the vehicle for the dry-powder pigment to merge with the plaster, and with the setting of the plaster, the painting becomes an integral part of the wall. The word fresco is derived from the Italian adjective fresco meaning "fresh", and may thus be contrasted with fresco-secco or secco mural painting techniques, which are applied to dried plaster, to supplement painting in fresco. The fresco technique has been employed since antiquity and is closely associated with Italian Renaissance painting.

A mural is any piece of graphic artwork that is painted or applied directly to a wall, ceiling or other permanent substrate. Mural techniques include fresco, mosaic, graffiti and marouflage.

Tempera, also known as egg tempera, is a permanent, fast-drying painting medium consisting of pigments mixed with a water-soluble binder medium, usually glutinous material such as egg yolk. Tempera also refers to the paintings done in this medium. Tempera paintings are very long-lasting, and examples from the first century AD still exist. Egg tempera was a primary method of painting until after 1500 when it was superseded by oil painting. A paint consisting of pigment and binder commonly used in the United States as poster paint is also often referred to as "tempera paint", although the binders in this paint are different from traditional tempera paint.

Yellow is the color between green and orange on the spectrum of light. It is evoked by light with a dominant wavelength of roughly 575–585 nm. It is a primary color in subtractive color systems, used in painting or color printing. In the RGB color model, used to create colors on television and computer screens, yellow is a secondary color made by combining red and green at equal intensity. Carotenoids give the characteristic yellow color to autumn leaves, corn, canaries, daffodils, and lemons, as well as egg yolks, buttercups, and bananas. They absorb light energy and protect plants from photo damage in some cases. Sunlight has a slight yellowish hue when the Sun is near the horizon, due to atmospheric scattering of shorter wavelengths.

Ultramarine is a deep blue color pigment which was originally made by grinding lapis lazuli into a powder. Its lengthy grinding and washing process makes the natural pigment quite valuable—roughly ten times more expensive than the stone it comes from and as expensive as gold.

A set of primary colors or primary colours consists of colorants or colored lights that can be mixed in varying amounts to produce a gamut of colors. This is the essential method used to create the perception of a broad range of colors in, e.g., electronic displays, color printing, and paintings. Perceptions associated with a given combination of primary colors can be predicted by an appropriate mixing model that reflects the physics of how light interacts with physical media, and ultimately the retina. The most common color mixing models are the additive primary colors and the subtractive primary colors. Red, yellow and blue are also commonly taught as primary colours, despite some criticism due to its lack of scientific basis.

Oil paint is a type of slow-drying paint that consists of particles of pigment suspended in a drying oil, commonly linseed oil. For several centuries the oil painting has been perhaps the most prestigious form in Western art, but oil paint has many practical uses, mainly because it is waterproof.
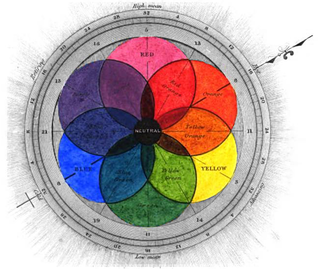
RYB is a subtractive color model used in art and applied design in which red, yellow, and blue pigments are considered primary colors. Under traditional color theory, this set of primary colors was advocated by Moses Harris, Michel Eugène Chevreul, Johannes Itten and Josef Albers, and applied by countless artists and designers. The RYB color model underpinned the color curriculum of the Bauhaus, Ulm School of Design and numerous art and design schools that were influenced by the Bauhaus, including the IIT Institute of Design, Black Mountain College, Design Department Yale University, the Shillito Design School, Sydney, and Parsons School of Design, New York.

Fresco-secco is a wall painting technique where pigments mixed with an organic binder and/or lime are applied onto dry plaster. The paints used can e.g. be casein paint, tempera, oil paint, silicate mineral paint. If the pigments are mixed with lime water or lime milk and applied to a dry plaster the technique is called lime secco painting. The secco technique contrasts with the fresco technique, where the painting is executed on a layer of wet plaster.

Sittanavasal Cave is a 2nd-century Tamil Śramaṇa complex of caves in Sittanavasal village in Pudukottai district of Tamil Nadu, India. Its name is a distorted form of Sit-tan-na-va-yil, a Tamil word which means "the abode of great saints".

Mysore painting is an important form of classical South Indian painting style that originated in and around the town of Mysore in Karnataka. The painting style was encouraged and nurtured by the Mysore rulers. Painting in Karnataka has a long and illustrious history, tracing its origins back to the Ajanta Caves period. The distinct school of Mysore painting evolved from the paintings during the Vijayanagara Empire period, the rulers of Vijayanagara and their feudatories encouraged literature, art and architecture as well as religious and philosophical discussions. With the fall of the Vijayanagara Empire after the 1565 Battle of Talikota, the artists who were until then under royal patronage migrated to various places such as Mysore, Tanjore and Surpur among others. Absorbing the local artistic traditions and customs, the erstwhile Vijayanagara school of painting gradually evolved into the many styles of painting in South India, including the Mysore and Tanjore schools of painting.

Dancheong refers to Korean decorative colouring on wooden buildings and artifacts for the purpose of style. It is an adaptation of the Chinese practice danqing. It literally means "cinnabar and blue-green", and is sometimes translated as "red and blue" in English. Along with its decorations and the choice of paint colours, Dancheong carries various symbolic meanings. It is based on five basic colours; blue (east), white (west), red (south), black (north), and yellow (center). The use of those five colours reflected the use of the yin and yang principle and the philosophy of the five elements.

The St. Antony's Syro-Malabar Catholic Forane Church is located at Ollur, Thrissur city in Kerala, India. The church belongs to Syro-Malabar Catholic Archdiocese of Thrissur. According to rough figures there are around 4,000 Christian families in the parish. Because of the huge presence of Christian people in Ollur, with its religious, educational, medical, social-service, and secular organisations and institution, Ollur has been called as Chinna Roma. The church is constructed on a hill-top which is the highest location in the area. The church is surrounded by a huge protective compound wall called Elephant Wall. When Thrissur Vicariate Apostolic was erected in 1887, Ollur was the richest, most populous, and influential parish, so much that the Vicar of the Ollur parish were included in Adolph Medlycott's four-member diocesan apex council. St. Anthony's Forane Church has 18 churches under its jurisdiction.

Patachitra or Pattachitra is a general term for traditional, cloth-based scroll painting, based in the eastern Indian states of Odisha, West Bengal and parts of Bangladesh. Patachitra artform is known for its intricate details as well as mythological narratives and folktales inscribed in it. Pattachitra is one of the ancient artworks of Odisha, originally created for ritual use and as souvenirs for pilgrims to Puri, as well as other temples in Odisha. Patachitras are a component of an ancient Bengali narrative art, originally serving as a visual device during the performance of a song.

The Krishnapuram Palace is a palace and museum located in Kayamkulam near Alappuzha in Alappuzha district, Kerala in southwestern India. It was built in the 18th century by Anizham Thirunal Marthanda Varma, the Travancore kingdom. It is built in the architectural style of Kerala with gabled roof, narrow corridor and dormer windows, near the Krishnaswamy Temple at Krishnapuram.

Kerala architecture is a style of architecture found in the Indian state of Kerala, and in parts of the Tulu Nadu region of Karnataka. Kerala's architectural style includes a unique Hindu temple architecture that emerged in southwestern India, and varies slightly from the Dravidian architecture observed in other parts of southern India. The architecture of Kerala is derived from the Indian Vedic architectural tradition and forms a part of Dravidian architecture, one of the three styles of temple mentioned in the ancient books on Vastu Shastra. The Tantrasamuchaya, Thachu-Shastra, Manushyalaya Chandrika, and Silparatna are all architectural treatises that have had an impact on the architecture of Kerala. The Manushyalaya Chandrika, a work devoted to domestic architecture, has its roots in Kerala.

The region of Shekhawati in Rajasthan is remarkable for its wealth of mural paintings which adorn the walls of many buildings, including havelis.

Kaavi art is a form of murals found in Konkan region especially in temples of Goa, parts of coastal Maharashtra and Karnataka. Kaavi murals can also be seen in old houses, small shrines.

K. Syamalakumari aka Syamala Kumari is an Indian temple painter. This was an occupation traditionally carried out by men. Her work includes painting at the Sri Padmanabhaswamy Temple in Kerala. She has been awarded the Nari Shakti Puraskar.

Chitra or citra is an Indian genre of art that includes painting, sketch and any art form of delineation. The earliest mention of the term Chitra in the context of painting or picture is found in some of the ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism and Pali texts of Buddhism.






















