
Beetles are insects that form the order Coleoptera, in the superorder Holometabola. Their front pair of wings are hardened into wing-cases, elytra, distinguishing them from most other insects. The Coleoptera, with about 400,000 described species, is the largest of all orders, constituting almost 40% of described insects and 25% of all known animal species; new species are discovered frequently, with estimates suggesting that there are between 0.9 and 2.1 million total species. Found in almost every habitat except the sea and the polar regions, they interact with their ecosystems in several ways: beetles often feed on plants and fungi, break down animal and plant debris, and eat other invertebrates. Some species are serious agricultural pests, such as the Colorado potato beetle, while others such as Coccinellidae eat aphids, scale insects, thrips, and other plant-sucking insects that damage crops. Some others also have unusual characteristics, such as fireflies, which use a light-emitting organ for mating and communication purposes.

The insects of the beetle family Chrysomelidae are commonly known as leaf beetles, and include over 37,000 species in more than 2,500 genera, making up one of the largest and most commonly encountered of all beetle families. Numerous subfamilies are recognized, but the precise taxonomy and systematics are likely to change with ongoing research.
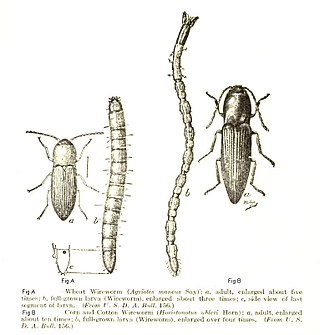
Elateridae or click beetles are a family of beetles. Other names include elaters, snapping beetles, spring beetles or skipjacks. This family was defined by William Elford Leach (1790–1836) in 1815. They are a cosmopolitan beetle family characterized by the unusual click mechanism they possess. There are a few other families of Elateroidea in which a few members have the same mechanism, but most elaterid subfamilies can click. A spine on the prosternum can be snapped into a corresponding notch on the mesosternum, producing a violent "click" that can bounce the beetle into the air. Clicking is mainly used to avoid predation, although it is also useful when the beetle is on its back and needs to right itself. There are about 9300 known species worldwide, and 965 valid species in North America.
Glowworm or glow-worm is the common name for various groups of insect larvae and adult larviform females that glow through bioluminescence. They include the European common glow-worm and other members of the Lampyridae, but bioluminescence also occurs in the families Elateridae, Phengodidae and Rhagophthalmidae among beetles; as well as members of the genera Arachnocampa, Keroplatus and Orfelia among keroplatid fungus gnats.

Histeridae is a family of beetles commonly known as clown beetles or hister beetles. This very diverse group of beetles contains 3,900 species found worldwide. They can be easily identified by their shortened elytra that leaves two of the seven tergites exposed, and their geniculate (elbowed) antennae with clubbed ends. These predatory feeders are most active at night and will fake death if they feel threatened. This family of beetles will occupy almost any kind of niche throughout the world. Hister beetles have proved useful during forensic investigations to help in time of death estimation. Also, certain species are used in the control of livestock pests that infest dung and to control houseflies. Because they are predacious and will even eat other hister beetles, they must be isolated when collected.

The Elateroidea are a large superfamily of beetles. It contains the familiar click beetles, fireflies, and soldier beetles and their relatives. It consists of about 25,000 species.

Pyrophorus is a genus of click beetle. They are one of several genera in the tribe Pyrophorini, all of which are bioluminescent. Their bioluminescence is similar to that of another group of beetles, the fireflies, although click beetles do not flash, but remain constantly glowing. They have two luminescent spots at the posterior corners of the pronotum, and another brighter light organ on the most-anterior surface of the ventral abdomen. This light organ is even brighter and can only be seen when in flight. Bioluminescent click beetles are found throughout tropical, subtropical and temperate America. Species from Texas, Florida, Puerto Rico, and Cuba are now in different genera in the tribe Pyrophorini, such as Deilelater and Ignelater.

The Goliath beetles are any of the six species in the genus Goliathus. Goliath beetles are among the largest insects on Earth, if measured in terms of size, bulk and weight. They are members of subfamily Cetoniinae, within the family Scarabaeidae. Goliath beetles can be found in many of Africa's tropical forests, where they feed primarily on tree sap and fruit. Little appears to be known of the larval cycle in the wild, but in captivity, Goliathus beetles have been successfully reared from egg to adult using protein-rich foods such as commercial cat and dog food. Goliath beetles measure from 60–110 millimetres (2.4–4.3 in) for males and 50–80 millimetres (2.0–3.1 in) for females, as adults, and can reach weights of up to 80–100 grams (2.8–3.5 oz) in the larval stage, though the adults are only about half this weight. The females range from a dark chestnut brown to silky white, but the males are normally brown/white/black or black/white.

Cleridae are a family of beetles of the superfamily Cleroidea. They are commonly known as checkered beetles. The family Cleridae has a worldwide distribution, and a variety of habitats and feeding preferences.

Creophilus maxillosus, the hairy rove beetle, is a species of rove beetle.

Alaus oculatus, commonly called the eastern eyed click beetle or eyed elater, is a species of click beetle.

Agrypnus murinus is a species of click beetle belonging to the family Elateridae subfamily Agrypninae.

Pyrophorus noctilucus, common name headlight elater, is a species of click beetle.

Hemicrepidius hirtus is a species of click beetle belonging to the family Elateridae.

Calais parreysii is a species of click beetle belonging to the family Elateridae subfamily Agrypninae.

Athous bicolor is a species of click beetle.

Amychus granulatus, commonly known as the Cook Strait click beetle, is a large flightless click beetle in the family Elateridae.

Prosternon tessellatum, the chequered click beetle, is a species of click beetle belonging to the family Elateridae.

Ctenicera virens is a species of click beetles.

Megathous nigerrimus is a species of click beetles in the family Elateridae.


















