
Mother of vinegar is a biofilm composed of a form of cellulose, yeast, and bacteria that sometimes develops on fermenting alcoholic liquids during the process that turns alcohol into acetic acid with the help of oxygen from the air and acetic acid bacteria (AAB). It is similar to the symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast (SCOBY) mostly known from production of kombucha, but develops to a much lesser extent due to lesser availability of yeast, which is often no longer present in wine/cider at this stage, and a different population of bacteria. Mother of vinegar is often added to wine, cider, or other alcoholic liquids to produce vinegar at home, although only the bacteria is required, but historically has also been used in large scale production.

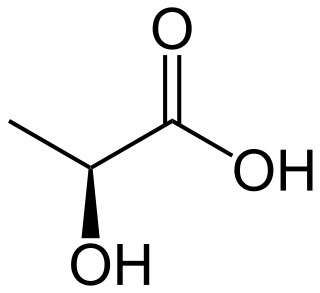
Lactic acid is an organic acid. It has the molecular formula CH3CH(OH)COOH. It is white in the solid state and it is miscible with water. When in the dissolved state, it forms a colorless solution. Production includes both artificial synthesis as well as natural sources. Lactic acid is an alpha-hydroxy acid (AHA) due to the presence of a hydroxyl group adjacent to the carboxyl group. It is used as a synthetic intermediate in many organic synthesis industries and in various biochemical industries. The conjugate base of lactic acid is called lactate. The name of the derived acyl group is lactoyl.

Sourdough or sourdough bread is a bread made by the fermentation of dough using wild lactobacillaceae and yeast. Lactic acid from fermentation imparts a sour taste and improves keeping qualities.
Lactic acid fermentation is a metabolic process by which glucose or other six-carbon sugars are converted into cellular energy and the metabolite lactate, which is lactic acid in solution. It is an anaerobic fermentation reaction that occurs in some bacteria and animal cells, such as muscle cells.

Silage is a type of fodder made from green foliage crops which have been preserved by fermentation to the point of acidification. It can be fed to cattle, sheep, and other such ruminants. The fermentation and storage process is called ensilage, ensiling, or silaging. Silage is usually made from grass crops, including maize, sorghum, or other cereals, using the entire green plant.

Lactobacillus bulgaricus is the main bacterium used for the production of yogurt. It also plays a crucial role in the ripening of some cheeses, as well as in other processes involving naturally fermented products. It is defined as homofermentive lactic acid bacteria due to lactic acid being the single end product of its carbohydrate digestion. It is also considered a probiotic.

Winemaking or vinification is the production of wine, starting with the selection of the fruit, its fermentation into alcohol, and the bottling of the finished liquid. The history of wine-making stretches over millennia. There are authentic proofs that suggest that the earliest Wine production took place in Georgia and Iran around 6000 to 5000 B.C. The science of wine and winemaking is known as oenology. A winemaker may also be called a vintner. The growing of grapes is viticulture and there are many varieties of grapes.

Malolactic conversion is a process in winemaking in which tart-tasting malic acid, naturally present in grape must, is converted to softer-tasting lactic acid. Malolactic fermentation is most often performed as a secondary fermentation shortly after the end of the primary fermentation, but can sometimes run concurrently with it. The process is standard for most red wine production and common for some white grape varieties such as Chardonnay, where it can impart a "buttery" flavor from diacetyl, a byproduct of the reaction.
Lactiplantibacillus plantarum is a widespread member of the genus Lactiplantibacillus and commonly found in many fermented food products as well as anaerobic plant matter. L. plantarum was first isolated from saliva. Based on its ability to temporarily persist in plants, the insect intestine and in the intestinal tract of vertebrate animals, it was designated as a nomadic organism. L. plantarum is Gram positive, bacilli shaped bacterium. L. plantarum cells are rods with rounded ends, straight, generally 0.9–1.2 μm wide and 3–8 μm long, occurring singly, in pairs or in short chains. L. plantarum has one of the largest genomes known among the lactic acid bacteria and is a very flexible and versatile species. It is estimated to grow between pH 3.4 and 8.8. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum can grow in the temperature range 12 °C to 40 °C. The viable counts of the "L. plantarum" stored at refrigerated condition (4 °C) remained high, while a considerable reduction in the counts was observed stored at room temperature.
A wine fault is a sensory-associated (organoleptic) characteristic of a wine that is unpleasant, and may include elements of taste, smell, or appearance, elements that may arise from a "chemical or a microbial origin", where particular sensory experiences might arise from more than one wine fault. Wine faults may result from poor winemaking practices or storage conditions that lead to wine spoilage.

Lactobacillales are an order of gram-positive, low-GC, acid-tolerant, generally nonsporulating, nonrespiring, either rod-shaped (bacilli) or spherical (cocci) bacteria that share common metabolic and physiological characteristics. These bacteria, usually found in decomposing plants and milk products, produce lactic acid as the major metabolic end product of carbohydrate fermentation, giving them the common name lactic acid bacteria (LAB).

The Lactobacillaceae are a family of lactic acid bacteria. It is the only family in the lactic acid bacteria which includes homofermentative and heterofermentative organisms; in the Lactobacillaceae, the pathway used for hexose fermentation is a genus-specific trait. Lactobacillaceae include the homofermentative lactobacilli Lactobacillus, Holzapfelia, Amylolactobacillus, Bombilactobacillus, Companilactobacillus, Lapidilactobacillus, Agrilactobacillus, Schleiferilactobacillus, Loigolactobacillus, Lacticaseibacillus, Latilactobacillus, Dellaglioa, Liquorilactobacillus, Ligilactobacillus, and Lactiplantibacillus; the heterofermentative lactobacilli Furfurilactobacillus, Paucilactobacillus, Limosilactobacillus, Fructilactobacillus, Acetilactobacillus, Apilactobacillus, Levilactobacillus, Secundilactobacillus, and Lentilactobacillus, which were previously classified in the genus Lactobacillus; and the heterofermentative genera Convivina, Fructobacillus, Leuconostoc, Oenococcus, and Weissella which were previously classified in the Leuconostocaceae.
Levilactobacillus brevis is a gram-positive, rod shaped species of lactic acid bacteria which is heterofermentative, creating CO2, lactic acid and acetic acid or ethanol during fermentation. L. brevis is the type species of the genus Levilactobacillus (previously L. brevis group), which comprises 24 species. It can be found in many different environments, such as fermented foods, and as normal microbiota. L. brevis is found in food such as sauerkraut and pickles. It is also one of the most common causes of beer spoilage. Ingestion has been shown to improve human immune function, and it has been patented several times. Normal gut microbiota L. brevis is found in human intestines, vagina, and feces.

Symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast (SCOBY) is a culinary symbiotic fermentation culture (starter) consisting of lactic acid bacteria (LAB), acetic acid bacteria (AAB), and yeast which arises in the preparation of sour foods and beverages such as kombucha. Beer and wine also undergo fermentation with yeast, but the lactic acid bacteria and acetic acid bacteria components unique to SCOBY are usually viewed as a source of spoilage rather than a desired addition. Both LAB and AAB enter on the surface of barley and malt in beer fermentation and grapes in wine fermentation; LAB lowers the pH of the beer/wine while AAB takes the ethanol produced from the yeast and oxidizes it further into vinegar, resulting in a sour taste and smell. AAB are also responsible for the formation of the cellulose SCOBY.

The process of fermentation in winemaking turns grape juice into an alcoholic beverage. During fermentation, yeasts transform sugars present in the juice into ethanol and carbon dioxide. In winemaking, the temperature and speed of fermentation are important considerations as well as the levels of oxygen present in the must at the start of the fermentation. The risk of stuck fermentation and the development of several wine faults can also occur during this stage, which can last anywhere from 5 to 14 days for primary fermentation and potentially another 5 to 10 days for a secondary fermentation. Fermentation may be done in stainless steel tanks, which is common with many white wines like Riesling, in an open wooden vat, inside a wine barrel and inside the wine bottle itself as in the production of many sparkling wines.
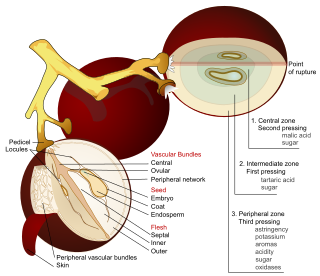
The acids in wine are an important component in both winemaking and the finished product of wine. They are present in both grapes and wine, having direct influences on the color, balance and taste of the wine as well as the growth and vitality of yeast during fermentation and protecting the wine from bacteria. The measure of the amount of acidity in wine is known as the “titratable acidity” or “total acidity”, which refers to the test that yields the total of all acids present, while strength of acidity is measured according to pH, with most wines having a pH between 2.9 and 3.9. Generally, the lower the pH, the higher the acidity in the wine. There is no direct connection between total acidity and pH. In wine tasting, the term “acidity” refers to the fresh, tart and sour attributes of the wine which are evaluated in relation to how well the acidity balances out the sweetness and bitter components of the wine such as tannins. Three primary acids are found in wine grapes: tartaric, malic, and citric acids. During the course of winemaking and in the finished wines, acetic, butyric, lactic, and succinic acids can play significant roles. Most of the acids involved with wine are fixed acids with the notable exception of acetic acid, mostly found in vinegar, which is volatile and can contribute to the wine fault known as volatile acidity. Sometimes, additional acids, such as ascorbic, sorbic and sulfurous acids, are used in winemaking.
Sporolactobacillus is a genus of anaerobic, endospore-forming, gram-positive, motile, rod-shaped, lactic acid bacteria.
Pediococcus damnosus is a species of Gram-positive bacteria. The genus Pediococcus is a spherical cocci shaped bacteria with nonmotile, non spore-forming and homofermentative properties. P. damnosus is a chemo-organotrophic, catalase negative, facultative anaerobe. Strains of this species frequently grow in wine and beer, where they overproduce glucan and spoil products by increasing their viscosity. P. damnosus is a lactic acid bacteria (LAB), that can tolerate the low pH and higher ethanol levels that are found in beer. The ability to grow in beer is a strain specific characteristic of the species P. damnosus. Pediococcus damnosus LMG 28219 is a lactic acid bacterium that has proved to be capable of growing in beer.
Lentilactobacillus hilgardii is a species of bacterium found in wine, dairy products, and wine musts.

Bokashi is a process that converts food waste and similar organic matter into a soil amendment which adds nutrients and improves soil texture. It differs from traditional composting methods in several respects. The most important are:













