
Genus is a taxonomic rank above species and below family as used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus.

The International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) is a widely accepted convention in zoology that rules the formal scientific naming of organisms treated as animals. It is also informally known as the ICZN Code, for its publisher, the International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature. The rules principally regulate:

Requiem sharks are sharks of the family Carcharhinidae in the order Carcharhiniformes. They are migratory, live-bearing sharks of warm seas and include such species as the bull shark, lemon shark, blacktip shark, and whitetip reef shark.

Glyphis is a genus in the family Carcharhinidae, commonly known as the river sharks. They live in rivers or coastal regions in and around south-east Asia, Africa and parts of Australia.

Carpet sharks are sharks classified in the order Orectolobiformes. Sometimes the common name "carpet shark" is used interchangeably with "wobbegong", which is the common name of sharks in the family Orectolobidae. Carpet sharks have five gill slits, two spineless dorsal fins, and a small mouth that does not extend past the eyes. Many species have barbels.

Plumeria, also known as frangipani, is a genus of flowering plants in the subfamily Rauvolfioideae, of the family Apocynaceae. Most species are deciduous shrubs or small trees. The species are native to the Neotropical realm, but are often grown as cosmopolitan ornamentals in tropical regions, especially in Hawaii, as well as hot desert climates in the Arabian Peninsula with proper irrigation.

Hevea is a genus of flowering plants in the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, with about ten members. It is also one of many names used commercially for the wood of the most economically important rubber tree, H. brasiliensis. The genus is native to tropical South America but is widely cultivated in other tropical countries and naturalized in several of them. It was first described in 1775.

Phyllanthus is the largest genus in the plant family Phyllanthaceae. Estimates of the number of species in this genus vary widely, from 750 to 1200. Phyllanthus has a remarkable diversity of growth forms including annual and perennial herbs, shrubs, climbers, floating aquatics, and pachycaulous succulents. Some have flattened leaflike stems called cladodes. It has a wide variety of floral morphologies and chromosome numbers and has one of the widest range of pollen types of any seed plant genus.

Acalypha is a genus of flowering plants in the family Euphorbiaceae. It is the sole genus of the subtribe Acalyphinae. It is one of the largest euphorb genera, with approximately 450 to 462 species. The genus name Acalypha is from the Ancient Greek ἀκαλύφη (akalúphē) ("nettle"), an alternative form of ἀκαλήφη (akalḗphē), and was inspired by the nettle-like leaves. General common names include copperleaf and three-seeded mercury. Native North American species are generally inconspicuous most of the year until the fall when their stems and foliage turn a distinctive coppery-red.
In zoological nomenclature, author citation is the process in which a person is credited with the creation of the scientific name of a previously unnamed taxon. When citing the author of the scientific name, one must fulfill the formal requirements listed under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature. According to Article 51.1 of the Code, "The name of the author does not form part of the name of a taxon and its citation is optional, although customary and often advisable." However, recommendation 51A suggests, "The original author and date of a name should be cited at least once in each work dealing with the taxon denoted by that name. This is especially important and has a unique character between homonyms and in identifying species-group names which are not in their native combinations." For the sake of information retrieval, the author citation and year appended to the scientific name, e.g. genus-species-author-year, genus-author-year, family-author-year, etc., is often considered a "de-facto" unique identifier, although this usage may often be imperfect.

Ham Hill is a hill and area of chalk downland in Wiltshire, England, on the steep banks running alongside the road from the village of Ham to Buttermere, close to the Berkshire border. A biological Site of Special Scientific Interest, notified in 1971, covers 1.5 hectares of the site; this designation is due to the site's species-rich plant and insect communities, which include some rare species. Notable among these is the musk orchid, which has been confirmed at only one other site in Wiltshire.

Carcharias is a genus of mackerel sharks belonging to the family Odontaspididae. Once bearing many prehistoric species, all have gone extinct with the exception of the critically endangered sand tiger shark.

Euplotes is a genus of ciliates in the subclass Euplotia. Species are widely distributed in marine and freshwater environments, as well as soil and moss. Most members of the genus are free-living, but two species have been recorded as commensal organisms in the digestive tracts of sea urchins.
Defretinella is a genus of parasitic alveolates of the phylum Apicomplexa.
Leiocolea rutheana is a species of liverwort belonging to the family Jungermanniaceae.
Leiocolea turbinata is a species of liverwort belonging to the family Jungermanniaceae.

Maehary is an extinct genus of probable gracilisuchid pseudosuchian archosaurs from the Late Triassic (Norian) Caturrita Formation of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. The genus contains a single species, M. bonapartei, known from a partial skull and fragmentary postcrania. Maehary was originally described as the basalmost member of the Pterosauromorpha, but several subsequent studies have suggested pseudosuchian affinities are more likely. If this is correct, it would represent the youngest known member of the Gracilisuchidae.
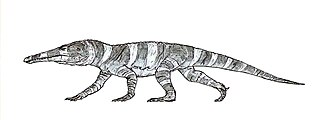
Stenoscelida is a genus of proterochampsid archosauriforms from the Late Triassic Santa Maria Supersequence of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. The genus contains a single species, S. aurantiacus, known from a right hind limb.














