
Torosaurus is a genus of herbivorous ceratopsid dinosaur that lived during the late Maastrichtian stage of the Cretaceous period, between 68 and 66 million years ago, though it is possible that the species range might extend to as far as 69 million years ago. Fossils have been discovered across the Western Interior of North America, from Saskatchewan to southern Texas.

Pliosauroidea is an extinct clade of marine reptiles. Pliosauroids, also commonly known as pliosaurs, are known from the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. The pliosauroids were crocodile-like short-necked plesiosaurs with large heads and massive toothed jaws. They were sauropterygian swimming reptiles, and were not dinosaurs. They originally included only members of the family Pliosauridae, of the order Plesiosauria, but several other genera and families are now also included, the number and details of which vary according to the classification used.

Dryosaurus is a genus of an ornithopod dinosaur that lived in the Late Jurassic period. It was an iguanodont. Fossils have been found in the western United States and were first discovered in the late 19th century. Valdosaurus canaliculatus and Dysalotosaurus lettowvorbecki were both formerly considered to represent species of Dryosaurus.

Dakosaurus is an extinct genus of crocodylomorph within the family Metriorhynchidae that lived during the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous. It was large, with teeth that were serrated and compressed lateromedially. The genus was established by Friedrich August von Quenstedt in 1856 for an isolated tooth named Geosaurus maximus by Theodor Plieninger in 1846. Dakosaurus was a carnivore that spent much, if not all, its life out at sea. The extent of its adaptation to a marine lifestyle means that it is most likely that it mated at sea, but since no eggs or nests have been discovered that have been referred to Dakosaurus, whether it gave birth to live young at sea like dolphins and ichthyosaurs or came ashore like turtles is not known. The name Dakosaurus means "biter lizard", and is derived from the Greek dakos ("biter") and σαῦρος -sauros ("lizard").

Saurophaganax is a genus of large allosaurid dinosaur from the Morrison Formation of Late Jurassic Oklahoma, United States. Some paleontologists consider it to be a junior synonym and species of Allosaurus. Saurophaganax represents a very large Morrison allosaurid characterized by horizontal laminae at the bases of the dorsal neural spines above the transverse processes, and "meat-chopper" chevrons. The maximum size of S. maximus has been estimated at anywhere from 10.5 meters (34 ft) to 13 meters (43 ft) in length, and 3 metric tons to 4.5 metric tons in weight.

Stokesosaurus is a genus of small, carnivorous early tyrannosauroid theropod dinosaurs from the late Jurassic period of Utah, United States.

Phyllodon was a genus of small ornithischian dinosaur from the Kimmeridgian-age Upper Jurassic Camadas de Guimarota Formation of Leiria, Portugal and possibly also the Chipping Norton Limestone of England. It may have been closely related to contemporaneous dinosaurs in North America.
Mesadactylus is an extinct genus of pterosaur from the Kimmeridgian-Tithonian-age Upper Jurassic Morrison Formation of Colorado, United States. The genus was named in 1989 by James Jensen and Kevin Padian. The type species is Mesadactylus ornithosphyos.

Docodon was a mammaliaform from the Late Jurassic of western North America. It was the first docodontan cynodont to be named.
Kepodactylus is an extinct genus of ctenochasmatid pterodactyloid pterosaur from the Kimmeridgian-Tithonian-age Upper Jurassic Morrison Formation of Colorado, United States.
Puntanipterus is a genus of pterodactyloid pterosaur from the Early Cretaceous period La Cruz Formation of San Luis, Argentina.
Cricosaurus is an extinct genus of marine crocodyliforms of the Late Jurassic. belonging to the family Metriorhynchidae. The genus was established by Johann Andreas Wagner in 1858 for three skulls from the Tithonian of Germany. The name Cricosaurus means "Ring lizard", and is derived from the Greek Cricos- ("ring") and σαῦρος -sauros ("lizard").
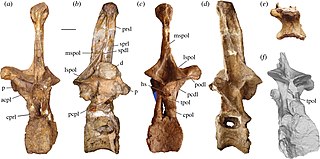
Amphicoelias is a genus of herbivorous sauropod dinosaur that lived approximately 150 million years ago during the Tithonian of what is now Colorado, United States. A herbivore, Amphicoelias was moderately sized at about 25 m (82 ft) long–roughly the same length as Diplodocus, to which it was related. Its hindlimbs were very long and thin, and its forelimbs were proportionally longer than in relatives.
The Villar del Arzobispo Formation is a Late Jurassic to possibly Early Cretaceous geologic formation in eastern Spain. It is equivalent in age to the Lourinhã Formation of Portugal. It was originally thought to date from the Late Tithonian-Middle Berriasian, but more recent work suggests a Kimmeridigan-Late Tithonian, possibly dating to the Early Berriasian in some areas. The Villar del Arzobispo Formation's age in the area of Riodeva in Spain has been dated based on stratigraphic correlations as middle-upper Tithonian, approximately 145-141 million years old. In the area of Galve, the formation potentially dates into the earliest Cretaceous.

Uteodon is a genus of herbivorous iguanodontian dinosaur. It is a basal iguanodontian which lived during the late Jurassic period in what is now Uintah County, Utah. It is known from the middle of the Brushy Basin Member, Morrison Formation. The genus was named by Andrew T. McDonald in 2011 and the type species is U. aphanoecetes.
The La Caja Formation is a geologic formation in Mexico. It preserves fossils datiting from the Kimmeridgian to the lower Berriasian. La Caja Formation is widespread in northeastern and central Mexico and known for their abundant and diverse well-preserved ammonites. It was deposited in hemipelagic conditions, and predominantly consists of siliclastic sediments, including marl, with limestone. It is laterally equivalent to the La Casita Formation, which represent more proximal facies. The ichthyosaurs Ophthalmosaurus icenicus and Parrassaurus yacahuitztli, metriorhynchid Cricosaurus saltillensis and the undescribed giant pliosaur "Monster of Aramberri" are known from the formation.

The La Casita Formation is a geologic formation in Mexico. It preserves fossils dating back to the Kimmeridgian to lowermost Berriasian. It is laterally equivalent to the La Caja Formation and the Pimienta Formation. The ichthyosaur Acuetzpalin is known from the formation, as well as the metriorhynchid Dakosaurus and indeterminate pliosaurs.
Pandoravenator is a genus of basal tetanuran theropod dinosaur from the Late Jurassic of central Patagonia. Fossils of this dinosaur were discovered in the sediments of the Cañadón Calcáreo Formation and were scientifically described in 2017 by paleontologists Oliver Rauhut and Diego Pol. The type and only known species is Pandoravenator fernandezorum.
Acuetzpalin is an extinct genus of platypterygiine ophthalmosaurid ichthyosaur found in the Kimmeridgian La Casita Formation in Mexico. It is known from a partial skeleton, of which the skull is surprisingly well preserved. It was the first ichthyosaur described in 2020 and the first new ichthyosaur genus described since 2017.
Parrassaurus is an ophthalmosaurid ichthyosaur from the late Jurassic La Caja Formation of Mexico found in 2021. Parrassaurus includes one species, Parrassaurus yacahuitztli.












