Ascochyta medicaginicola is a plant pathogen infecting alfalfa and Medicago truncatula. One particular disease is spring black stem.
Ascochyta tarda or Phoma tarda is a fungal plant pathogen that causes dieback and leafspot on coffee and was first observed in Ethiopia in 1954. It poses a potentially serious threat to coffee crops, but climate change may reduce the prevalence of environmental conditions favorable to its spread.
Phoma glomerata is a fungus pathogen with several hosts. It mainly spoils wool because it badly alters the fibers.

Neocamarosporium betae is a plant pathogen infecting Beta vulgaris (beet) and causes Phoma leaf spot. It was originally published and described in 1877 as Pleospora betae before being resolved as Neocamarosporium betae(Berl.) Ariyaw. & K.D. Hyde in 2015. It also causes leaf spot on Spinach plants.
Didymella arachidicola is a plant pathogen.
Coniothyrium glycines is a fungal plant pathogen infecting soybean.
Phoma herbarum is a fungal plant pathogen infecting various plant species, including Alchemilla vulgaris, Arabis petraea, Arenaria norvegica, Armeria maritima, Bartsia alpina, Capsella bursa-pastoris, Erysimum, Euphrasia frigida, Honckenya peploides, Matricaria maritima, Rumex longifolius, Thymus praecox and Urtica dioica.
Phoma microspora is a fungal plant pathogen known for infecting peanuts.
Didymella pinodella is a fungal plant pathogen infecting pea and red clover.
Phoma tracheiphila is a fungal plant pathogen. It causes a disease known as Mal secco on citrus trees. It occurs in dry, cool climates such as the Mediterranean, Black Sea and Asia Minor. It forms pycniospores that are carried short distances by rain, or by wind to new leaves, where germinated hyphae invade stomata or more likely fresh wounds.
Phoma macdonaldii is a plant pathogenic fungus that is a major causal force for the disease Phoma Black Stem.

Phoma destructiva is a fungal plant pathogen infecting tomatoes and potatoes.
The laimosphere is the microbiologically enriched zone of soil that surrounds below-ground portions of plant stems; the laimosphere is analogous to the rhizosphere and spermosphere. The combining form laim- from laimos denotes a connecting organ (neck) while -sphere indicates a zone of influence. Topographically, the laimosphere includes the soil around any portion of subterranean plant organs other than roots where exuded nutrients stimulate microbial activities. Subterranean plant organs with a laimosphere include hypocotyls, epicotyls, stems, stolons, corms, bulbs, and leaves. Propagules of soil-borne plant pathogens, whose germination is stimulated by a plant exudates in the laimosphere, can initiate hypocotyl and stem rots leading to "damping-off". Pathogens commonly found to cause such diseases are species of Fusarium, Phoma, Phytophthora, Pythium, Rhizoctonia and Sclerotinia.
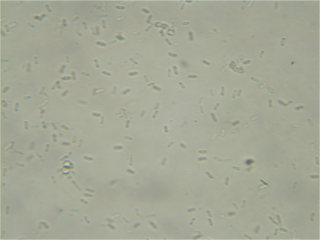
Phoma is a genus of common coelomycetous soil fungi. It contains many plant pathogenic species.
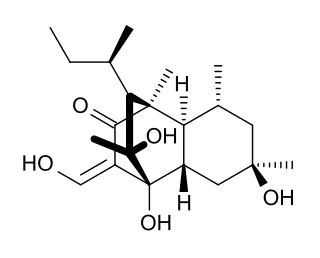
Betaenone A, like other betaenones, is a secondary metabolite isolated from the fungus Pleospora betae, a plant pathogen. Of the seven phytotoxins isolated in fungal leaf spots from sugar beet, it showed 73% growth inhibition.
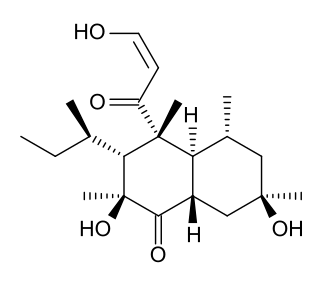
Betaenone C, like other betaenones, is a secondary metabolite isolated from the fungus Pleospora betae, a plant pathogen. Of the seven phytotoxins isolated in fungal leaf spots from sugar beet, it showed 89% growth inhibition. Betaenone C has been shown to act by inhibiting RNA and protein synthesis.

Barceloneic acid A is a farnesyl transferase inhibitor isolate of Phoma.

The Didymellaceae are a family of fungi in the order Pleosporales. They have a world-wide distribution.
Phoma wilt is a disease of the common hop plant caused by several species of fungal plant pathogens in the genus Phoma. These include Phoma herbarum and Phoma exigua, and possibly other as yet unidentified species. Phoma infection may cause decreased yields, but Phoma wilt is not considered to be a very common or destructive disease of the hop plant.






