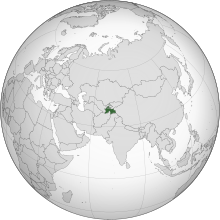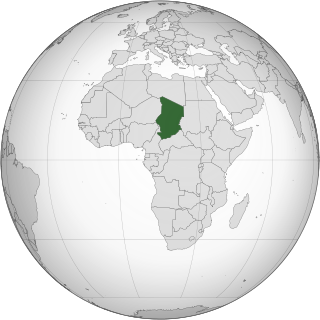
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Chad face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Both male and female forms of same-sex sexual activity are illegal in the country. Before the new penal code took effect in August 2017, homosexual activity between adults had never been criminalised. There is no legal protection against discrimination based on sexual orientation and gender identity.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) face discrimination and legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Same-sex sexual activity is legal for both males and females in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, although LGBT individuals may still be targeted for prosecution under public indecency provisions on occasion.
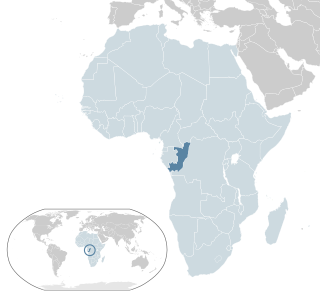
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in the Republic of the Congo face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Both male and female expressions of homosexuality are legal in the Republic of the Congo, but same-sex couples and households headed by same-sex couples are not eligible for the same legal protections available to opposite-sex couples, with reports of discrimination and abuses towards LGBT people.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender (LGBT) people in the Bahamas have limited legal protections. While same-sex sexual activity is legal in the Bahamas, there are no laws that address discrimination or harassment on the account of sexual orientation or gender identity, nor does it recognize same sex unions in any form, whether it be marriage or partnerships. Households headed by same-sex couples are also not eligible for any of the same rights given to opposite-sex married couples.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Cyprus have evolved in recent years, but LGBTQ people still face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Both male and female expressions of same-sex sexual activity were decriminalised in 1998, and civil unions which grant several of the rights and benefits of marriage have been legal since December 2015. Conversion therapy was banned in Cyprus in May 2023. However, adoption rights in Cyprus are reserved for heterosexual couples only.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Angola have seen improvements in the early 21st century. In November 2020, the National Assembly approved a new penal code, which legalised consenting same-sex sexual activity. Additionally, employment discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation has been banned, making Angola one of the few African countries to have such protections for LGBTQ people.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Botswana face legal issues not experienced by non-LGBTQ citizens. Both female and male same-sex sexual acts have been legal in Botswana since 11 June 2019 after a unanimous ruling by the High Court of Botswana. Despite an appeal by the government, the ruling was upheld by the Botswana Court of Appeal on 29 November 2021.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Comoros face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. LGBT persons are regularly prosecuted by the government and additionally face stigmatization among the broader population.
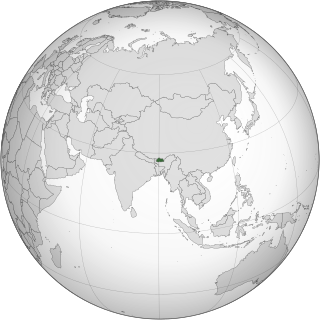
Lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender (LGBT) people in Bhutan face legal challenges that are not faced by non-LGBTQ people. Bhutan does not provide any anti-discrimination laws for LGBT people, and same-sex unions are not recognised. However, same-sex sexual activity was decriminalised in Bhutan on 17 February 2021.
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Papua New Guinea face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Male same-sex sexual activity is illegal, punishable by up to 14 years' imprisonment. The law is rarely enforced, but arrests still do happen, having occurred in 2015 and 2022. There are no legal restrictions against lesbian sex in the country.
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Eswatini have limited legal rights. According to Rock of Hope, a Swati LGBT advocacy group, "there is no legislation recognising LGBTIs or protecting the right to a non-heterosexual orientation and gender identity and as a result [LGBT people] cannot be open about their orientation or gender identity for fear of rejection and discrimination." Homosexuality is illegal in Eswatini, though this law is in practice unenforced. According to the 2021 Human Rights Practices Report from the US Department of State, "there has never been an arrest or prosecution for consensual same-sex conduct."

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Kosovo have improved in recent years, most notably with the adoption of the new Constitution, banning discrimination based on sexual orientation. Kosovo remains one of the few Muslim-majority countries that hold regular pride parades.
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in São Tomé and Príncipe face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Both male and female forms of same-sex sexual activity are legal in São Tomé and Príncipe, however LGBT persons face stigmatization among the broader population.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Mongolia face legal and social challenges not experienced by non-LGBT people, though there have been substantial improvements since the 1990s. Homosexuality was criminalised in Mongolia in 1961 through its Criminal Code. Following the Mongolian Revolution of 1990 and the peaceful transition to a democracy, homosexuality was legalised and awareness about LGBT people has become more prevalent. Hate crimes on the basis of sexual orientation and gender identity result in additional legal penalties. Hate speech based on these two categories has been outlawed in the country since 1 July 2017. Households headed by same-sex couples are, however, not eligible for the same legal protections available to opposite-sex couples.
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in East Timor face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Both male and female same-sex sexual activity are legal in East Timor, but same-sex couples and households headed by same-sex couples are not eligible for the same legal protections available to opposite-sex married couples.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Mauritius have expanded in the 21st century, although LGBT Mauritians may still face legal difficulties not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Prior to 2023, sodomy was criminalized by Section 250 of the Criminal Code. However, Mauritius fully decriminalized homosexuality in October 2023. Although same-sex marriage is not recognized in Mauritius, LGBT people are broadly protected from discrimination in areas such as employment and the provision of goods and services, making it one of the few African countries to have such protections for LGBT people. The Constitution of Mauritius guarantees the right of individuals to a private life.
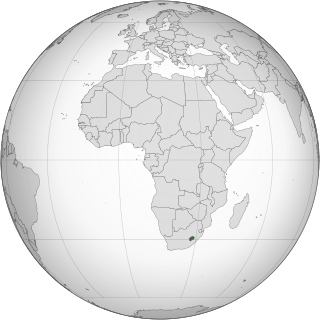
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Lesotho face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Lesotho does not recognise same-sex marriages or civil unions, nor does it ban discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation or gender identity.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Mozambique face legal challenges not faced by non-LGBTQ people. Same-sex sexual activity became legal in Mozambique under the new Criminal Code that took effect in June 2015. Discrimination based on sexual orientation in employment has been illegal since 2007.

The following outline offers an overview and guide to LGBTQ topics:

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) persons in Anguilla face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Same-sex sexual activity is legal in Anguilla, but same-sex couples cannot marry or obtain civil partnerships. Anguillian law does not forbid discrimination based on sexual orientation or gender identity.