
A column or pillar in architecture and structural engineering is a structural element that transmits, through compression, the weight of the structure above to other structural elements below. In other words, a column is a compression member. The term column applies especially to a large round support with a capital and a base or pedestal, which is made of stone, or appearing to be so. A small wooden or metal support is typically called a post. Supports with a rectangular or other non-round section are usually called piers.

A skyscraper is a tall, continuously habitable building having multiple floors. Modern sources currently define skyscrapers as being at least 100 meters (330 ft) or 150 meters (490 ft) in height, though there is no universally accepted definition, other than being very tall high-rise buildings. Historically, the term first referred to buildings with between 10 and 20 stories when these types of buildings began to be constructed in the 1880s. Skyscrapers may host offices, hotels, residential spaces, and retail spaces.

In architecture, post and lintel is a building system where strong horizontal elements are held up by strong vertical elements with large spaces between them. This is usually used to hold up a roof, creating a largely open space beneath, for whatever use the building is designed. The horizontal elements are called by a variety of names including lintel, header, architrave or beam, and the supporting vertical elements may be called columns, pillars, or posts. The use of wider elements at the top of the post, called capitals, to help spread the load, is common to many traditions.

A window is an opening in a wall, door, roof, or vehicle that allows the exchange of light and may also allow the passage of sound and sometimes air. Modern windows are usually glazed or covered in some other transparent or translucent material, a sash set in a frame in the opening; the sash and frame are also referred to as a window. Many glazed windows may be opened, to allow ventilation, or closed, to exclude inclement weather. Windows may have a latch or similar mechanism to lock the window shut or to hold it open by various amounts.

The Minoan civilization was a Bronze Age culture which was centered on the island of Crete. Known for its monumental architecture and its energetic art, it is often regarded as the first civilization in Europe.

Knossos is a Bronze Age archaeological site in Crete. The site was a major center of the Minoan civilization and is known for its association with the Greek myth of Theseus and the minotaur. It is located on the outskirts of Heraklion, and remains a popular tourist destination.

A courtyard or court is a circumscribed area, often surrounded by a building or complex, that is open to the sky.

The sky is an unobstructed view upward from the surface of the Earth. It includes the atmosphere and outer space. It may also be considered a place between the ground and outer space, thus distinct from outer space.

Japanese architecture has been typified by wooden structures, elevated slightly off the ground, with tiled or thatched roofs. Sliding doors (fusuma) and other traditional partitions were used in place of walls, allowing the internal configuration of a space to be customized for different occasions. People usually sat on cushions or otherwise on the floor, traditionally; chairs and high tables were not widely used until the 20th century. Since the 19th century, however, Japan has incorporated much of Western, modern, and post-modern architecture into construction and design, and is today a leader in cutting-edge architectural design and technology.

In architecture, a clerestory is a high section of wall that contains windows above eye-level. Its purpose is to admit light, fresh air, or both.

A portico is a porch leading to the entrance of a building, or extended as a colonnade, with a roof structure over a walkway, supported by columns or enclosed by walls. This idea was widely used in ancient Greece and has influenced many cultures, including most Western cultures.

A sunbeam, in meteorological optics, is a beam of sunlight that appears to radiate from the position of the Sun. Shining through openings in clouds or between other objects such as mountains and buildings, these beams of particle-scattered sunlight are essentially parallel shafts separated by darker shadowed volumes. Their apparent convergence in the sky is a visual illusion from linear perspective. The same illusion causes the apparent convergence of parallel lines on a long straight road or hallway at a distant vanishing point. The scattering particles that make sunlight visible may be air molecules or particulates.

Chinese architecture is the embodiment of an architectural style that has developed over millennia in China and has influenced architecture throughout East Asia. Since its emergence during the early ancient era, the structural principles of its architecture have remained largely unchanged. The main changes involved diverse decorative details. Starting with the Tang dynasty, Chinese architecture has had a major influence on the architectural styles of neighbouring East Asian countries such as Japan, Korea, Vietnam, and Mongolia in addition to minor influences on the architecture of Southeast and South Asia including the countries of Malaysia, Singapore, Indonesia, Sri Lanka, Thailand, Laos, Cambodia and the Philippines.
In architecture, an atrium is a large open-air or skylight-covered space surrounded by a building. Atria were a common feature in Ancient Roman dwellings, providing light and ventilation to the interior. Modern atria, as developed in the late 19th and 20th centuries, are often several stories high, with a glazed roof or large windows, and often located immediately beyond a building's main entrance doors.

A heliodon (HEE-leo-don) is a device for adjusting the angle between a flat surface and a beam of light to match the angle between a horizontal plane at a specific latitude and the solar beam. Heliodons are used primarily by architects and students of architecture. By placing a model building on the heliodon’s flat surface and making adjustments to the light/surface angle, the investigator can see how the building would look in the three-dimensional solar beam at various dates and times of day.
This page is a glossary of architecture.
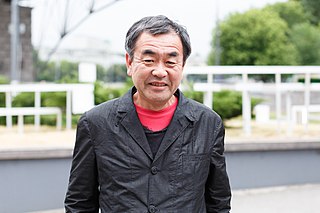
Kengo Kuma is a Japanese architect and emeritus professor in the Department of Architecture at the University of Tokyo. Frequently compared to contemporaries Shigeru Ban and Kazuyo Sejima, Kuma is also noted for his prolific writings. He is the designer of the Japan National Stadium in Tokyo, which was built for the 2020 Summer Olympics. He is married to architect Satoko Shinohara, and they have one son, Taichi, also an architect. He is an advisor for Kitakyushu-city in Japan.

A vestibule is a small room leading into a larger space such as a lobby, entrance hall or passage, for the purpose of waiting, withholding the larger space view, reducing heat loss, providing storage space for outdoor clothing, etc. The term applies to structures in both modern and classical architecture since ancient times. In modern architecture, a vestibule is typically a small room next to the outer door and connecting it with the interior of the building. In ancient Roman architecture, a vestibule was a partially enclosed area between the interior of the house and the street.

In subterranean civil engineering, ventilation shafts, also known as airshafts or vent shafts, are vertical passages used in mines and tunnels to move fresh air underground, and to remove stale air.

The Richards Medical Research Laboratories, located on the campus of the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, were designed by architect Louis Kahn and are considered to have been a breakthrough in his career. The building is configured as a group of laboratory towers with a central service tower. Brick shafts on the periphery hold stairwells and air ducts, producing an effect reminiscent of the ancient Italian towers that Kahn had painted several years earlier.




















