| Ligula intestinalis | |
|---|---|
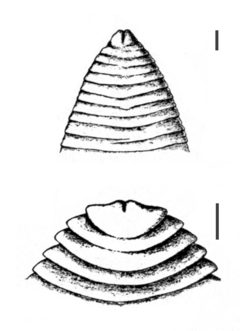 | |
| Anterior end of adult Ligula intestinalis (top) and larval Schistocephalus solidus (bottom) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | L. intestinalis |
| Binomial name | |
| Ligula intestinalis (Linnaeus, 1758) | |
Ligula intestinalis is a tapeworm of fish, fish-eating birds and copepods, with species from each group featuring in its complex life cycle. [1] It is a parasite that changes its intermediate host's behavior to become more vulnerable to its predators. In this case, it uses copepods and cyprinid fish as their intermediate host and develops inside of them to get to its final destination which is fish-eating birds. [2] Plerocercoids, Ligula intestinalis larvae, influence secondary intermediate hosts’ behavior, health, and fecundity. [3] Additionally, this species can cause the gonads of fish to remain undeveloped. [4]