
Algae is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic, eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular microalgae, such as Chlorella, Prototheca and the diatoms, to multicellular forms, such as the giant kelp, a large brown alga which may grow up to 50 metres (160 ft) in length. Most are aquatic and lack many of the distinct cell and tissue types, such as stomata, xylem and phloem that are found in land plants. The largest and most complex marine algae are called seaweeds, while the most complex freshwater forms are the Charophyta, a division of green algae which includes, for example, Spirogyra and stoneworts. Algae that are carried by water are plankton, specifically phytoplankton.

Chlorophyta is a taxon of green algae informally called chlorophytes. The name is used in two very different senses, so care is needed to determine the use by a particular author. In older classification systems, it is a highly paraphyletic group of all the green algae within the green plants (Viridiplantae) and thus includes about 7,000 species of mostly aquatic photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. In newer classifications, it is the sister clade of the streptophytes/charophytes. The clade Streptophyta consists of the Charophyta in which the Embryophyta emerged. In this latter sense the Chlorophyta includes only about 4,300 species. About 90% of all known species live in freshwater. Like the land plants, green algae contain chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b and store food as starch in their plastids.

Cyprinodontiformes is an order of ray-finned fish, comprising mostly small, freshwater fish. Many popular aquarium fish, such as killifish and live-bearers, are included. They are closely related to the Atheriniformes and are occasionally included with them. A colloquial term for the order as a whole is toothcarps, though they are not actually close relatives of the true carps – the latter belong to the superorder Ostariophysi, while the toothcarps are Acanthopterygii.

Alcyonacea are a species of sessile colonial cnidarians that are found throughout the oceans of the world, especially in the deep sea, polar waters, tropics and subtropics. Whilst not in a strict taxonomic sense, Alcyonacea are commonly known as "soft corals" (Octocorallia) that are quite different from "true" corals (Scleractinia). The term “soft coral” generally applies to organisms in the two orders Pennatulacea and Alcyonacea with their polyps embedded within a fleshy mass of coenenchymal tissue. Consequently, the term “gorgonian coral” is commonly handed to multiple species in the order Alcyonacea that produce a mineralized skeletal axis composed of calcite and the proteinaceous material gorgonin only and corresponds to only one of several families within the formally accepted taxon Gorgoniidae (Scleractinia). These can be found in order Malacalcyonacea (taxonomic synonyms of include : Alcyoniina, Holaxonia, Protoalcyonaria, Scleraxonia, and Stolonifera. They are sessile colonial cnidarians that are found throughout the oceans of the world, especially in the deep sea, polar waters, tropics and subtropics. Common names for subsets of this order are sea fans and sea whips; others are similar to the sea pens of related order Pennatulacea. Individual tiny polyps form colonies that are normally erect, flattened, branching, and reminiscent of a fan. Others may be whiplike, bushy, or even encrusting. A colony can be several feet high and across, but only a few inches thick. They may be brightly coloured, often purple, red, or yellow. Photosynthetic gorgonians can be successfully kept in captive aquaria.

The ochrophytes are is a group of mostly photosynthetic stramenopiles (heterokonts), placed either in phylum Ochrophyta or subphylum Ochrophytina. Their plastid is of red algal origin.

The Delesseriaceae is a family of about 100 genera of marine red alga.
The Academia Costarricense de la Lengua is an association of academics and experts on the use of the Spanish language in Costa Rica. It was founded in San José on October 12, 1923. It is a member of the Association of Spanish Language Academies.

Psocodea is a taxonomic group of insects comprising the bark lice, book lice and parasitic lice. It was formerly considered a superorder, but is now generally considered by entomologists as an order. Despite the greatly differing appearance of parasitic lice (Phthiraptera), they are believed to have evolved from within the former order Psocoptera, which contained the bark lice and book lice, now found to be paraphyletic. They are often regarded as the most primitive of the hemipteroids. Psocodea contains around 11,000 species, divided among four suborders and more than 70 families. They range in size from 1–10 millimetres (0.04–0.4 in) in length.
The Rhodogorgonales are an order of red algae, a sister group to the corallines. They are always thalloid and calcified; their calcification is very different from the corallines, as individual calcite crystals are deposited in the cell wall of specialised cells; this suggests that the evolution of calcification may have been independent from the corallines. They have no fossil record.

Verrucariaceae is a family of lichens and a few non-lichenised fungi in the order Verrucariales. The lichens have a wide variety of thallus forms, from crustose (crust-like) to foliose (bushy) and squamulose (scaly). Most of them grow on land, some in freshwater and a few in the sea. Many are free-living but there are some species that are parasites on other lichens, while one marine species always lives together with a leafy green alga.
The Sporolithaceae is the only known family of algae in the Sporolithales order.

Galaxauraceae is a family of red algae (Rhodophyta) in the order Nemaliales.
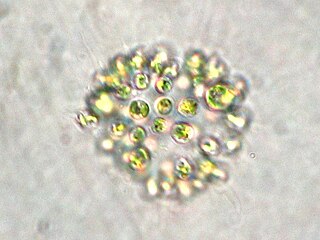
Microcystis aeruginosa is a species of freshwater cyanobacteria that can form harmful algal blooms of economic and ecological importance. They are the most common toxic cyanobacterial bloom in eutrophic fresh water. Cyanobacteria produce neurotoxins and peptide hepatotoxins, such as microcystin and cyanopeptolin. Microcystis aeruginosa produces numerous congeners of microcystin, with microcystin-LR being the most common. Microcystis blooms have been reported in at least 108 countries, with the production of microcystin noted in at least 79.

Kallymeniaceae is a red algae family in the order Gigartinales.
Streptomyces tsukubensis is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil in Ibaraki in Japan. Streptomyces tsukubensis produces the immunosuppressant tacrolimus.
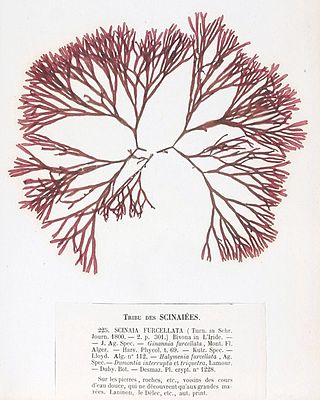
Scinaiaceae is a family of red algae (Rhodophyta) in the order Nemaliales.

Liagoraceae is a family of red algae (Rhodophyta) in the order Nemaliales. The type genus is LiagoraJ.V.Lamouroux.

Thoreales is an order of red algae belonging to the class Florideophyceae. The order consists only one family, ThoreaceaeHassall, 1845. The family of Thoreaceae was circumscribed by Arthur Hill Hassall in A history of the British freshwater algae, including descriptions of the Desmideae and Diatomaceae in 1845.

Halymeniales is an order of red algae belonging to the class Florideophyceae and the subclass Rhodymeniophycidae.

Peyssonneliales is a monotypic order of red algae belonging to the class Florideophyceae and the subclass Rhodymeniophycidae. It contains only 1 known family, PeyssonneliaceaeDenizot, M., 1968.















