
The peach is a deciduous tree first domesticated and cultivated in Zhejiang province of Eastern China. It bears edible juicy fruits with various characteristics, most called peaches and others, nectarines.

A cherry is the fruit of many plants of the genus Prunus, and is a fleshy drupe.
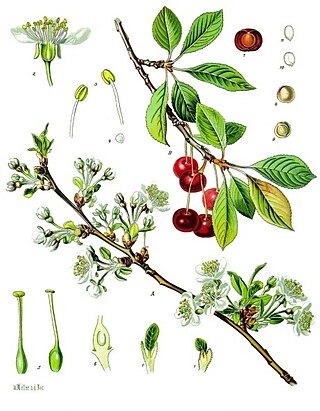
Prunus cerasus is a species of Prunus in the subgenus Cerasus (cherries), native to much of Europe, North Africa and West Asia. It is closely related to the sweet cherry, but has a fruit that is more acidic. Its sour pulp is edible.

The cherry blossom, or sakura, is the flower of trees in Prunus subgenus Cerasus. "Sakura" usually refers to flowers of ornamental cherry trees, such as cultivars of Prunus serrulata, not trees grown for their fruit. Cherry blossoms have been described as having a vanilla-like smell, which is mainly attributed to coumarin.

Prunus laurocerasus, also known as cherry laurel, common laurel and sometimes English laurel in North America, is an evergreen species of cherry (Prunus), native to regions bordering the Black Sea in southwestern Asia and southeastern Europe, from Albania and Bulgaria east through Turkey to the Caucasus Mountains and northern Iran.

The damson or damson plum, also archaically called the "damascene", is an edible drupaceous fruit, a subspecies of the plum tree. Varieties of insititia are found across Europe, but the name damson is derived from and most commonly applied to forms that are native to Great Britain. Damsons are relatively small ovoid plum-like fruit with a distinctive, somewhat astringent taste, and are widely used for culinary purposes, particularly in fruit preserves and jams.

Prunus cerasifera is a species of plum known by the common names cherry plum and myrobalan plum. It is native to Southeast Europe and Western Asia, and is naturalised in the British Isles and scattered locations in North America. Also naturalized in parts of SE Australia where it is considered to be a mildly invasive weed of bushland near urban centers. P. cerasifera is believed to one of the parents of the Cultivated Plum, Prunus domestica perhaps crossing with the sloe, Prunus spinosa, or perhaps the sole parent. This would make it a parent of most of the commercial varieties of plum in the UK and mainland Europe - Victoria, greengages, bullace etc.

Prunus serrulata or Japanese cherry is a species of cherry tree that grows naturally in Japan, China, Korea, and Vietnam, and it also refers to a cultivar produced from Prunus speciosa, a cherry tree endemic in Japan. Historically, the Japanese have developed many cultivars by selective breeding of cherry trees, which are produced by the complicated crossing of several wild species, and they are used for ornamental purposes all over the world. Of these, the cultivars produced by complex interspecific hybrids based on the Oshima cherry are also known as the Cerasus Sato-zakura Group.

Prunus incisa, the Fuji cherry, is a species of flowering plant in the family Rosaceae, which gets its scientific name from the deep incisions on the leaves. It is an endemic species in Japan and grows wild in Kantō, Chūbu and Kinki regions. It is called the Fuji cherry because it grows in particular abundance around Mount Fuji and Hakone. A dainty slow-growing, early white-flowering cherry tree, this century-old cultigen from Hondo, Japan is highly regarded as an ornamental but the wood has no industrial value. It is hardy to -20 °C, and crossed with Prunus speciosa, has yielded the cultivar Prunus 'Umineko'. It is in the ornamental section Pseudocerasus of the cherry subgenus Cerasus of the genus Prunus. Ma et al. classified it in a group with Prunus nipponica.

Prunus domestica is a species of flowering plant in the family Rosaceae. A deciduous tree, it includes many varieties of the fruit trees known as plums in English, though not all plums belong to this species. The greengages and damsons also belong to subspecies of P. domestica.

Prunus avium, commonly called wild cherry, sweet cherry or gean is a species of cherry, a flowering plant in the rose family, Rosaceae. It is native to Europe, Anatolia, Maghreb, and Western Asia, from the British Isles south to Morocco and Tunisia, north to the Trondheimsfjord region in Norway and east to the Caucasus and northern Iran, with a small isolated population in the western Himalaya. The species is widely cultivated in other regions and has become naturalized in North America, New Zealand and Australia.

Prunus serrula, called birch bark cherry, birchbark cherry, paperbark cherry, or Tibetan cherry, is a species of cherry native to China, and is used as an ornamental in many parts of the world for its striking coppery-red bark.

Stella is a cultivar of cherry developed in British Columbia, Canada. It is notable as the first self-fertile sweet cherry to be named. It has been awarded the Royal Horticultural Society's Award of Garden Merit.
The Pacific Agri-Food Research Centre is an agricultural research centre in British Columbia, Canada. The centre has been historically important in the development of tree fruits. It is administered by Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada and includes sites at Summerland and Agassiz.
Van is a cultivar of cherry originating from Canada.
The Sweetheart cherry is a cultivar of cherry. It is a hybrid of the Van and Newstar cultivars first developed in Canada.
Skeena is a cultivar of cherry originating in Canada.

The Balaton cherry is a cultivar of sour cherry native to Hungary, where it was originally named Újfehértói Fürtös. It was introduced to the United States in the 1980s and is now grown there commercially.

The Concorde is a cultivar of pear originating in England. A cross of the Conference and Comice varieties, it has some of the traits of both parents.

Regina is a cultivar of sweet cherry developed in Germany.

















