
Alcamo is the fourth-largest town and commune of the Province of Trapani, Sicily, with a population of 44.925 inhabitants. It is on the borderline with the Metropolitan City of Palermo at a distance of about 50 kilometres from Palermo and Trapani.

Cagliari is an Italian municipality and the capital and largest city of the island of Sardinia, an autonomous region of Italy. It has about 155,000 inhabitants, while its metropolitan city has about 420,000 inhabitants. According to Eurostat, the population of the functional urban area, the commuting zone of Cagliari, rises to 476,975. Cagliari is the 26th largest city in Italy and the largest city on the island of Sardinia.

The province of Lecco is a province in the Lombardy region of Italy. Its capital is the city of Lecco.

Avezzano is a city and comune with a population of 40,785 inhabitants, situated in the Abruzzo region, province of L'Aquila, Italy. It is the second most populous municipality in the province and the sixth in the region. Avezzano was documented as an existing urban center in the ninth century. The city was destroyed by the earthquake of 1915. It was rebuilt after the 1944 Allied bombing. The city was decorated with the silver medal for civil merit, an award granted by the Italian Republic.

Malcesine is a comune (municipality) on the eastern shore of Lake Garda in the Province of Verona in the Italian region Veneto, located about 120 kilometres northwest of Venice and about 40 kilometres northwest of Verona. It is one of I Borghi più belli d'Italia.

Cereseto is a comune (municipality) in the Province of Alessandria in the Italian region Piedmont.

Montano Lucino is an Italian town of 5,302 inhabitants in the province of Como in Lombardy.
Musso is a small town in the Province of Como in the Italian region Lombardy. It lies on the western shore of the northern branch of Lake Como about 35 kilometres (22 mi) northeast of the city of Como. The comune of Musso, which includes the town itself and the surrounding area of lake and mountainside, extends over an area of 412 hectares, with a minimum elevation of 199 metres (653 ft) and a maximum of 1,325 metres (4,347 ft) and has a population of 1,020. It borders the communes of Dongo to the north, Pianello del Lario to the south and Colico across the lake in the Province of Lecco.

Brugherio is a comune (municipality) in the Province of Monza and Brianza in the Italian region Lombardy, located about 10 kilometres northeast of Milan. It was established December 9, 1866 unifying the suppressed municipalities of Baraggia, San Damiano and Moncucco, together with the villages of Bindellera, Cesena, Gelosa, San Paolo, Torazza, Occhiate and Increa.

Gromo is a comune (municipality) in the Province of Bergamo in the Italian region of Lombardy, located about 80 kilometres (50 mi) northeast of Milan and about 35 kilometres (22 mi) northeast of Bergamo. As of 31 December 2004, it had a population of 1,246 and an area of 20.0 square kilometres (7.7 sq mi).

Esino Lario is a municipality (comune) of the Province of Lecco in the Italian region of Lombardy. It is about 60 kilometres (37 mi) north of Milan, 15 kilometres (9.3 mi) northwest of Lecco, and about 4.3 kilometres (2.7 mi) from the eastern shore of Lake Como.

Lierna is a comune in the province of Lecco in Lombardy, in north-west Italy. It lies on the eastern shore of Lake Como, about 60 kilometres (37 mi) north of Milan and about 15 kilometres (9 mi) north-west of Lecco.

Varenna is a comune (municipality) on Lake Como in the Province of Lecco in the Italian region of Lombardy, located about 60 kilometres (37 mi) north of Milan and about 20 kilometres (12 mi) northwest of Lecco.

Verrès Castle is a fortified 14th-century castle in Verrès, in the lower Aosta Valley, in north-western Italy. It has been called one of the most impressive buildings from the Middle Ages in the area. Built as a military fortress by Yblet de Challant in the fourteenth century, it was one of the first examples of a castle constructed as a single structure rather than as a series of buildings enclosed in a circuit wall.
The castle stands on a rocky promontory on the opposite side of the Dora Baltea from Issogne Castle. The castle dominates the town of Verrès and the access to the Val d'Ayas. From the outside it looks like an austere cube, thirty metres long on each side and practically free of decorative elements.

The Castello di Milazzo is a castle and citadel in Milazzo, Sicily. It is located on the summit of a hill overlooking the town, on a site first fortified in the Neolithic era. The Greeks modified it into an acropolis, and it was later enlarged into a castrum by the Romans and Byzantines. The Normans built a castle, which was further modified and enlarged during the Medieval and Early Modern periods. It is now in good condition, and open to the public.

Castello Orsini-Odescalchi is a castle in Bracciano, Lazio, Italy. It is located on the southern shore of Lake Bracciano. It was built in the 15th century, and combines the functions of a military defence structure and a civilian residence of the feudal lords of the period, the Orsini and Borgia, both papal families. As one of the largest and best-maintained castles in Italy, it also houses a museum; as a centre of cultural events, the Castello has hosted several high-profile weddings such as those of Tom Cruise/Katie Holmes, Eros Ramazzotti/Michelle Hunziker, and Petra Ecclestone/James Stunt.

Castello Barbarossa is an archaeological ruin and ornithological station in Anacapri, on the island of Capri, Italy. It is named after the former corsair and Ottoman Kapudan Pasha (Admiral) Hayreddin Barbarossa, who stormed it in 1535 and destroyed it in 1544. The construction date is uncertain but it perhaps dates back to the late ninth century. From 1898, the structure, now in ruins, was owned by the Swedish psychiatrist Axel Munthe who donated it to his foundation. The surroundings, interesting for their botanical features, are home to the island's ornithological station.

Giannino Castiglioni was an Italian sculptor and medallist. He worked mostly in monumental and funerary sculpture; his style was representational, and far from the modernist and avant-garde trends of the early twentieth century.

Castello Piccolomini is a castle in Capestrano, Province of L'Aquila (Abruzzo).
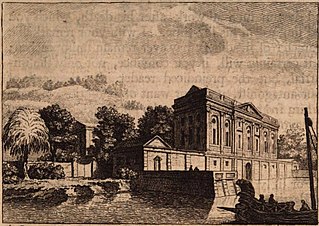
Pliny's Comedy and Tragedy villas were two of the several villas owned by Pliny the Younger during the 1st century in the area surrounding Lake Como in northern Italy. In one of Pliny's letters to his boyhood friend Voconius Romanus, he named them as his favourites. In his letter, Pliny wrote that the Tragedy villa was atop a ridge above the lake, but the Comedy villa was right on the water's edge and that "each of them has particular beauties; a diversity which renders them to their master as still more agreeable." According to the letter, Pliny had derived the villas' names from their geographical positions and the conventions of Roman theatre. He saw the Tragedy villa as rising from its setting like an actor wearing the tragedian's high platform boots, while the Comedy villa down by the lake wore the lowly comedian's slippers. Both villas have long since vanished, and their exact locations remain a subject of speculation.




















