
Ansar al-Islam in Kurdistan, simply called Ansar al-Islam, is a Kurdish Islamist militant and separatist group. It was established in northern Iraq around the Kurdistan Region by Kurdish Islamists who were former Taliban and former Al-Qaeda volunteers, which were coming back from Afghanistan in 2001 after the Fall of Kabul. It was formed with the motive of establishing an Islamic state around the Kurdistan region and protecting Kurds from other armed insurgent groups during the Iraqi insurgency. It imposed strict Sharia in villages it controlled around Byara near the Iranian border.

The Peshmerga are the armed forces of Iraqi Kurdistan, an autonomous region in northern Iraq. According to the Constitution of Iraq, regional governments are responsible for "the establishment and organization of the internal security forces for the region such as police, security forces, and guards of the region". Other Kurdish defence and security agencies include the Zêrevanî (gendarmerie), Asayish, and the Parastin û Zanyarî. The Peshmerga's history dates back to the 18th century, when they began as a tribal paramilitary border guard under the Ottoman Turks and the Safavid Iranians. By the 19th century, they had evolved into a disciplined and well-trained guerrilla force.

Najmadin Faraj Ahmad, better known as Mullah Krekar, is a Kurdish Sunni Islamic scholar who was the founder and former leader of Ansar al-Islam. He is currently serving a prison sentence in Italy, after having been extradited from Norway in 2020. He came to Norway as a refugee from Iraqi Kurdistan in 1991. His wife, Rukhosh Ahmad, and his four children have Norwegian citizenship, but not Krekar himself. He speaks Kurdish, Arabic, Persian, Norwegian and English.

The Kurdistan Islamic Movement is a Kurdish Islamist party founded in 1987 by mufti Osman Abdulaziz and several other Kurdish Islamic scholars who were all part of the non-political "Union of Religious Scholars" group. The party's main support comes from in and around the town of Halabja.

The Kurdistan Free Life Party, or PJAK, is a Kurdish leftist anti-Islamic Republic of Iran armed militant group. It has waged an intermittent armed struggle since 2004 against the Iranian Government, seeking self-determination through some degree of autonomy for Kurds in Iran.

Ali Bapir, also known as Mamosta Ali Bapir, is a Kurdish Islamic scholar and politician in Iraqi Kurdistan. He is the founder and current president of the Kurdistan Justice Group. He was born in 1961 in the Pshdar district, Iraqi Kurdistan. He has written over 150 books on politics, Islam, society, Kurds, and Kurdistan. He is the most popular politician with the Kurdish Islamism ideology.

The Iraqi–Kurdish conflict consists of a series of wars, rebellions and disputes between the Kurds and the central authority of Iraq starting in the 20th century shortly after the defeat of the Ottoman Empire in World War I. Some put the marking point of the conflict beginning to the attempt by Mahmud Barzanji to establish an independent Kingdom of Kurdistan, while others relate to the conflict as only the post-1961 insurrection by the Barzanis.

The People's Defense Units (YPG), also called People's Protection Units, is a libertarian socialist US-backed Kurdish militant group in Syria and the primary component of the Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF).

The Rojava–Islamist conflict, a major theater in the Syrian civil war, started after fighting erupted between the Kurdish People's Protection Units (YPG) and Islamist rebel factions in the city of Ras al-Ayn. Kurdish forces launched a campaign in an attempt to take control of the Islamist-controlled areas in the governorate of al-Hasakah and some parts of Raqqa and Aleppo governorates after al-Qaeda in Syria used those areas to attack the YPG. The Kurdish groups and their allies' goal was also to capture Kurdish areas from the Arab Islamist rebels and strengthen the autonomy of the region of Rojava. The Syrian Democratic Forces would go on to take substantial territory from Islamist groups, in particular the Islamic State (IS), provoking Turkish involvement in the Syrian Civil War.
The 2005 Erbil bombing was a suicide attack on the offices of Kurdish political parties in Erbil, Kurdistan Region, on May 4, 2005. The attacker detonated explosives strapped to his body as people lined up outside a police recruiting center in Erbil. Ansar al-Sunna claimed responsibility. This attack is an example of religious terrorism, groups who commit terrorist acts because of religion believe that their deity or deities are on their side and that their violence is divinely inspired and approved. This attack is also an example of Strategic terrorism. Which is a form of terrorism where the terrorist plans to inflict mass casualties. The goals of Strategic terrorism are normally not local objectives but global objectives or regional objectives. Ansar al-Sunna's goal is to transform the country of Iraq into an Islamic state so their goals are regional.
Relations between the People's Protection Units (YPG) and the Free Syrian Army (FSA) are unclear and varied among the different FSA factions. Both are opposed to the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant. However, several clashes between the two have taken place. Under pressure from the United States, some FSA groups coordinate with the YPG to battle ISIL under the name of the Syrian Democratic Forces, although some other FSA groups remained in conflict with the YPG and the SDF, including FSA groups in the SDF.

The Descendants of Saladin Brigade was a Free Syrian Army group active in the northern Aleppo Governorate. The group was supported by Turkey and was initially funded and armed by the United States, mainly fighting the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant but also opposing the Syrian government and the Democratic Union Party's (PYD) affiliates such as the Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF). The brigade was largely disbanded by the Turkish Army in 2017, following disagreements over the participation in a planned Turkish-led offensive against Afrin Canton, although a small faction within the group remained active and participated in the offensive since January 2018.
2016–present clashes in West Iran refers to the ongoing military clashes between Kurdish insurgent party Democratic Party of Iranian Kurdistan (PDKI) and the Iranian Revolutionary Guards, which began in April 2016. Kurdistan Freedom Party (PAK) and Komalah expressed their support to the Kurdish cause of PDKI as well, with both clashing with Iranian security forces in 2016 and 2017 respectively. In parallel, a leftist Iranian Kurdish rebel group PJAK resumed military activities against Iran in 2016, following a long period of stalemate.
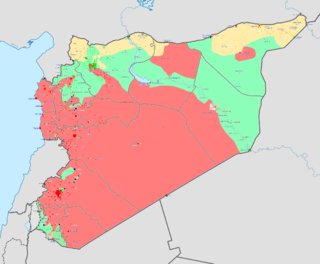
The 2013 battle of Tell Abyad was a military confrontation in the town of Tell Abyad between the Kurdish Front and the Democratic Union Party-affiliated People's Protection Units and Women's Protection Units against the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant, the al-Nusra Front, and Ahrar al-Sham, resulting in a Kurdish defeat and the jihadist capture of the town.

The al-Hasakah Governorate campaign was a multi-sided military conflict between Syrian government forces, Kurdish forces, armed Syrian opposition groups, and Salafist jihadist forces, including al-Qaeda's Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant and the al-Nusra Front in the al-Hasakah Governorate as part of the Syrian Civil War. The clashes began with the People's Protection Units (YPG)'s entrance into the civil war in July 2012 and spread across the governorate.

The Kurdish mujahideen is a term used for Kurdish Islamists who fought the Ba'athist Iraqi government.

The Islamic Emirate of Kurdistan, was an unrecognized Kurdish Islamic state located in the Halabja Governorate. It had been outside the control of the Iraqi government since 1991, and was a self-governing entity within the Kurdistan Region in 1994, and officially declared independence in 2001. It ceased to exist after Operation Viking Hammer.

The Islamic State – Kurdistan Province was the regional branch of the Islamic State which operated in Kurdistan. It was one of the earliest branches of the Islamic State, along with the Iraq Province and Sham Province. Various organized clandestine cell systems operated in support of the group.

The Second Soran Unit was a Kurdish Salafi elite militant group active from the late 1980s until 2003.
Islamism in Kurdistan dates back to as early as the 1920s. Islamism is a political movement which aims to implement Islam into political systems. The history of Islamism in Kurdistan is not contiguous and has a different history depending on which part of Kurdistan.














