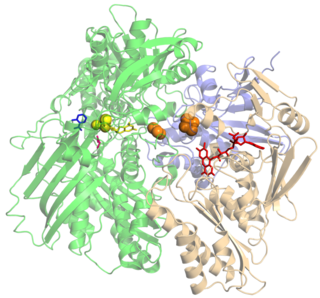
Xanthine oxidase is a form of xanthine oxidoreductase, a type of enzyme that generates reactive oxygen species. These enzymes catalyze the oxidation of hypoxanthine to xanthine and can further catalyze the oxidation of xanthine to uric acid. These enzymes play an important role in the catabolism of purines in some species, including humans.
In biochemistry, an oxidase is an oxidoreductase (any enzyme that catalyzes a redox reaction) that uses dioxygen (O2) as the electron acceptor. In reactions involving donation of a hydrogen atom, oxygen is reduced to water (H2O) or hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Some oxidation reactions, such as those involving monoamine oxidase or xanthine oxidase, typically do not involve free molecular oxygen.
L-Gulonolactone oxidase is an enzyme that produces vitamin C, but is non-functional in Haplorrhini, in some bats, and in guinea pigs. It catalyzes the reaction of L-gulono-1,4-lactone with oxygen to form L-xylo-hex-3-gulonolactone (2-keto-gulono-γ-lactone) and hydrogen peroxide. It uses FAD as a cofactor. The L-xylo-hex-3-gulonolactone then converts to ascorbic acid spontaneously, without enzymatic action.
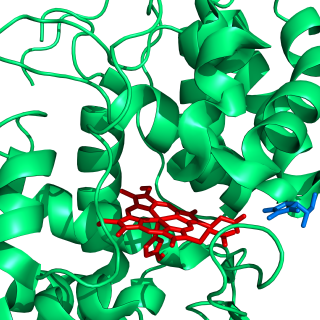
Ascorbate peroxidase (or L-ascorbate peroxidase, APX or APEX) (EC 1.11.1.11) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a bilirubin oxidase, BOD or BOx, (EC 1.3.3.5) is an enzyme encoded by a gene in various organisms that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a L-galactonolactone oxidase (EC 1.3.3.12) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an aminocyclopropanecarboxylate oxidase (EC 1.14.17.4) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a peptidylglycine monooxygenase (EC 1.14.17.3) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an abscisic-aldehyde oxidase (EC 1.2.3.14) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an indole-3-acetaldehyde oxidase (EC 1.2.3.7) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a retinal oxidase (EC 1.2.3.11) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Ascorbate 2,3-dioxygenase (EC 1.13.11.13) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an indole 2,3-dioxygenase (EC 1.13.11.17) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a lysine 2-monooxygenase (EC 1.13.12.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a phenylalanine 2-monooxygenase (EC 1.13.12.9) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a tryptophan 2-monooxygenase (EC 1.13.12.3) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a glutathione dehydrogenase (ascorbate) (EC 1.8.5.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a L-glutamate oxidase (EC 1.4.3.11) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-methyl-L-amino-acid oxidase (EC 1.5.3.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
L-galactonolactone dehydrogenase (EC 1.3.2.3, galactonolactone dehydrogenase, L-galactono-gamma-lactone dehydrogenase, L-galactono-gamma-lactone:ferricytochrome-c oxidoreductase, GLDHase, GLDase) is an enzyme with systematic name L-galactono-1,4-lactone:ferricytochrome-c oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction






