
Zieria adenodonta, commonly known as the Wollumbin zieria, is a plant in the citrus family Rutaceae and is endemic to eastern Australia. It is a dense, bushy shrub with leaves composed of three leaflets which are warty on the upper surface. In winter and early spring it has groups of five to eight flowers, each with four white petals, the groups usually shorter than the leaves.

Leucopogon plumuliflorus is a species of flowering plant in the heath family Ericaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is a weakly erect shrub with egg-shaped leaves and spikes of white or pinkish-white, tube-shaped flowers.

Styphelia conostephioides is a flowering plant in the family Ericaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is an erect, straggling shrub with lance-shaped leaves with a sharp point on the tip, and white flowers arranged in pairs in leaf axils.

Styphelia crassifolia is a species of flowering plant in the family Ericaceae and is endemic to [the south-west of Western Australia. It is an erect, bushy shrub that typically grows to a height of 60 cm (24 in). Its leaves are oblong, 4–9 mm (0.16–0.35 in) long on a short petiole, with 3 prominent ribs on the lower surface. One or two flowers are borne in leaf axils on a short peduncle with tiny bracts and bracteoles about half the length of the sepals. The sepals are about 1.6 mm (0.063 in) long and the petals are about 3.2 mm (0.13 in) long and joined at the base, the lobes about as long as the tube.

Leucopogon concurvus is a species of flowering plant in the heath family Ericaceae and is endemic to a restricted part of South Australia. It is a slender shrub with egg-shaped leaves, and white, tube-shaped flowers arranged along the branches.

Styphelia cordifolia, commonly known as heart-leaved beard-heath, is a species of flowering plant in the heath family Ericaceae and is endemic to Australia. It is an erect shrub with broadly egg-shaped to round leaves, and white, tube-shaped flowers, the petals bearded on the inside.

Styphelia blepharolepis is a species of flowering plant in the heath family Ericaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is an erect shrub with sharply-pointed, oblong to lance-shaped leaves and small flowers in racemes of two to five in leaf axils with small bracts and bracteoles about 1 mm (0.039 in) long. The sepals are about 2 mm (0.079 in) long and the petals are joined at the base forming an urn shape about 4 mm (0.16 in) long with lobes longer than the petal tube.

Styphelia breviflora is a species of flowering plant in the heath family Ericaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is an erect, spindly, glabrous shrub that typically grows to a height of up to about 1.5 m. It has oblong to lance-shaped or linear leaves 4–9 mm (0.16–0.35 in) long on a short petiole and with a small, rigid point on the tip. The flowers are borne singly or in pairs in leaf axils on a short peduncle with small bracts and bracteoles about half as long as the sepals. The sepals are about 2 mm (0.079 in) long and the petals white and about 4 mm (0.16 in) long, the petal lobes longer than the petal tube.
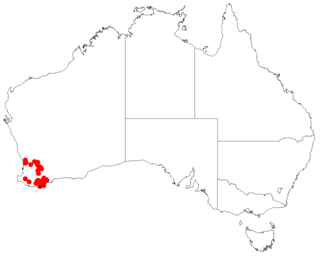
Styphelia cymbiformis is a flowering plant in the family Ericaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is a bushy or wiry shrub that typically grows to a height of 30–50 cm (12–20 in) and has more or less glabrous branches. Its leaves are erect, linear to lance-shaped and sharply-pointed, mostly 2–4 mm (0.079–0.157 in) long. The flowers are arranged in short spikes, sometimes of only two or three flowers, with lance-shaped, leaf-like bracts, and bracteoles half as long as the sepals at the base of the spikes. The sepals are 2.5–3.0 mm (0.098–0.118 in) long and the petals slightly longer than the sepals, the lobes shorter than the petal tube.

Styphelia flavescens is a species of flowering plant in the heath family Ericaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is a shrub with oblong leaves and white, tube-shaped flowers that are densely bearded on the inside.

Leucopogon opponens is a species of flowering plant in the heath family Ericaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is an erect, slender shrub with its leaves arranged in opposite pairs, and white, tube-shaped flowers.

Styphelia erubescens is a species of flowering plant in the heath family Ericaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is an erect shrub with variably-shaped leaves with a small, sharp point on the tip, and white, pink or red, tube-shaped flowers.

Leucopogon strongylophyllus is a species of flowering plant in the heath family Ericaceae and is endemic to the southwest of Western Australia. It is an erect shrub with crowded egg-shaped or round leaves and white, tube-shaped flower arranged singly or in pairs in leaf axils.

Styphelia epacridis is a flowering plant in the family Ericaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is a straggling shrub with lance-shaped or linear leaves with a sharp point on the tip, and red, tube-shaped flowers arranged singly in leaf axils.
Styphelia exserta is a species of flowering plant in the heath family Ericaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is an erect shrub with broadly egg-shaped leaves, and white, tube-shaped flowers.

Styphelia hainesii is a species of flowering plant in the heath family Ericaceae and is endemic to the south coast of Western Australia. It is a bushy shrub with egg-shaped leaves, the narrower end towards the base, and red, tube-shaped flowers arranged singly in leaf axils.

Seringia hookeriana is a species of flowering plant in the mallow family and is endemic to Queenland. It is a compact suckering shrub with rusty-hairy new growth, oblong leaves and deep purple flowers arranged in groups of 2 to 4.

Styphelia lissanthoides is a species of flowering plant in the heath family Ericaceae and is endemic to the south of Western Australia. It is an erect, bushy shrub with egg-shaped to lance-shaped leaves with the narrower end towards the base, and white, tube-shaped flowers arranged singly or in pairs in leaf axils.
Lissanthe pleurandroides is a species of flowering plant in the family Ericaceae and is endemic to the south of Western Australia. It is an erect, moderately dense shrub with oblong leaves and spikes of tube-shaped, white or pink flowers.

Styphelia macrocalyx, commonly known as Swan berry, is a species of flowering plant in the heath family Ericaceae and is endemic to the south west of Western Australia. It is a shrub with sharply pointed, narrowly lance-shaped leaves and white, tube-shaped flowers with tufts of hairs on the inside.


















