
Gracilaria is a genus of red algae (Rhodophyta) notable for its economic importance as an agarophyte, as well as its use as a food for humans and various species of shellfish. Various species in the genus are cultivated among Asia, South America, Africa and Oceania.

Codium is a genus of edible green macroalgae under the order Bryopsidales. The genus name is derived from a Greek word that pertains to the soft texture of its thallus. One of the foremost experts on Codium taxonomy was Paul Claude Silva at the University of California, Berkeley. P.C. Silva was able to describe 36 species for the genus and in honor of his work on Codium, the species C. silvae was named after the late professor.

The Delesseriaceae is a family of about 100 genera of marine red alga.

Halymenia a genus of a macroscopic red algae that grows in oceans worldwide.

Rhodomelaceae is estimated to be the largest red algae family, with about 125 genera and over 700 species.

Galaxaura is a genus of thalloid red algae.

Galaxauraceae is a family of red algae (Rhodophyta) in the order Nemaliales.

Nemaliales is an order of red algae.

Laurencia is a genus of red algae that grow in temperate and tropical shore areas, in littoral to sublittoral habitats, at depths up to 65 m (213 ft).

Desmarestia is a genus of brown algae found worldwide. It is also called acid weed, acidweed, oseille de mer, sea sorrel, ウルシグサ, stacheltang, mermaid's hair, landlady's wig, or gruagach. However, 'sea sorrel' can also specifically refer to Desmarestia viridis. Members of this genus can be either annual or perennial. Annual members of this genus store sulfuric acid in intracellular vacuoles. When exposed to air they release the acid, thereby destroying themselves and nearby seaweeds in the process. They are found in shallow intertidal zones.
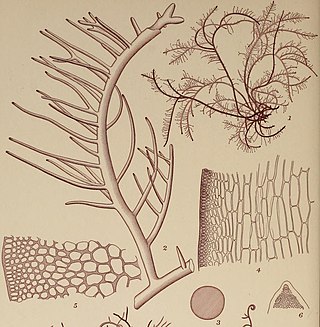
Hypnea is a genus of red algae, and a well known carrageenophyte.

Crouania is a genus of red algae (Rhodophyta) in the Callithamniaceae family. The name of the genus honours the French born Crouan brothers, Pierre-Louis Crouan and Hippolyte-Marie Crouan. It was first described by Jacob Georg Agardh in 1842, and the type species is Crouania attenuata.

Callithamniaceae is a family of red algae (Rhodophyta) in the order Ceramiales. The family was first described by Friedrich Traugott Kützing in 1843.

Aglaothamnion is a genus of algae belonging to the family Callithamniaceae.
Balliales is an order of red algae belonging to the class Florideophyceae. The order consists only one family, Balliaceae. with only one genus - BalliaHarvey.

Naccariaceae is a family of red algae in the order Bonnemaisoniales, with 3 monotypic genera that are found in both the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans.

Callithamnion is a genus of algae belonging to the family Callithamniaceae.
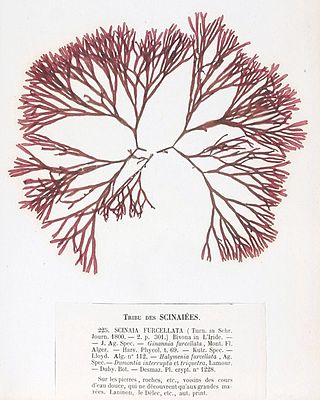
Scinaiaceae is a family of red algae (Rhodophyta) in the order Nemaliales.

Halymeniales is an order of red algae belonging to the class Florideophyceae and the subclass Rhodymeniophycidae.

Peyssonneliales is a monotypic order of red algae belonging to the class Florideophyceae and the subclass Rhodymeniophycidae. It contains only 1 known family, PeyssonneliaceaeDenizot, M., 1968.
















