
Energy is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat and light. Energy is a conserved quantity—the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed; matter and energy may also be converted to one another. The unit of measurement for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (J).

HTTP is an application layer protocol in the Internet protocol suite model for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems. HTTP is the foundation of data communication for the World Wide Web, where hypertext documents include hyperlinks to other resources that the user can easily access, for example by a mouse click or by tapping the screen in a web browser.

The single transferable vote (STV), a type of proportional ranked choice voting, is a multi-winner electoral system in which each voter casts a single vote in the form of a ranked-choice ballot. Voters have the option to rank candidates, and their vote may be transferred according to alternative preferences if their preferred candidate is eliminated or elected with surplus votes, so that their vote is used to elect someone they prefer over others in the running. STV aims to approach proportional representation based on votes cast in the district where it is used, so that each vote is worth about the same as another.

Universal Serial Bus (USB) is an industry standard that allows data exchange and delivery of power between many types of electronics. It specifies its architecture, in particular its physical interface, and communication protocols for data transfer and power delivery to and from hosts, such as personal computers, to and from peripheral devices, e.g. displays, keyboards, and mass storage devices, and to and from intermediate hubs, which multiply the number of a host's ports.
Uploading refers to transmitting data from one computer system to another through means of a network. Common methods of uploading include: uploading via web browsers, FTP clients, and terminals (SCP/SFTP). Uploading can be used in the context of clients that send files to a central server. While uploading can also be defined in the context of sending files between distributed clients, such as with a peer-to-peer (P2P) file-sharing protocol like BitTorrent, the term file sharing is more often used in this case. Moving files within a computer system, as opposed to over a network, is called file copying.
The File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a standard communication protocol used for the transfer of computer files from a server to a client on a computer network. FTP is built on a client–server model architecture using separate control and data connections between the client and the server. FTP users may authenticate themselves with a plain-text sign-in protocol, normally in the form of a username and password, but can connect anonymously if the server is configured to allow it. For secure transmission that protects the username and password, and encrypts the content, FTP is often secured with SSL/TLS (FTPS) or replaced with SSH File Transfer Protocol (SFTP).

In vitro fertilisation (IVF) is a process of fertilisation where an egg is combined with sperm in vitro. The process involves monitoring and stimulating a woman's ovulatory process, removing an ovum or ova from their ovaries and letting a man's sperm fertilise them in a culture medium in a laboratory. After the fertilised egg (zygote) undergoes embryo culture for 2–6 days, it is transferred by catheter into the uterus, with the intention of establishing a successful pregnancy.

Redox is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in the oxidation state. The oxidation and reduction processes occur simultaneously in the chemical reaction.

Arlington National Cemetery is the largest cemetery in the United States National Cemetery System, one of two maintained by the United States Army. Over 400,000 people are buried in its 639 acres in Arlington County, Virginia.

The first law of thermodynamics is a formulation of the law of conservation of energy in the context of thermodynamic processes. The law distinguishes two principal forms of energy transfer, heat and thermodynamic work, that modify a thermodynamic system containing a constant amount of matter. The law also defines the internal energy of a system, an extensive property for taking account of the balance of heat and work in the system. Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can be transformed from one form to another. In an isolated system the sum of all forms of energy is constant.

Heat transfer is a discipline of thermal engineering that concerns the generation, use, conversion, and exchange of thermal energy (heat) between physical systems. Heat transfer is classified into various mechanisms, such as thermal conduction, thermal convection, thermal radiation, and transfer of energy by phase changes. Engineers also consider the transfer of mass of differing chemical species, either cold or hot, to achieve heat transfer. While these mechanisms have distinct characteristics, they often occur simultaneously in the same system.

Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) or lateral gene transfer (LGT) is the movement of genetic material between organisms other than by the ("vertical") transmission of DNA from parent to offspring (reproduction). HGT is an important factor in the evolution of many organisms. HGT is influencing scientific understanding of higher-order evolution while more significantly shifting perspectives on bacterial evolution.
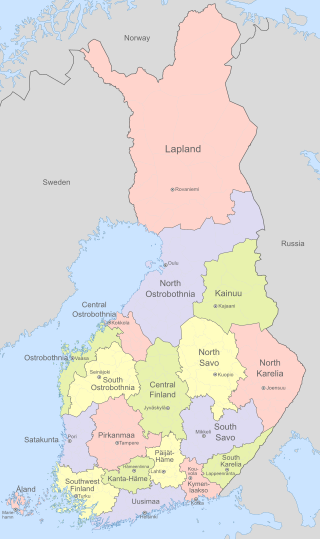
Finland is divided into 19 regions which are governed by regional councils that serve as forums of cooperation for the municipalities of each region. The councils are composed of delegates from the municipal councils. The main tasks of regional councils are regional planning, the development of enterprises, and education. Between 2004 and 2012, the regional council of Kainuu was elected via popular elections as part of an experimental regional administration.
In professional association football, a free transfer, also known as a Bosman transfer, involves a professional association football club releasing a player when the player's contract has expired or made available just before the end of the contract. The player can then sign for any club offering them a contract.
A transfer window is the period during the year in which a football club can add players to their squad who were previously under contract with another club. Such a transfer is completed by registering the player into the new club through FIFA. "Transfer window" is the unofficial term commonly used by the media for the concept of "registration period" as described in the FIFA Regulations on the Status and Transfer of Players. According to the rules, each national football association decides on the time of the 'window' but it may not exceed 12 weeks. The second registration period occurs during the season and may not exceed four weeks.
In professional football, a transfer is the action taken whenever a player under contract moves between clubs. It refers to the transferring of a player's registration from one association football club to another. In general, the players can only be transferred during a transfer window and according to the rules set by a governing body. A negotiated transfer fee is agreed financial compensation paid from an interested club to the club that possesses the player's exclusive contracted playing rights. When a player moves from one club to another, their old contract is terminated whilst the player and their new destination club will both negotiate on new contract terms. As such, the transfer fee functions as financial compensation for the early mutually agreed termination of the contract of a professional football player. Transfer fees are contingent on the player’s current football abilities, future potential, duration of the existing contract, amount of future salary owed and the willingness of clubs to agree on an economic equilibrium through supply and demand.

Electronic funds transfer (EFT) is the electronic transfer of money from one bank account to another, either within a single financial institution or across multiple institutions, via computer-based systems, without the direct intervention of bank staff. Funds transfers are the primary mechanism used by the business community for fast and reliable transfer of funds between two parties. The funds transfer process generally consists of a series of electronic messages sent between financial institutions directing each to make the debit and credit accounting entries necessary to complete the transaction. A funds transfer can generally be described as a series of payment instruction messages, beginning with the originator's instructions, and including a series of further instructions between the participating institutions, with the purpose of making payment to the beneficiary.

The states and territories are the second level of government of Australia. The states are administrative divisions that are self-governing polities that are partly sovereign, having ceded some sovereign rights to the federal government. They have their own constitutions, legislatures, executive governments, judiciaries and law enforcement agencies that administer and deliver public policies and programs. Territories can be autonomous and administer local policies and programs much like the states in practice, but are still legally subordinate to the federal government.

In thermodynamics, heat is the thermal energy transferred between systems due to a temperature difference. In colloquial use, heat sometimes refers to thermal energy itself. Thermal energy is the kinetic energy of vibrating and colliding atoms in a substance.













