
Light rail transit (LRT) is a form of passenger urban rail transit characterized by a combination of tram and rapid transit features. While its rolling stock is more similar to a traditional tram, it operates at a higher capacity and speed, and often on an exclusive right-of-way. In many cities, light rail transit systems more closely resemble, and are therefore indistinguishable from, traditional underground or at-grade subways and heavy-rail metros.

Transport in Argentina is mainly based on a complex network of routes, crossed by relatively inexpensive long-distance buses and by cargo trucks. The country also has a number of national and international airports. The importance of the long-distance train is minor today, though in the past it was widely used and is now regaining momentum after the re-nationalisation of the country's commuter and freight networks. Fluvial transport is mostly used for cargo.

The Tren Urbano is a 10.7-mile (17.2 km) fully-automated rapid transit system that serves the municipalities of San Juan, Guaynabo, and Bayamón, in Puerto Rico. The Tren Urbano consists of 16 stations operating on 10.7 miles (17.2 km) of track along a single line. In 2021, the system had a ridership of 1,649,500, or about 9,500 per weekday as of the third quarter of 2022.

Conservation and restoration of rail vehicles aims to preserve historic rail vehicles.

A tram-train is a type of light rail vehicle that meets the standards of a light rail system, but which also meets national mainline standards permitting operation alongside mainline trains. This allows services that can utilise both existing urban light rail systems and mainline railway networks and stations. It combines the urban accessibility of a tram or light rail with a mainline train's greater speed in the suburbs.

The Rio de Janeiro Metro, commonly referred to as just the Metrô is a rapid transit network that serves the city of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. The Metrô was inaugurated on 5 March 1979, and consisted of five stations operating on a single line. The system currently covers a total of 58 kilometres (36 mi), serving 41 stations, divided into three lines: Line 1 ; Line 2, which together travel over a shared stretch of line that covers 10 stations of an approximate distance of 5 kilometres (3.1 mi); and Line 4. Metrô Rio has the second highest passenger volume of the metro systems in Brazil, after the São Paulo Metro.

The Transandine Railway was a 1,000 mmmetre gauge combined rack and adhesion railway which operated from Mendoza in Argentina, across the Andes mountain range via the Uspallata Pass, to Santa Rosa de Los Andes in Chile, a distance of 248 km. The railway has been out of service since 1984, and has been partly dismantled. There has been talk about restoring the railway, but there is currently no indication of any restorative work underway.

A premetro is a tramway or light railway which includes segments built to rapid transit standards, generally as part of a process of conversion to a metro-standards railway usually by the construction of tunnels in the central city area.

Light rail is a commonly used mode of public transit in North America. The term light rail was coined in 1972 by the Urban Mass Transportation Administration to describe new streetcar transformations which were taking place in Europe and the United States. The Germans used the term Stadtbahn, which is the predecessor to North American light rail, to describe the concept, and many in UMTA wanted to adopt the direct translation, which is city rail. However, in its reports, UMTA finally adopted the term light rail instead.

The history of rapid transit began in London with the opening of the Metropolitan Railway, which is now part of the London Underground, in 1863. By World War I, electric underground railways were being used in Athens, Berlin, Boston, Buenos Aires, Budapest, Glasgow, Hamburg, Istanbul, Liverpool, New York City, Paris, and Philadelphia.

The Tranvía del Este, also known as the Puerto Madero Tramway, was a 12-block "demonstration" light rail line in the Puerto Madero neighborhood of Buenos Aires, Argentina, in operation from 2007 to 2012. It used French-built Alstom Citadis 302 trams on loan, initially from Mulhouse, France, and later from Madrid, Spain, and was operated by the rail company Ferrovías.

Although tram systems date to the late 19th and early 20th centuries, many old systems were closed during the mid-20th century because of the advent of automobile travel. This was especially the case in North America, but postwar reductions and shutdowns also occurred on British, French and other Western European urban rail networks. However, traditional tramway systems survived, and eventually even began to thrive from the late 20th century onward, some eventually operating as much as when they were first built over a century ago. Their numbers have been augmented by modern tramway or light rail systems in cities which had discarded this form of transport.

The Premetro is a 7.4-kilometer long (4.6 mi) light rail line that runs along the outskirts of Buenos Aires, connecting with the Buenos Aires Underground line E, at Plaza de los Virreyes station and then to General Savio, with a short branch to Centro Cívico. It opened in 1987 and is operated by Metrovías. Originally, the Premetro was to include many more lines, but shortly after the privatisation of the railways the projects were postponed and never materialised and only "Premetro E2" was built.
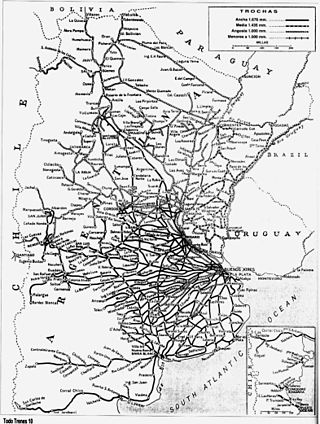
The Argentine railway network consisted of a 47,000 km (29,204 mi) network at the end of the Second World War and was, in its time, one of the most extensive and prosperous in the world. However, with the increase in highway construction, there followed a sharp decline in railway profitability, leading to the break-up in 1993 of Ferrocarriles Argentinos (FA), the state railroad corporation. During the period following privatisation, private and provincial railway companies were created and resurrected some of the major passenger routes that FA once operated.
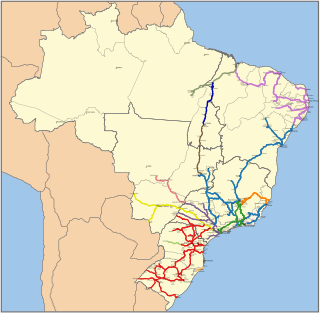
Rail transport in Brazil began in the 19th century and there were many different railway companies. The railways were nationalised under RFFSA in 1957. Between 1999 and 2007, RFFSA was broken up and services are now operated by a variety of private and public operators, including América Latina Logística, Companhia Paulista de Trens Metropolitanos and SuperVia.

Rio de Janeiro Light Rail is a modern light rail system serving Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. The system is among several new public transport developments in the region ahead of the city's successful bid for the 2016 Summer Olympics. Its official name is VLT Carioca, the initialism "VLT" being equivalent to the English term light rail.

The first trams in Buenos Aires began operating in 1863 in what quickly became a vast network of tramways with the city being known as the "City of Trams" for having the highest tramway-to-population ratio in the world. In the 1920s, Buenos Aires had 875 km (544 mi) of tramways and 99 tram lines using 3000 carriages running throughout the city. By 1963, the vast majority of the network began to be dismantled, though some minor tram services continue in the city today.
Rapid transit in Brazil consists of seven metro systems, one hybrid metro-suburban system, and several tram/light rail systems.

















